
(a)
Interpretation: The shortest
Concept introduction: There is an inverse relationship between bond length and bond strength. Shorter bonds are stronger bonds or higher the bond order, shorter is the bond length.
Answer to Problem 1.74P
The shortest
Explanation of Solution
In hybridization, one
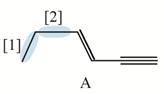
Figure 1
Both
The shortest
(b)
Interpretation: The longest
Concept introduction: There is an inverse relationship between bond length and bond strength. Shorter bonds are stronger bonds or higher the bond order shorter is the bond length.
Answer to Problem 1.74P
The longest
Explanation of Solution
In hybridization, one
The longest
(c)
Interpretation: The shortest
Concept introduction: There is an inverse relationship between bond length and bond strength. Shorter bonds are stronger bonds or higher the bond order shorter is the bond length.
Answer to Problem 1.74P
The shortest
Explanation of Solution
In hybridization, one
The shortest
(d)
Interpretation: The weakest
Concept introduction: There is an inverse relationship between bond length and bond strength. Shorter bonds are stronger bonds or higher the bond order shorter is the bond length.
Answer to Problem 1.74P
The weakest
Explanation of Solution
In hybridization, one
Both
The weakest
(e)
Interpretation: The strongest
Concept introduction: There is an inverse relationship between bond length and bond strength. Shorter bonds are stronger bonds or higher the bond order shorter is the bond length.
Answer to Problem 1.74P
The strongest
Explanation of Solution
The length and strength of a
Triple bond is formed by
The strongest
(f)
Interpretation: Bond
Concept introduction: There is an inverse relationship between bond length and bond strength. Shorter bonds are stronger bonds or higher the bond order shorter is the bond length.
Answer to Problem 1.74P
Bond
Explanation of Solution
In hybridization, one
Bond
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 1 Solutions
Organic Chemistry-Package(Custom)
- Help me understand this! Thank you in advance.arrow_forward22.22 For each compound, indicate which group on the ring is more strongly activating and then draw a structural formula of the major product formed by nitration of the compound. Br CHO (a) CH3 (b) (c) CHO CH3 SO₂H (d) ☑ OCHS NO₂ (e) (f) CO₂H NHCOCH3 NHCOCH, (h) CHS 22.23 The following molecules each contain two aromatic rings. (b) 000-100- H3C (a) (c) Which ring in each undergoes electrophilic aromatic substitution more readily? Draw the major product formed on nitration.arrow_forwardV Consider this step in a radical reaction: Br: ? What type of step is this? Check all that apply. Draw the products of the step on the right-hand side of the drawing area below. If more than one set of products is possible, draw any set. Also, draw the mechanism arrows on the left-hand side of the drawing area to show how this happens. ⚫ionization termination initialization neutralization none of the abc Explanation Check 80 Ο F3 F1 F2 2 F4 01 % do5 $ 94 #3 X 5 C MacBook Air 25 F5 F6 66 ©2025 ˇ F7 29 & 7 8arrow_forward
- Show how to convert ethyl benzene to (a) 2,5-dichlorobenzoic acid and (b) 2,4-dichlorobenzoic acid.arrow_forwardno aiarrow_forwardPolymers may be composed of thousands of monomers. Draw three repeat units (trimer) of the polymer formed in this reaction. Assume there are hydrogen atoms there are hydrogen atoms on the two ends of the trimer. Ignore inorganic byproducts.arrow_forward
- 8:44 PM Sun Apr 13 Earn Freecash.com O Measurement and Matter =1 Setting up a unit conversion 110 Eddie says... ✰ www-awu.aleks.com A student sets up the following equation to convert a measurement. (The ? stands for a number the student is going to calculate.) Fill in the missing part of this equation. Note: your answer should be in the form of one or more fractions multiplied together. (- 4 J kJ -7.0 × 10 ☐ = ? mmol.°C mol °C x10 μ Explanation Check □·□ torox.io Grey Hill LLC. All Rightsarrow_forwardPolymers may be composed of thousands of monomers. Draw three repeat units (trimer) of the polymer formed in this reaction. Assume there are hydrogen atoms there are hydrogen atoms on the two ends of the trimer. Ignore inorganic byproducts please.arrow_forwardi need help with the folarrow_forward

 Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning





