
Organic Chemistry
8th Edition
ISBN: 9781305580350
Author: William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. Foote
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 1, Problem 1.77AP
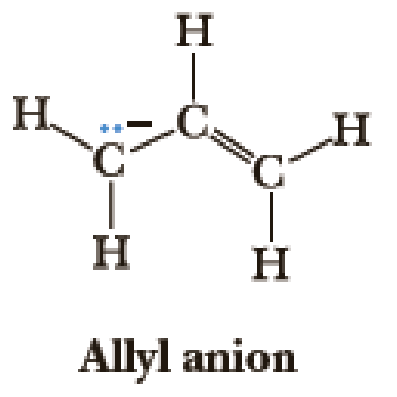
In future chapters, we will encounter carbanions—ions in which a carbon atom has three bonds and a lone pair of electrons and bears a negative charge. Draw another contributing structure for the allyl anion. Now using cartoon representations, draw the three orbitals that represent the delocalized π system (look at Figure 1.26 for a hint). Which of the three orbitals are populated with electrons?
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
Draw the major product of
this reaction. Ignore inorganic
byproducts.
Assume that the water side
product is continuously
removed to drive the reaction
toward products.
(CH3)2NH,
TSOH
Drawing
So, the first image is what I'm trying to understand regarding my approach. The second image illustrates my teacher's method, and the third image includes my notes on the concepts behind these types of problems.
HAND DRAW
Chapter 1 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
Ch. 1.1 - Prob. 1.1PCh. 1.2 - Prob. 1.2PCh. 1.2 - Judging from their relative positions in the...Ch. 1.2 - Classify each bond as nonpolar covalent or polar...Ch. 1.2 - Using the symbols and +, indicate the direction...Ch. 1.2 - Draw Lewis structures showing all valence...Ch. 1.2 - Draw Lewis structures for these ions and show...Ch. 1.3 - Draw Lewis structures and condensed structural...Ch. 1.3 - Prob. 1.9PCh. 1.3 - Prob. 1.10P
Ch. 1.3 - Prob. 1.11PCh. 1.3 - Prob. 1.12PCh. 1.4 - Predict all bond angles for these molecules. (a)...Ch. 1.5 - The geometry of carbon in diamond is tetrahedral,...Ch. 1.5 - Because of their spherical shape, C60 molecules...Ch. 1.5 - What best describes the CCC bond angles in C60? 1....Ch. 1.5 - Prob. 1.14PCh. 1.7 - Describe the bonding in these molecules in terms...Ch. 1.8 - Prob. 1.16PCh. 1.8 - Prob. 1.17PCh. 1.8 - Prob. 1.18PCh. 1.9 - Draw three contributing structures of the...Ch. 1.9 - What is the hybridization state of the circled...Ch. 1.9 - The molecule shown on the right in the example in...Ch. 1.9 - Prob. CQCh. 1.9 - The following structure is called imidazolium....Ch. 1 - Write the ground-state electron configuration for...Ch. 1 - Identify the atom that has each ground-state...Ch. 1 - Define valence shell and valence electron.Ch. 1 - How many electrons are in the valence shell of...Ch. 1 - Prob. 1.24PCh. 1 - Prob. 1.25PCh. 1 - Prob. 1.26PCh. 1 - Write Lewis structures for these compounds. Show...Ch. 1 - Write Lewis structures for these ions. Show all...Ch. 1 - Prob. 1.29PCh. 1 - Some of these structural formulas are incorrect...Ch. 1 - Following the rule that each atom of carbon,...Ch. 1 - Following are several Lewis structures showing all...Ch. 1 - Which statements are true about electronegativity?...Ch. 1 - Why does fluorine, the element in the upper right...Ch. 1 - Arrange the single covalent bonds within each set...Ch. 1 - Using the values of electronegativity given in...Ch. 1 - Prob. 1.37PCh. 1 - Use VSEPR to predict bond angles about each...Ch. 1 - Use VSEPR to predict bond angles about each atom...Ch. 1 - Use VSEPR to predict the geometry of these ions....Ch. 1 - Prob. 1.41PCh. 1 - Prob. 1.42PCh. 1 - What is the meaning of the term tertiary (3) when...Ch. 1 - What is the meaning of the term tertiary (3) when...Ch. 1 - Draw structural formulas for (a) The four primary...Ch. 1 - Draw structural formulas for the three tertiary...Ch. 1 - Prob. 1.47PCh. 1 - Identify the functional groups in each compound.Ch. 1 - Draw a three-dimensional representation for each...Ch. 1 - Tetrafluoroethylene, C2F4, is the starting...Ch. 1 - Which statements are true about resonance...Ch. 1 - Prob. 1.52PCh. 1 - Prob. 1.53PCh. 1 - Prob. 1.54PCh. 1 - Are the structures in each set valid contributing...Ch. 1 - State the orbital hybridization of each...Ch. 1 - Describe each highlighted bond in terms of the...Ch. 1 - Following is a structural formula of the...Ch. 1 - Draw a Lewis structure for methyl isocyanate,...Ch. 1 - What is the hybridization of the highlighted atoms...Ch. 1 - Using cartoon representations, draw a molecular...Ch. 1 - In what kind of orbitals do the lone-pair...Ch. 1 - Draw the delocalized molecular orbitals for the...Ch. 1 - Prob. 1.64APCh. 1 - Each compound contains both ions and covalent...Ch. 1 - Predict whether the carbon-metal bond in these...Ch. 1 - Prob. 1.67APCh. 1 - Phosphorus is immediately under nitrogen in the...Ch. 1 - Draw a Lewis structure for the azide ion, N3. (The...Ch. 1 - Cyanic acid, HOCN, and isocyanic acid, HNCO,...Ch. 1 - In Chapter 6, we study a group of organic cations...Ch. 1 - Many reactions involve a change in hybridization...Ch. 1 - Following is a structural formula of benzene,...Ch. 1 - Following are three contributing structures for...Ch. 1 - (a) Draw a Lewis structure for the ozone molecule,...Ch. 1 - The following two compounds are isomers; that is,...Ch. 1 - In future chapters, we will encounter...Ch. 1 - Prob. 1.78AP
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Draw a mental model for calcium chloride mixed with sodium phosphatearrow_forwardhere is my question (problem number 20) please explain to me thanks!arrow_forwardThe bromination of anisole is an extremely fast reaction. Complete the resonance structures of the intermediate arenium cation for the reaction (Part 1), and then answer the question that follows (Part 2).arrow_forward
- Drawing of 3-fluro-2methylphenolarrow_forwardWhich compound(s) will be fully deprotonated (>99%) by reaction with one molar equivalent of sodium hydroxide? I, II, III I, || I, III I only II, III SH | H3C-C=C-H || III NH2arrow_forwardWill NBS (and heat or light) work for this reaction, or do we have to use Br2?arrow_forward
- HAND DRAWarrow_forwardPredict the major products of the following organic reaction: Some important notes: Δ CN ? • Draw the major product, or products, of the reaction in the drawing area below. • If there aren't any products, because no reaction will take place, check the box below the drawing area instead. Be sure to use wedge and dash bonds when necessary, for example to distinguish between major products that are enantiomers. ONO reaction. Click and drag to start drawing a structure.arrow_forwardThe following product was made from diethyl ketone and what other reagent(s)? £ HO 10 2-pentyne 1-butyne and NaNH2 ☐ 1-propanol ☐ pyridine butanal ☐ pentanoatearrow_forward
- Which pair of reagents will form the given product? OH X + Y a. CH3 b. CH2CH3 ༧་་ C. CH3- CH2CH3 d.o6.(རི॰ e. CH3 OCH2CH3 -MgBr f. CH3-MgBr g. CH3CH2-MgBr -C-CH3 CH2CH3arrow_forwardQuestion 3 What best describes the product of the following reaction? 1. CH3CH2MgBr (2 eq) 2. H a new stereocenter will not be formed a new stereocenter will be formed an alkyl halide will result an alkane will result an aromatic compound will result 1 ptsarrow_forwardRank the following from most to least reactive toward nucleophilic attack. 1. [Select] [Select] 2. Acyl halide Aldehyde 3. Carboxylate ion 4. Carboxylic acid Ketone 5. [Select]arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305580350
Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. Foote
Publisher:Cengage Learning
ENVIRONMENTAL POLLUTION; Author: 7activestudio;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=oxtMFmDTv3Q;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY