
Organic Chemistry
8th Edition
ISBN: 9781305580350
Author: William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. Foote
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 1, Problem 1.71AP
In Chapter 6, we study a group of organic cations called carbocations. Following is the structure of one such carbocation, the tert-butyl cation.
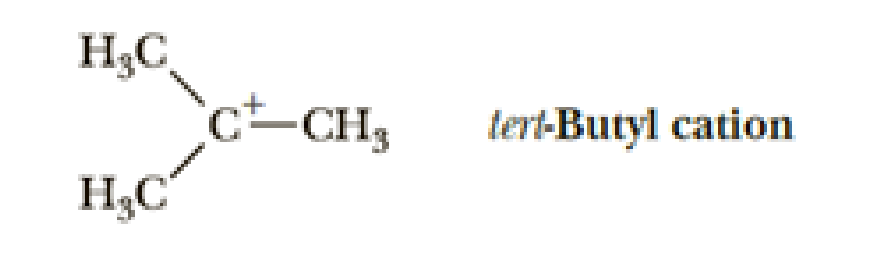
- (a) How many electrons are in the valence shell of the carbon bearing the positive charge?
- (b) Using VSEPR, predict the bond angles about this carbon.
- (c) Given the bond angle you predicted in (b), what hybridization do you predict for this carbon?
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
5. A buffer consists of 0.45 M NH, and 0.25 M NH-CI (PK of NH 474) Calculate the pH of the butter. Ans: 9.52
BAS
PH-9.26 +10g (10.95))
14-4.59
PH=4.52
6. To 500 ml of the buffer on #5 a 0.20 g of sample of NaOH was added
a Write the net ionic equation for the reaction which occurs
b. Should the pH of the solution increase or decrease sightly?
Calculate the pH of the buffer after the addition Ans: 9.54
Explain the inductive effect (+I and -I) in benzene derivatives.
The inductive effect (+I and -I) in benzene derivatives, does it guide ortho, meta or para?
Chapter 1 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
Ch. 1.1 - Prob. 1.1PCh. 1.2 - Prob. 1.2PCh. 1.2 - Judging from their relative positions in the...Ch. 1.2 - Classify each bond as nonpolar covalent or polar...Ch. 1.2 - Using the symbols and +, indicate the direction...Ch. 1.2 - Draw Lewis structures showing all valence...Ch. 1.2 - Draw Lewis structures for these ions and show...Ch. 1.3 - Draw Lewis structures and condensed structural...Ch. 1.3 - Prob. 1.9PCh. 1.3 - Prob. 1.10P
Ch. 1.3 - Prob. 1.11PCh. 1.3 - Prob. 1.12PCh. 1.4 - Predict all bond angles for these molecules. (a)...Ch. 1.5 - The geometry of carbon in diamond is tetrahedral,...Ch. 1.5 - Because of their spherical shape, C60 molecules...Ch. 1.5 - What best describes the CCC bond angles in C60? 1....Ch. 1.5 - Prob. 1.14PCh. 1.7 - Describe the bonding in these molecules in terms...Ch. 1.8 - Prob. 1.16PCh. 1.8 - Prob. 1.17PCh. 1.8 - Prob. 1.18PCh. 1.9 - Draw three contributing structures of the...Ch. 1.9 - What is the hybridization state of the circled...Ch. 1.9 - The molecule shown on the right in the example in...Ch. 1.9 - Prob. CQCh. 1.9 - The following structure is called imidazolium....Ch. 1 - Write the ground-state electron configuration for...Ch. 1 - Identify the atom that has each ground-state...Ch. 1 - Define valence shell and valence electron.Ch. 1 - How many electrons are in the valence shell of...Ch. 1 - Prob. 1.24PCh. 1 - Prob. 1.25PCh. 1 - Prob. 1.26PCh. 1 - Write Lewis structures for these compounds. Show...Ch. 1 - Write Lewis structures for these ions. Show all...Ch. 1 - Prob. 1.29PCh. 1 - Some of these structural formulas are incorrect...Ch. 1 - Following the rule that each atom of carbon,...Ch. 1 - Following are several Lewis structures showing all...Ch. 1 - Which statements are true about electronegativity?...Ch. 1 - Why does fluorine, the element in the upper right...Ch. 1 - Arrange the single covalent bonds within each set...Ch. 1 - Using the values of electronegativity given in...Ch. 1 - Prob. 1.37PCh. 1 - Use VSEPR to predict bond angles about each...Ch. 1 - Use VSEPR to predict bond angles about each atom...Ch. 1 - Use VSEPR to predict the geometry of these ions....Ch. 1 - Prob. 1.41PCh. 1 - Prob. 1.42PCh. 1 - What is the meaning of the term tertiary (3) when...Ch. 1 - What is the meaning of the term tertiary (3) when...Ch. 1 - Draw structural formulas for (a) The four primary...Ch. 1 - Draw structural formulas for the three tertiary...Ch. 1 - Prob. 1.47PCh. 1 - Identify the functional groups in each compound.Ch. 1 - Draw a three-dimensional representation for each...Ch. 1 - Tetrafluoroethylene, C2F4, is the starting...Ch. 1 - Which statements are true about resonance...Ch. 1 - Prob. 1.52PCh. 1 - Prob. 1.53PCh. 1 - Prob. 1.54PCh. 1 - Are the structures in each set valid contributing...Ch. 1 - State the orbital hybridization of each...Ch. 1 - Describe each highlighted bond in terms of the...Ch. 1 - Following is a structural formula of the...Ch. 1 - Draw a Lewis structure for methyl isocyanate,...Ch. 1 - What is the hybridization of the highlighted atoms...Ch. 1 - Using cartoon representations, draw a molecular...Ch. 1 - In what kind of orbitals do the lone-pair...Ch. 1 - Draw the delocalized molecular orbitals for the...Ch. 1 - Prob. 1.64APCh. 1 - Each compound contains both ions and covalent...Ch. 1 - Predict whether the carbon-metal bond in these...Ch. 1 - Prob. 1.67APCh. 1 - Phosphorus is immediately under nitrogen in the...Ch. 1 - Draw a Lewis structure for the azide ion, N3. (The...Ch. 1 - Cyanic acid, HOCN, and isocyanic acid, HNCO,...Ch. 1 - In Chapter 6, we study a group of organic cations...Ch. 1 - Many reactions involve a change in hybridization...Ch. 1 - Following is a structural formula of benzene,...Ch. 1 - Following are three contributing structures for...Ch. 1 - (a) Draw a Lewis structure for the ozone molecule,...Ch. 1 - The following two compounds are isomers; that is,...Ch. 1 - In future chapters, we will encounter...Ch. 1 - Prob. 1.78AP
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 19.57 Using one of the reactions in this chapter, give the correct starting material (A-L) needed to produce each structure (a-f). Name the type of reaction used. (b) ہ مرد (d) HO (c) དང་ ་་ཡིན་ད་དང་ (f) HO Br B D of oli H J Br K C 人 ↑arrow_forwardInductive effect (+I and -I) in benzene derivatives.arrow_forward7. Helparrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305580350
Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. Foote
Publisher:Cengage Learning
INTRODUCTION TO MOLECULAR QUANTUM MECHANICS -Valence bond theory - 1; Author: AGK Chemistry;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=U8kPBPqDIwM;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY