
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
To label each bond in the compounds as ionic or covalent.
Concept introduction:
In chemistry
Ionic bond is the bond that is formed when one or more electrons from the valence shell of an atom are completely transfer to another atom valence shell. Formation of ionic bond is shown below in Fig.1.
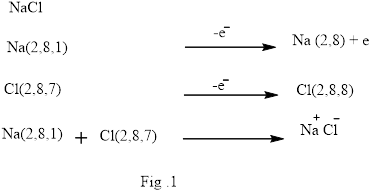
Covalent bond is formed between two atoms by mutual sharing of electrons pairs between them. By mutual sharing of electron pairs the atom attains the stable noble gas configuration. Thus in the covalent bonding the combining atom have equal claim of the shared electron pair. Illustration of covalent bond is shown below in Fig.2.
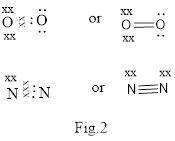
(b)
Interpretation:
To label each bond in the compounds as ionic or covalent.
Concept introduction:
In chemistry chemical bond is defined as an attractive force that contains various constituent particles (atoms, ions and molecules) in different chemical species. The chemical bond is off many types. Ionic or electrovalent bond, covalent bond and coordinate covalent bond.
Ionic bond is the bond that is formed when one or more electrons from the valence shell of an atom are completely transfer to another atom valence shell. Formation of ionic bond is shown below in Fig.1.

Covalent bond is formed between two atoms by mutual sharing of electrons pairs between them. By mutual sharing of electron pairs the atom attains the stable noble gas configuration. Thus in the covalent bonding the combining atom have equal claim of the shared electron pair. Illustration of covalent bond is shown below in Fig.2.
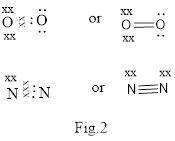
(c)
Interpretation:
To label each bond in the compounds as ionic or covalent.
Concept introduction:
In chemistry chemical bond is defined as an attractive force that contains various constituent particles (atoms, ions and molecules) in different chemical species. The chemical bond is off many types. Ionic or electrovalent bond, covalent bond and coordinate covalent bond.
Ionic bond is the bond that is formed when one or more electrons from the valence shell of an atom are completely transfer to another atom valence shell. Formation of ionic bond is shown below in Fig.1.

Covalent bond is formed between two atoms by mutual sharing of electrons pairs between them. By mutual sharing of electron pairs the atom attains the stable noble gas configuration. Thus in the covalent bonding the combining atom have equal claim of the shared electron pair. Illustration of covalent bond is shown below in Fig.2.
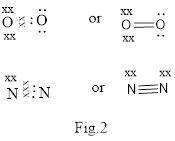
(d)
Interpretation:
To label each bond in the compounds as ionic or covalent.
Concept introduction:
In chemistry chemical bond is defined as an attractive force that contains various constituent particles (atoms, ions and molecules) in different chemical species. The chemical bond is off many types. Ionic or electrovalent bond, covalent bond and coordinate covalent bond.
Ionic bond is the bond that is formed when one or more electrons from the valence shell of an atom are completely transfer to another atom valence shell. Formation of ionic bond is shown below in Fig.1.

Covalent bond is formed between two atoms by mutual sharing of electrons pairs between them. By mutual sharing of electron pairs the atom attains the stable noble gas configuration. Thus in the covalent bonding the combining atom have equal claim of the shared electron pair. Illustration of covalent bond is shown below in Fig.2.
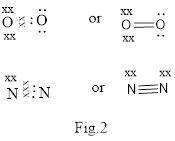
(d)
Interpretation:
To label each bond in the compounds as ionic or covalent.
Concept introduction:
In chemistry chemical bond is defined as an attractive force that contains various constituent particles (atoms, ions and molecules) in different chemical species. The chemical bond is off many types. Ionic or electrovalent bond, covalent bond and coordinate covalent bond.
Ionic bond is the bond that is formed when one or more electrons from the valence shell of an atom are completely transfer to another atom valence shell. Formation of ionic bond is shown below in Fig.1.

Covalent bond is formed between two atoms by mutual sharing of electrons pairs between them. By mutual sharing of electron pairs the atom attains the stable noble gas configuration. Thus in the covalent bonding the combining atom have equal claim of the shared electron pair. Illustration of covalent bond is shown below in Fig.2.
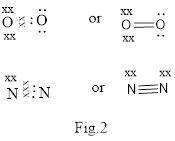
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 1 Solutions
Organic Chemistry-Package(Custom)
- Provide the reagents for the following reactions.arrow_forwardIf I have 1-bromopropene, to obtain compound Z, I have to add two compounds A1 and A2. Indicate which compounds are needed. P(C6H5)3arrow_forwardDraw the major product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts. Assume that the water side product is continuously removed to drive the reaction toward products. O CH3CH2NH2, TSOH Select to Draw >arrow_forward
- Indicate the products obtained by reacting fluorobenzene with a sulfonitric mixture.arrow_forwardIf I have 1-bromopropene, to obtain compound A, I have to add NaOH and another compound. Indicate which compound that would be. C6H5 CH3arrow_forwardIf I have 1-bromopropene and I want to obtain (1,1-dipropoxyethyl)benzene, indicate the compound that I should add in addition to NaOH.arrow_forward
- Draw the major product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts. Ο HSCH2CH2CH2SH, BF3 Select to Draw I Submitarrow_forwardFeedback (7/10) Draw the major product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts. Assume that the water side product is continuously removed to drive the reaction toward products. Incorrect, 3 attempts remaining Ο (CH3CH2)2NH, TSOH Select to Draw V N. 87% Retryarrow_forwardIf I want to obtain (1,1-dipropoxyethyl)benzene from 1-bromopropene, indicate the product that I have to add in addition to NaOH.arrow_forward

 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning Living By Chemistry: First Edition TextbookChemistryISBN:9781559539418Author:Angelica StacyPublisher:MAC HIGHER
Living By Chemistry: First Edition TextbookChemistryISBN:9781559539418Author:Angelica StacyPublisher:MAC HIGHER World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning





