
Concept explainers
The human RefSeq of the entire first exon of a gene involved in Brugada syndrome (a cardiac disorder characterized by an abnormal electrocardiogram and an increased risk of sudden heart failure) is:
5′ CAACGCTTAGGATGTGCGGAGCCT 3′
The genomic DNA of four people (1–4), three of whom have the disorder, was subjected to single-molecule sequencing. The following sequences represent all those obtained from each person.
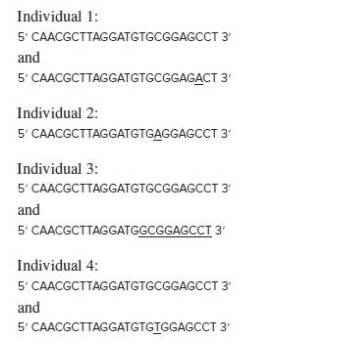
| a. | The first exon of the RefSeq copy of this gene includes the start codon. Write as much of the amino acid sequence of the encoded protein as possible, indicating the N-to-C polarity. |
| b. | Are any of these individuals homozygotes? If so, which person and what allele? |
| c. | Is the inheritance of Brugada syndrome among these individuals dominant or recessive? |
| d. | Is Brugada syndrome associated with allelic heterogeneity? |
| e. | Are any of these individuals compound heterozygotes? |
| f. | Do the data show any evidence for locus heterogeneity? |
| g. | Which person has normal heart function? |
| h. | For each variant from the RefSeq, describe: (i) what the mutation does to the coding sequence; and (ii) whether the variation is a loss-of-function allele, a gain-of-function allele, or a wild-type allele. |
| i. | For each variant, indicate which of the following terms apply: null, hypomorphic, hypermorphic, nonsense, frameshift, missense, silent, SNP, DIP, SSR, anonymous. |
| j. | Is the function of this gene haploinsufficient? Explain. |
a.
To determine:
The amino acid sequence for the RefSeq obtained from individual 1.
Introduction:
The mutation is the change in the nucleotide sequence of the gene, which results in either the formation of a defective protein or no protein at all. The mutation can also alter the regulation of certain genes leading to their hyperactivity or hypoactivity. It is different from recombination where gametes from parents are interchanged to produce new zygotes.
Explanation of Solution
The amino acid sequence for the RefSeq data 5' CAACGCTTAGGATGTGCGGAGCCT 3' will be N-glutamine-arginine-leucine-glycine-cysteine-alanine-glutamic acid-proline-C. The amino acid sequence for 5' CAACGCTTAGGATGTGCGGAGACT 3' is N-glutamine-arginine-leucine-glycine-cysteine-alanine-glutamic acid-threonine-C. The amino acid makes up large polypeptide chains that fold into functional proteins and perform different activities in the body of living organisms.
b.
To determine:
The presence of the homozygous individual.
Introduction:
The genes are the sequence of nucleotides that are present on the chromosomes and encode for a specific protein that plays a crucial role in the functioning of the different processes in an organism. The gene is located at specific gene loci and can be structural or regulatory in nature.
Explanation of Solution
The individual 2 is homozygous as the two strands of genetic material in the individual is same, and for all other individuals, the composition of nucleotides on both the strands is different. So, they are not homozygous for the given trait. The individual 2 has a nucleotide sequence 5' CAACGCTTAGGATGTGAGGAGCCT 3'. It implies that both the strands have similar nucleotide sequence. However, the homozygous allele cannot be predicted through the nucleotide sequence of the individual.
c.
To determine:
The inheritance pattern of Brugada syndrome among individuals.
Introduction:
The proteins are made of amino acids. The amino acids are of 20 types that combine in a varied manner to form proteins. The amino acids join together by peptide bonds. Proteins act as major substrates and reactants for the metabolic pathways. All the enzymes in the body that are crucial for the biochemical reactions are proteins.
Explanation of Solution
The inheritance of the disease, Brugada syndrome, is dominant as the disease develops by the inheritance of particular nucleotide sequence 5′ CAACGCTTAGGATGTGCGGAGCCT 3′ that is inherited by three organisms and has very little variation in the sequence structure due to mutation. The sequence is present in individual 1, 3, and 4, and accounts for the development of the disease when only one strand of the exon contains the sequence. So, implying that one copy is enough to cause the disease and therefore, the inheritance of the Brugada syndrome is dominant.
d.
To determine:
The association of Brugada syndrome with allelic heterogeneity.
Introduction:
The cardiovascular system is made of different components. The heart constitutes the primary organs of the system, and the arteries, veins, and blood capillaries form the associated structures of the cardiovascular system.
Explanation of Solution
Brugada syndrome is associated with allelic heterogeneity as the presence of only one copy of the sequence or allele in the exon can lead to the development of the disease. It implies that the disease can occur in heterozygous condition, where only one copy of allele is enough to cause disease. Hence, it can be concluded that Brugada syndrome is associated with allelic heterogeneity.
e.
To determine:
The presence of compound heterozygotes among individuals.
Introduction:
A genetic disorder is an alteration in the genetic composition of the individual for one or more genes that are manifested in the form of altered protein sequence for that particular trait. The genetic disorder is phenotypically manifested in various forms of abnormalities and malfunctions.
Explanation of Solution
Compound heterozygotes are the individuals who have two different mutations occurring in the two alleles of an individual. None of the individuals are compound heterozygotes, as only one of the copies of exon/allele is affected by mutation at a given time. The presence of only one mutation in one of the allele is a heterozygous condition. Hence, individuals 1, 3, and 4 are heterozygous, but not compound heterozygous.
f.
To determine:
The presence of locus heterogeneity among individuals.
Introduction:
The human consists of 23 pairs of chromosomes, condensed form of chromatids which divide during cell division into daughter cells. The human has 22 autosomes and one pair of sex chromosomes. The sex chromosomes determine the sex in an individual based on the type of sex chromosomes that are present in the fusing gametes.
Explanation of Solution
Locus heterogeneity is the condition where two different kinds of mutation occur at a different locus in the same chromosomes. None of the individuals has locus heterogeneity as all the individuals have only one mutation at one site or locus in the chromosome. Hence, none of the individuals shows locus heterogeneity.
g.
To determine:
The individual with normal heart function.
Introduction:
The chromosomes are condensed structures that are formed during the early phases of cell division from the loose network of chromatin thread and then regain their original structure after being divided into daughter cells.
Explanation of Solution
The individual who does not have the Brugada syndrome is individual 2, as the nucleotide sequence of the individual varies from the person who is positive for the cardiac disorder. The individual has changed single nucleotide in both the alleles and is therefore homozygous in nature. The difference in the nucleotide sequence in both the alleles accounts for normal heart function in individual 2.
h.
To determine:
The effect of the mutation on the coding sequence.
Introduction:
Fertilization is the process by which the male gamete, sperm, fertilize with the female gamete, ovary. The process brings about the fusion of two haploid pronuclei into a diploid zygote.
Explanation of Solution
The changes occurred due to a mutation in coding sequence are that in individual 1 there is a change in amino acid sequence as the amino acid proline is changed to threonine. In individual 2, the change in amino acid sequence occurs from alanine to glutamine. In individual 3, there is a change of amino acid sequence cysteine to alanine, and in individual 4, the amino acid changes from alanine to valine. The effect of this mutation as loss-of-function or gain-of-function can be done by protein expression analysis. The three individuals are not wild type due to the presence of the mutation.
i.
To determine:
The type of mutation in the sequence.
Introduction:
There are a vast number of cardiovascular problems that can arise due to malformation in the heart or the dysfunction of some parts of the cardiovascular system. Some of these disorders are fibrillation, septal defects, and so on.
Explanation of Solution
The mutation in all the individuals is single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) as there is a change only in one nucleotide and not the entire codon. The presence of silent, missense, or nonsense mutation can only be done with the help of protein expression analysis through techniques like microarray and so on.
j.
To determine:
The presence of gene haploinsufficiency in the function.
Introduction:
The circulatory system and cardiovascular systems form the two very important different organ systems in the body. The system is responsible for pumping the blood carrying nutrients and oxygen and helping to remove waste products from the body.
Explanation of Solution
Gene haploinsufficiency is the condition in which normal phenotype needs the protein to encode by both the alleles, and there is a reduction in the function by 50% if any one of the alleles has the abnormal phenotype. The presence of a mutation in the genome of all the individual increases the probability of gene haploinsufficiency. The change in the phenotype of the alleles of the exon due to mutation can account for gene haploinsufficiency in the individuals.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 10 Solutions
Genetics: From Genes to Genomes, 5th edition
- Please answer the following chart so I can understand how to do it.arrow_forwardDigoxin: Intravenous Bolus - Two Compartment Model Drug Digoxin Route: IV Bolus Dose: 0.750 mg Plasma Concentration Time Profile Beta Alpha Time (hrs) Conc (ng/ml) LN (ng/ml) LN (ng/ml) LN 0.00 #NUM! #NUM! #NUM! 0.10 12.290 2.509 #NUM! #NUMI 0.60 6.975 1.942 #NUM! #NUMI 1.00 4.649 1.537 #NUM! #NUMI 2.00 2.201 0.789 #NUM! #NUM! 3.00 1.536 0.429 #NUM! #NUM! 4.00 1.342 0.294 #NUM! #NUM! 5.00 1.273 0.241 #NUM! #NUMI 6.00 1.238 0.213 #NUM! #NUM! 7.00 1.212 0.192 #NUM! #NUM! 8.00 1.188 0.172 #NUMI #NUM! 9.00 1.165 0.153 #NUM! #NUMI 10.00 1.143 0.134 #NUMI #NUM! 11.00 1.122 0.115 #NUM! 12.00 1.101 0.096 #NUMI 13.00 1.080 0.077 #NUMI 16.00 1.020 0.020 #NUMI 24.00 0.876 -0.132 #NUMI Pharmacokinetic Parameters Parameter Value Alpha B Beta Units ng/ml hr-1 ng/ml hr-1 CO ng/ml H.C AUC ng x hr/ml Vc Vbeta Vss C L/hr TK (alpha) hr TX (beta) days 5+ F3 F4 F5 0+ F6 F7 % 6 95 14 #3 29 & t F8 F9 FW EWarrow_forwardLinuron, a derivative of urea, is used as an herbicide. Linuron serum levels were measured in 4Kg rabbits following a bolus IV injection of 10mg/kg. Time (minutes) Serum Linuron Levels (ug/ml) following IV dose 10 15.48 20 8.60 30 5.90 45 3.78 60 2.42 90 1.49 120 0.93 180 0.60 240 0.41 300 0.29 360 0.22 Analyze this data and perform the necessary calculations to determine the following pharmacokinetic parameters from the IV data: (5 points per parameter, 24 parameters/variables ■ 120 points possible). You do NOT need to submit graphs or data tables. Give the terminal regression line equation and R or R² value: Give the x axis (name and units, if any) of the terminal line: Give the y axis (name and units, if any) of the terminal line: Give the residual regression line equation and R or R² value: Give the x axis (name and units, if any) of the residual line: Give the y axis (name and units, if any) of the residual line:arrow_forward
- 3. In the tomato, red fruit (O+) is dominant over orange fruit (0), and yellow flowers (W+) are dominant over white flowers (w). A cross was made between true-breeding plants with red fruit and yellow flowers, and plants with orange fruit and white flowers. The F₁ plants were then crossed to plants with orange fruit and white flowers, which produced the following results: a. b. 333 red fruit, yellow flowers 64 red fruit, white flowers 58 orange fruit, yellow flowers 350 orange fruit, white flowers Conduct a chi-square analysis to demonstrate that these two genes DO NOT assort independently. Make sure to interpret the P value obtained from your chi-square test. Calculate and provide the map distance (in map units) between the two genes.arrow_forwardName: Date: Investigation: Is a dog more closely related to a coyote or a wolf? Gray Wolf Species Name: Canis lupus Color: Light gray to black Size: 80-120 pounds, 2.5 feet tall Appearance: broad snout, round ears, long tail Coyote Species Name: Canis latrans Color: Light gray to brown Size: 20-50 pounds, 1.5 feet tall Appearance: narrow snout, pointed ears, long tail Dog, Alaskan Malamute Species Name: Canis lupus familiaris Color: Gray and white or brown and white Size: 70-80 pounds, 2 feet tall Appearance: broad snout, round ears, long tail 1. Examine the images and descriptions above. Underline any similarities between the dog and the wolf. Place a star next to any coyote traits that are similar to the dog. 2. Based on appearance alone, which do you think is the most closely related to a dog? www.biologycorner.comarrow_forwardyu yeuwyuyuierydtgcygucygzycghjcygyugfyudguygcywgduycgyudgs ygarrow_forward
- According to a recent study, 1 out of 50,000 people will be diagnosed with cystic fibrosis. Cystic fibrosis can be caused by a mutant form of the CFTR gene (dominant gene symbol is F and mutant is f). A. Using the rate of incidence above, what is the frequency of carriers of the cystic fibrosis allele for CFTR in the US? (3 pts) B. In a clinical study, 400 people from the population mentioned in (A.) were genotyped for BRCA1 Listed below are the results. Are these results in Hardy- Weinberg equilibrium? Use Chi Square to show whether or not they are. (3 pts) # of women BRCA1 genotype BB 390 Bb bb 12pt v 10 0 V Paragraph B IUA BIUA > V T² v <arrow_forwardCase Study—Ella Ella has a family history of diabetes. She wants to follow a healthful eating pattern that can lower her risk for developing this condition. Her dietitian recommends a goal of 450 to 600 kcal per meal and advises Ella to follow the Acceptable Macronutrient Distribution Range (AMDR) for carbohydrates and the Dietary Guidelines for Americans 2015-2020, which recommend limiting added sugar. She also recommends that Ella choose whole grains rather than processed grains. Ella decides to pack a lunch to take to work every day. This morning she’s making a sandwich for her lunch. Categories of Sandwich Options (Top of the screen) Breads Spreads Cheeses Vegetables Proteins Specific food items to select White Bread 6-inches Honey Mustard Provolone LettuceTomatoBell Peppers Turkey Part A - Reading Nutrition Facts Panels for Total Kilocalories How many total kilocalories are in Ella’s sandwich? _______ kcal ? Part B - Reading Nutrition Facts Panels for…arrow_forwardCase Study—Ella Ella has a family history of diabetes. She wants to follow a healthful eating pattern that can lower her risk for developing this condition. Her dietitian recommends a goal of 450 to 600 kcal per meal and advises Ella to follow the Acceptable Macronutrient Distribution Range (AMDR) for carbohydrates and the Dietary Guidelines for Americans 2015-2020, which recommend limiting added sugar. She also recommends that Ella choose whole grains rather than processed grains. Ella decides to pack a lunch to take to work every day. This morning she’s making a sandwich for her lunch. Categories of Sandwich Options (Top of the screen) Breads Spreads Cheeses Vegetables Proteins Specific food items to select White Bread 6-inches Honey Mustard Provolone LettuceTomatoBell Peppers Turkey Part A - Reading Nutrition Facts Panels for Total Kilocalories How many total kilocalories are in Ella’s sandwich exactl ______kcal ? Part B - Reading Nutrition Facts Panels for…arrow_forward
- In humans, red-green color blindness is recessive and X-linked, whereas albinism is recessive and autosomal. What types of children can be produced as the result of marriage between two homozygous parents, a normal-vision albino woman and a color-blind, normal male?arrow_forwardIn Drosophila, an X linked recessive mutation, scalloped (sd), causes irregular wing margins. Diagram the F1 and F2 results if a (a) scalloped female is crossed with a normal male; (b) a scalloped male is crossed with a normal female (assume the female is homozygous). Compare these results to what you would find if the trait was not sex linked.arrow_forwardCase Study—Ella Ella has a family history of diabetes. She wants to follow a healthful eating pattern that can lower her risk for developing this condition. Her dietitian recommends a goal of 450 to 600 kcal per meal and advises Ella to follow the Acceptable Macronutrient Distribution Range (AMDR) for carbohydrates and the Dietary Guidelines for Americans 2015-2020, which recommend limiting added sugar. She also recommends that Ella choose whole grains rather than processed grains. Ella decides to pack a lunch to take to work every day. This morning she’s making a sandwich for her lunch. Categories of Sandwich Options (Top of the screen) Breads Spreads Cheeses Vegetables Proteins Specific food items to select White Bread 6-inches Honey Mustard Provolone LettuceTomatoBell Peppers Turkey Part A - Reading Nutrition Facts Panels for Total Kilocalories How many total kilocalories are in Ella’s sandwich exactl ______kcal ? Part B - Reading Nutrition Facts Panels for…arrow_forward
 Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning- Case Studies In Health Information ManagementBiologyISBN:9781337676908Author:SCHNERINGPublisher:Cengage
 Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College
Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College





