
(a)
Interpretation: To classify each of the following molecules as (1) an oxidizing agent, (2) a reducing agent, or (3) neither an oxidizing agent nor a reducing agent.
a. NADH
b. ATP
c. FAD
d. CoA–SH
Concept introduction: The sum of various
ATP is a
Flavin adenine dinucleotideexists in two forms: oxidized form
Coenzyme A (CoA) is a coenzyme which is utilized in various metabolic reactions. The functions of coenzyme A include oxidation of pyruvate in the citric cycle and fatty acid oxidation.
Oxidizing agents are those species which gets reduced and oxidizes the other species present in the chemical reaction. Reducing agent is those species which gets oxidized and reduces the other species present in a chemical reaction. Generally, oxidizing agents are electron acceptor and reducing agents are electron donor.
(a)
Answer to Problem 12.44EP
Explanation of Solution
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide exists in two forms:
Here
(b)
Interpretation: To classify each of the following molecules as (1) an oxidizing agent, (2) a reducing agent, or (3) neither an oxidizing agent nor a reducing agent.
a. NADH
b. ATP
c. FAD
d. CoA–SH
Concept introduction: The sum of various chemical reactions occurring in the human body is called metabolism and the reactions individually are known as metabolic reactions. During these metabolic reactions, the various metabolic intermediates are formed for the short time to complete the reactions.ATP,
ATP is a nucleotide which provides energy for the completion of various metabolic reactions occurring in our human body. The structure of ATP consists of adenine base, ribose sugar unit and the three phosphate groupconnected to each other by phosphoanhydride bonds.
Flavin adenine dinucleotideexists in two forms: oxidized form
Coenzyme A (CoA) is a coenzyme which is utilized in various metabolic reactions. The functions of coenzyme A include oxidation of pyruvate in the citric cycle and fatty acid oxidation.
Oxidizing agents are those species which gets reduced and oxidizes the other species present in the chemical reaction. Reducing agent is those species which gets oxidized and reduces the other species present in a chemical reaction. Generally, oxidizing agents are electron acceptor and reducing agents are electron donor.
(b)
Answer to Problem 12.44EP
ATP molecule is neither a reducing agent nor an oxidizing agent in metabolic reactions.
Explanation of Solution
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is anucleotide which structural component is one unit of the adenine base, one unit of ribose sugar and three units of a phosphate group. It can be converted into its monophosphate form(AMP) and diphosphate form(ADP) by losing a phosphate group. The reaction to this change is:
Here ATP is not involved in electron transfer hence it is neither a reducing agent nor an oxidizing agent.
(c)
Interpretation: To classify each of the following molecules as (1) an oxidizing agent, (2) a reducing agent, or (3) neither an oxidizing agent nor a reducing agent.
a. NADH
b. ATP
c. FAD
d. CoA–SH
Concept introduction: The sum of various chemical reactions occurring in the human body is called metabolism and the reactions individually are known as metabolic reactions. During these metabolic reactions, the various metabolic intermediates are formed for the short time to complete the reactions.ATP,
ATP is a nucleotide which provides energy for the completion of various metabolic reactions occurring in our human body. The structure of ATP consists of adenine base, ribose sugar unit and the three phosphate groupconnected to each other by phosphoanhydride bonds.
Flavin adenine dinucleotideexists in two forms: oxidized form
Coenzyme A (CoA) is a coenzyme which is utilized in various metabolic reactions. The functions of coenzyme A include oxidation of pyruvate in the citric cycle and fatty acid oxidation.
Oxidizing agents are those species which gets reduced and oxidizes the other species present in the chemical reaction. Reducing agent is those species which gets oxidized and reduces the other species present in a chemical reaction. Generally, oxidizing agents are electron acceptor and reducing agents are electron donor.
(c)
Answer to Problem 12.44EP
Explanation of Solution
Flavin adenine dinucleotide exists in two forms:
Here
(d)
Interpretation: To classify each of the following molecules as (1) an oxidizing agent, (2) a reducing agent, or (3) neither an oxidizing agent nor a reducing agent.
a. NADH
b. ATP
c. FAD
d. CoA–SH
Concept introduction: The sum of various chemical reactions occurring in the human body is called metabolism and the reactions individually are known as metabolic reactions. During these metabolic reactions, the various metabolic intermediates are formed for the short time to complete the reactions.ATP,
ATP is a nucleotide which provides energy for the completion of various metabolic reactions occurring in our human body. The structure of ATP consists of adenine base, ribose sugar unit and the three phosphate groupconnected to each other by phosphoanhydride bonds.
Flavin adenine dinucleotideexists in two forms: oxidized form
Coenzyme A (CoA) is a coenzyme which is utilized in various metabolic reactions. The functions of coenzyme A include oxidation of pyruvate in the citric cycle and fatty acid oxidation.
Oxidizing agents are those species which gets reduced and oxidizes the other species present in the chemical reaction. Reducing agent is those species which gets oxidized and reduces the other species present in a chemical reaction. Generally, oxidizing agents are electron acceptor and reducing agents are electron donor.
(d)
Answer to Problem 12.44EP
Coenzyme A (CoA–SH) molecule is neither a reducing agent nor an oxidizing agent in metabolic reactions.
Explanation of Solution
Coenzyme A (CoA) is a coenzyme whose structure is based on the B vitamin pantothenic acid. Its structure consists of three subunits: 2-Aminoethanethiol, pantothenic acid, and phosphorylated ADP.
Coenzyme A is always in equilibrium with its acetyl form and therefore helps in transfer of acetyl group in metabolic reaction. The reaction for this change is
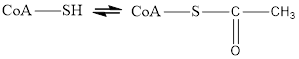
Here Coenzyme A (CoA) is not involved in electron transfer hence it is neithera reducing agent nor an oxidizing agent.
a.
b. ATP molecule is neither a reducing agent nor an oxidizing agent in metabolic reactions.
c.
d. Coenzyme A (CoA–SH) molecule is neither a reducing agent nor an oxidizing agent in metabolic reactions.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 12 Solutions
Organic And Biological Chemistry
- Indicate the formula of the product obtained by reacting methyl 5-chloro-5-oxopentanoate with 1 mole of 4-penten-1-ylmagnesium bromide.arrow_forwardIn the two chair conformations of glucose, the most stable is the one with all the OH groups in the equatorial position. Is this correct?arrow_forwardIndicate the formula of the product obtained by reacting D-Galactose with hydroxylamine.arrow_forward
- helparrow_forwardThe temperature on a sample of pure X held at 1.25 atm and -54. °C is increased until the sample boils. The temperature is then held constant and the pressure is decreased by 0.42 atm. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. pressure (atm) 2 0 0 200 400 temperature (K) Xarrow_forwardQUESTION: Answer Question 5: 'Calculating standard error of regression' STEP 1 by filling in all the empty green boxes *The values are all provided in the photo attached*arrow_forward
 Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co Chemistry In FocusChemistryISBN:9781305084476Author:Tro, Nivaldo J., Neu, Don.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry In FocusChemistryISBN:9781305084476Author:Tro, Nivaldo J., Neu, Don.Publisher:Cengage Learning
 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning





