
Concept explainers
Assign formal charges to each carbon atom in the given species. All lone pairs have been drawn in.
a.
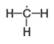 d.
d. 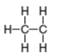
(a)
Interpretation: The formal charge on each carbon atom in the given species is to be assigned.
Concept introduction: The formal charge on an atom is calculated by the formula,
Answer to Problem 1.41P
In the given species, the formal charge on carbon atom of
Explanation of Solution
The given species is
The formal charge on an atom is calculated by the formula,
Substitute these values in the above equation to calculate the formal charge.
For the carbon present in
Substitute these values in above equation to calculate the formal charge on the carbon of
Thus, in the given species, the formal charge on carbon atom of
(a) In the given species, the formal charge on carbon atom of
(b)
Interpretation: The formal charge on each carbon atom in the given species is to be assigned.
Concept introduction: The formal charge on an atom is calculated by the formula,
Answer to Problem 1.41P
In the given species, the formal charge on carbon atom is zero as shown below.
Explanation of Solution
The given species is
The formal charge on an atom is calculated by the formula,
Substitute these values in above equation to calculate the formal charge on carbon atom.
Thus, in the given species, the formal charge on carbon atom is zero.
In the given species, the formal charge on carbon atom is zero.
(c)
Interpretation: The formal charge on each carbon atom in the given species is to be assigned.
Concept introduction: The formal charge on an atom is calculated by the formula,
Answer to Problem 1.41P
In the given species, the formal charge on carbon atom is zero as shown below.
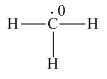
Explanation of Solution
The given species is,
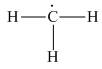
Figure 1
The formal charge on an atom is calculated by the formula,
For the given carbon atom,
Substitute these values in above equation, to calculate the formal charge on carbon atom.
Thus, in the given species, the formal charge on carbon atom is zero.

Figure 2
In the given species, the formal charge on carbon atom is zero.
(d)
Interpretation: The formal charge on each carbon atom in the given species is to be assigned.
Concept introduction: The formal charge on an atom is calculated by the formula,
Answer to Problem 1.41P
In the given species, the formal charge on carbon atom of
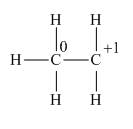
Explanation of Solution
The given species is,
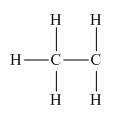
Figure 3
The formal charge on an atom is calculated by the formula,
Substitute these value in above equation to calculate the formal charge on the carbon of
For the carbon of
Substitute these value in above equation to calculate the formal charge on the carbon of
Thus, in the given species, the formal charge on carbon atom of

Figure 4
In the given species, the formal charge on carbon atom of
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 1 Solutions
Organic Chemistry-Package(Custom)
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Applications and Investigations in Earth Science (9th Edition)
Biology: Life on Earth with Physiology (11th Edition)
Human Biology: Concepts and Current Issues (8th Edition)
Brock Biology of Microorganisms (15th Edition)
General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry - 4th edition
- please helparrow_forwardExperiment 1 Data Table 1: Conservation of Mass - Initial Mass Data Table 1 Data Table 2 Data Table 3 Data Table 4 Panel 1 Photo 1 Data Table 5 Reaction Mass of test tube and 5.0% HC₂H₂O2 (g) # (A) (B) Mass of NaHCO, (g) Mass of balloon and NaHCO, (g) (C) 0.10 1 0829 14.38g 0.20 2 0.929 14.29g 0.35 1.00g 3 14.25g 0.50 1.14g 14.29 Experiment 1 Data Table 2: Moles of HC2H3O2 Reaction Volume of Mass of Moles of HC₂H₂O₂ 5.0% Vinegar (g) (ML) 5.0 0.25 0042 mol 2 5.0 0.25 0042 mol 3 5.0 0.25 0042 mol 5.0 0.25 0042 mol Experiment 1 Data Table 3: Moles of NaHCO3 Reaction Mass of NaHCO (g) 10g 20g 35g 50g Experiment 1 Data Table 4: Theoretical Yield of CO₂ Reaction # 1 2 3 Experiment 1 Total mass before reaction (g) (D=A+C) 15.29 15.21g 15.25g 15.349 Exercise 1 Data Table 1 Data Table 2 Data Table 3 Data Table 4 Panel 1 Photo 1 Data Table 5 Exercise 1- Data Table 1 Data Table 2 DataTable 3 Data Table 4 Panel 1 Photo 1 Data Table 5 Exercise 1- Moles of NaHCO 0012 mol 0025 mol 0044 mol 0062 mol…arrow_forwardThe chemical reaction you investigated is a two-step reaction. What type of reaction occurs in each step? How did you determine your answer?arrow_forward
- What is the relationship between the limiting reactant and theoretical yield of CO2?arrow_forwardFrom your calculations, which reaction experiment had closest to stoichiometric quantities? How many moles of NaHCO3 and HC2H3O2 were present in this reaction?arrow_forward18. Arrange the following carbocations in order of decreasing stability. 1 2 A 3124 B 4213 C 2431 D 1234 E 2134 SPL 3 4arrow_forward
- Acetic acid is added to DI water at an initial concentration of 10 -6 M (Ka=1.8x10-5) A. Using the "ICE" Method, what would the pH be at equilibrium? State assumptions and show your work. B. Using the simultaneous equations method, what would the pH be at equilibrium? Show your workarrow_forward1. Show that the change in entropy for a fixed amount of ideal gas held at a constant temperature undergoing a volume change is given by the simple equation AS = NkB In Hint: Start with the equation M dS = du + (Œ) dv - Ž (#) an, dU du+av-dN; j=1 Why doesn't the equation for the entropy of an ideal gas depend on the strength of the intermolecular forces for the gas?arrow_forward2. Make an ice cube at 1 bar pressure by freezing an amount of liquid water that is 2 cm x 2 cm x 2 cm in volume. The density of liquid water at 0 °C is 1.000 g cm³ and the density of ice at 0 °C is 0.915 g cm³. Note that this difference in density is the reason your water pipes burst if they freeze and why you shouldn't forget to take your bottle of pop out of the freezer if you put it in there to try and cool it down faster. A. What is the work of expansion upon freezing? B. Is work done on the system or by the system?arrow_forward
- I have a excitation/emission spectra of a quinine standard solution here, and I'm having trouble interpreting it. the red line is emission the blue line is excitation. i'm having trouble interpreting properly. just want to know if there is any evidence of raman or rayleigh peaks in the spectra.arrow_forwardGive the major product of the following reaction. excess 1. OH, H₂O 1.OH H CH3CH2CH21 H 2. A.-H₂O Draw the molecule on the canvas by choosing buttons from the Tools (for bonds), Atoms, and Advanced Template toolbars. The single bond is active by default.arrow_forward2. Use Hess's law to calculate the AH (in kJ) for: rxn CIF(g) + F2(g) → CIF 3 (1) using the following information: 2CIF(g) + O2(g) → Cl₂O(g) + OF 2(g) AH = 167.5 kJ ΔΗ 2F2 (g) + O2(g) → 2 OF 2(g) 2C1F3 (1) + 202(g) → Cl₂O(g) + 3 OF 2(g) о = = -43.5 kJ AH = 394.1kJarrow_forward
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning

