
(a)
Interpretation:
The amount composition & hardness of material at
Concept Introduction:
Microstructure is a very small structure of any material. For a material, it describes the physical properties like hardness, strength, ductility, temperature behaviour and corrosion resistance of the material. The properties of any substance can be observed under optical microstructure. Materials such as metals, polymers, ceramics or composites show optimistic properties under microstructure.
Answer to Problem 12.103P
The composition, hardness and amount are
Explanation of Solution
Given:
Graph showing
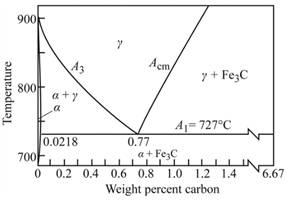
Calculation:
As shown in the given diagram, at the line
As from the figure, the effect of hardness of martensite in steel, the hardness of martensite at
Where, %M=amount of martensite
Put, the values in lever rule,
Therefore,
(b)
Interpretation:
The amount composition & hardness of material at
Concept Introduction:
Material hardness is the property of a metal due to which material resist the plastic deformation. Plastic deformation means material deformation which undergoes non-reversible change. Hardness is the property of any material which process stiffness resistance to bending, scratching or cutting. Hardness is not constant or fixed for all material, but it depends upon strength and plasticity of metal. Material hardness is expressed in terms of hardness number.
Answer to Problem 12.103P
The composition, hardness and amount are
Explanation of Solution
Given:
Graph showing
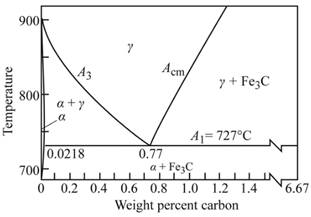
Calculations:
As shown in the given diagram, at the line
As from the figure, the effect of hardness of martensite in steel, the hardness of martensite at
Where, %M=amount of martensite
Put, the values in lever rule,
Therefore,
(c)
Interpretation:
The amount composition & hardness of material at
Concept Introduction:
Material hardness is the property of a metal due to which material resist the plastic deformation.Plastic deformation means material deformation which undergoes non-reversible change. Hardness is the property of any material which process stiffness resistance to bending, scratching or cutting. Hardness is not constant or fixed for all material, but it depends upon strength and plasticity of metal. Material hardness is expressed in terms of hardness number.
Answer to Problem 12.103P
The composition, hardness and amount are
Explanation of Solution
Given:
Graph showing
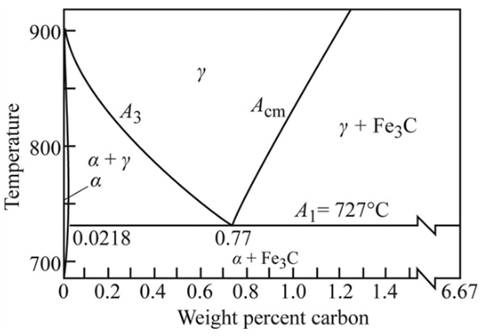
Calculations:
As shown in the given diagram, at the line
As from the figure, the effect of hardness of martensite in steel, the hardness of martensite at
Where, %M=amount of martensite
Put, the values in lever rule,
Therefore,
(d)
Interpretation:
The amount composition & hardness of material at
Concept Introduction:
Material hardness is the property of a metal due to which material resist the plastic deformation. Plastic deformation means material deformation which undergoes non-reversible change. Hardness is the property of any material which process stiffness resistance to bending, scratching or cutting. Hardness is not constant or fixed for all material, but it depends upon strength and plasticity of metal. Material hardness is expressed in terms of hardness number.
Answer to Problem 12.103P
The composition, hardness and amount are
Explanation of Solution
Given:
Graph showing
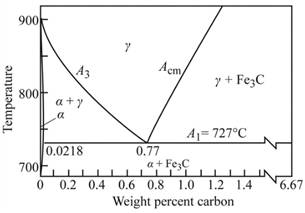
Calculations:
As shown in the given diagram, at the line
As from the figure, the effect of hardness of martensite in steel, the hardness of martensite at
Where, %M=amount of martensite
Put, the values in lever rule,
Therefore,
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 12 Solutions
Essentials of Materials Science and Engineering, SI Edition
- Don't use ai to answer I will report you answer..arrow_forwardA steam turbine operates at steady state with inlet conditions of P1 = 5 bar, T1 = 320°C. Steam leaves the turbine at a pressure of 1 bar. There is no significant heat transfer between the turbine and its surroundings, and kinetic and potential energy changes between inlet and exit are negligible. If the isentropic turbine efficiency is 75%, determine the work developed per unit mass of steam flowing through the turbine, in kJ/kgarrow_forwardDon't use ai to answer I will report you answerarrow_forward
- Homework#5arrow_forwardSolve for forces on pin C and Darrow_forwardMember AB has the angular velocity wAB = 2.5 rad/s and angular acceleration a AB = 9 rad/s². (Figure 1) Determine the magnitude of the velocity of point C at the instant shown. Determine the direction of the velocity of point C at the instant shown. Determine the magnitude of the acceleration of point C at the instant shown. Determine the direction of the acceleration of point C at the instant shown. A 300 mm WAB α AB B 500 mm 0=60° y 200 mmarrow_forwardShow the correct stereochemistry when needed!! mechanism: mechanism: Show the correct stereochemistry when needed!! Br NaOPh diethyl ether substitutionarrow_forwardchemical engineering Material-energy balance. Only focus on the nitrogen gas, which is H(3)arrow_forwardDon't use ai to answer I will report you answerarrow_forwardIn javaarrow_forwardYou are asked to design a unit to condense ammonia. The required condensation rate is 0.09kg/s. Saturated ammonia at 30 o C is passed over a vertical plate (10 cm high and 25 cm wide).The properties of ammonia at the saturation temperature of 30°C are hfg = 1144 ́10^3 J/kg andrv = 9.055 kg/m 3 . Use the properties of liquid ammonia at the film temperature of 20°C (Ts =10 o C):Pr = 1.463 rho_l= 610.2 kf/m^3 liquid viscosity= 1.519*10^-4 kg/ ms kinematic viscosity= 2.489*10^-7 m^2/s Cpl= 4745 J/kg C kl=0.4927 W/m Ca)Calculate the surface temperature required to achieve the desired condensation rate of 0.09 kg/s( should be 688 degrees C) b) Show that if you use a bigger vertical plate (2.5 m-wide and 0.8 m-height), the requiredsurface temperature would be now 20 o C. You may use all the properties given as an initialguess. No need to iterate to correct for Tf. c) What if you still want to use small plates because of the space constrains? One way to getaround this problem is to use small…arrow_forward1. The settling chamber, shown schematically in Figure 2E1.1, is used as a primary separation device in the removal of dust particles of density 1500 kg/m³ from a gas of density 0:7 kg/m³ and viscosity 1.90 x 10-5 Pa s. Gas inlet Elevation Gas Gas exit exit H Collection surface -W Section X-X Dimensions: H=3m L = 10 m W=2m Figure 2E1.1 Schematic diagram of settling chamber Assuming Stokes' law applies, show that the efficiency of collection of particles of size x is given by the expression collection efficiency, x = x²8(pp - Pi)L 18μHU where U is the uniform gas velocity through the parallel-sided section of the chamber. State any other assumptions made. (b) What is the upper limit of particle size for which Stokes' law applies? (c) When the volumetric flow rate of gas is 0.9 m³/s, and the dimensions of the chamber are those shown in Figure 2E1.1, determine the collection efficiency for spherical particles of diameter 30 mm.arrow_forwardarrow_back_iosSEE MORE QUESTIONSarrow_forward_ios
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsEngineeringISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsEngineeringISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Essentials Of Materials Science And EngineeringEngineeringISBN:9781337385497Author:WRIGHT, Wendelin J.Publisher:Cengage,
Essentials Of Materials Science And EngineeringEngineeringISBN:9781337385497Author:WRIGHT, Wendelin J.Publisher:Cengage, Industrial Motor ControlEngineeringISBN:9781133691808Author:Stephen HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Industrial Motor ControlEngineeringISBN:9781133691808Author:Stephen HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Basics Of Engineering EconomyEngineeringISBN:9780073376356Author:Leland Blank, Anthony TarquinPublisher:MCGRAW-HILL HIGHER EDUCATION
Basics Of Engineering EconomyEngineeringISBN:9780073376356Author:Leland Blank, Anthony TarquinPublisher:MCGRAW-HILL HIGHER EDUCATION Structural Steel Design (6th Edition)EngineeringISBN:9780134589657Author:Jack C. McCormac, Stephen F. CsernakPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Steel Design (6th Edition)EngineeringISBN:9780134589657Author:Jack C. McCormac, Stephen F. CsernakPublisher:PEARSON Fundamentals of Materials Science and Engineering...EngineeringISBN:9781119175483Author:William D. Callister Jr., David G. RethwischPublisher:WILEY
Fundamentals of Materials Science and Engineering...EngineeringISBN:9781119175483Author:William D. Callister Jr., David G. RethwischPublisher:WILEY





