
The Greenhouse Effect and Global Warming
Although seasons come and go, on average the earth’s climate is very steady. To maintain this stability, the earth must radiate thermal energy—electromagnetic waves—back into space at exactly the same average rate that it receives energy from the sun. Because the earth is much cooler than the sun, its thermal radiation is long-wavelength infrared radiation that we cannot see. A straightforward calculation using Stefan's law finds that the average temperature of the earth should be –18°C, or 0°F, for the incoming and outgoing radiation to lie in balance.
This result is clearly not correct; at this temperature, the entire earth would be covered in snow and ice. The measured global average temperature is actually a balmier 15°C, or 59°F. The straightforward calculation fails because it neglects to consider the earth’s atmosphere. At visible wavelengths, as the figure shows, the atmosphere has a wide “window” of transparency, but this is not true at the infrared wavelengths of the earth’s thermal radiation. The atmosphere lets in the visible radiation from the sun, but the outgoing thermal radiation from the earth sees a much smaller “window.” Most of this radiation is absorbed in the atmosphere.
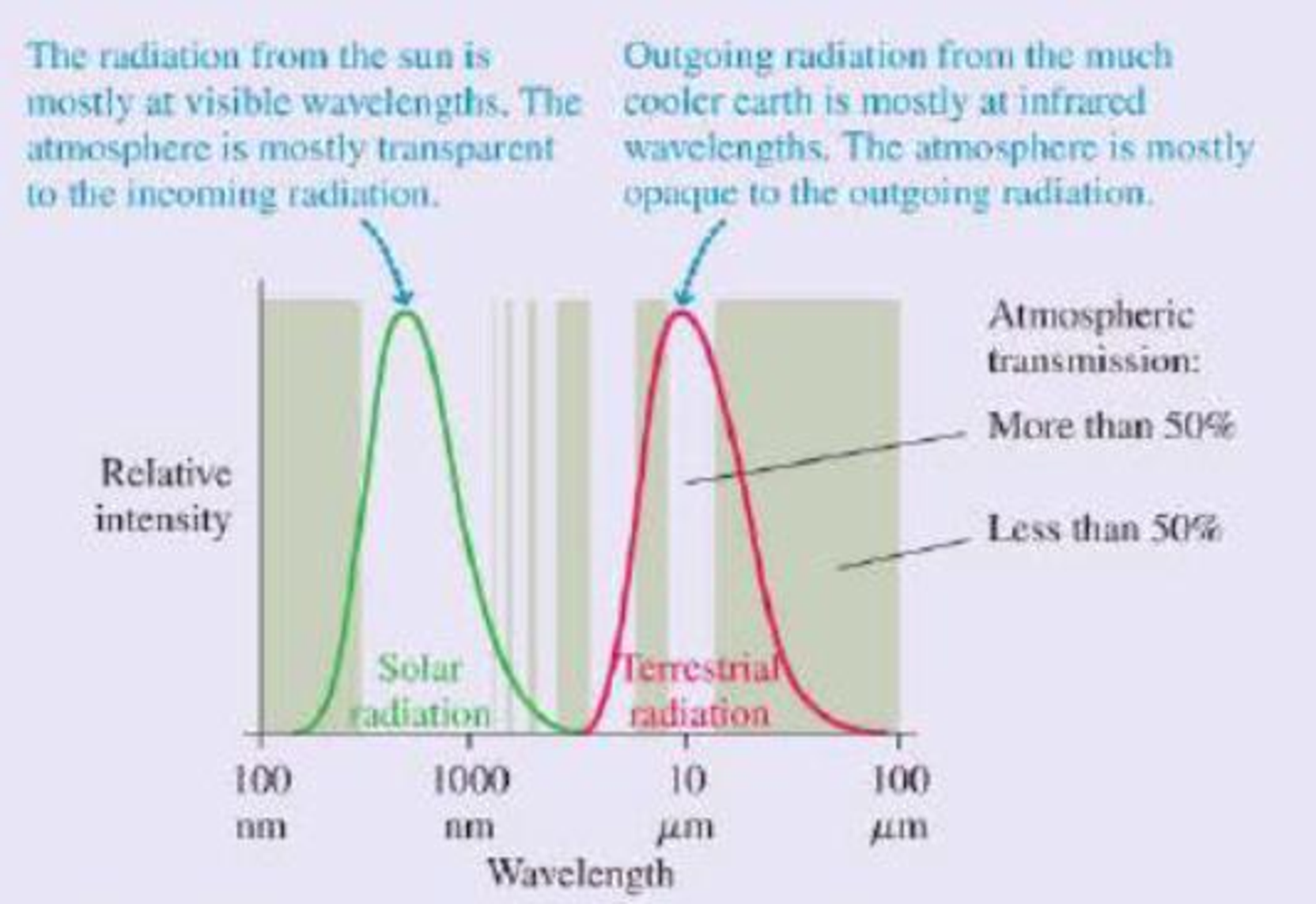
Thermal radiation curves for the sun and the earth. The shaded bands show regions for which the atmosphere is transparent (no shading) or opaque (shaded) to electromagnetic radiation.
Because it’s easier for visible radiant energy to get in than for infrared to get out, the earth is warmer than it would be without the atmosphere. The additional warming of the earth’s surface because of the atmosphere is called the greenhouse effect. The greenhouse effect is a natural part of the earth’s physics; it has nothing to do with human activities, although it’s doubtful any advanced life forms would have evolved without it.
The atmospheric gases most responsible for the greenhouse effect are carbon dioxide and water vapor, both strong absorbers of infrared radiation. These greenhouse gases are of concern today because humans, through the burning of fossil fuels (oil, coal, and natural gas), are rapidly increasing the amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. Preserved air samples show that carbon dioxide made up 0.027% of the atmosphere before the industrial revolution. In the last 150 years, human activities have increased the amount of carbon dioxide by nearly 50%, to about 0.040%. By 2050, the carbon dioxide concentration will likely increase to 0.054%, double the pre-industrial value, unless the use of fossil fuels is substantially reduced.
Carbon dioxide is a powerful absorber of infrared radiation. And good absorbers are also good emitters. The carbon dioxide in the atmosphere radiates energy back to the surface of the earth, warming it. Increasing the concentration of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere means more radiation: this increases the average surface temperature of the earth. The net result is global warming.
There is strong evidence that (he earth has warmed nearly 1°C in the last 100 years because of increased greenhouse gases. What happens next? Climate scientists, using sophisticated models of the earth’s atmosphere and oceans, calculate that a doubling of the carbon dioxide concentration will likely increase the earth’s average temperature by an additional 2°C (≈ 3°F) to 6°C (≈9°F) There is some uncertainty in these calculations; the earth is a large and complex system. Perhaps the earth will get cloudier as the temperature increases, moderating the increase. Or perhaps the arctic ice cap will melt, making the earth less reflective and leading to an even more dramatic
But the basic physics that leads to the greenhouse effect, and to global warming, is quite straightforward. Carbon dioxide in the atmosphere keeps the earth warm; more carbon dioxide will make it warmer. How much warmer? That’s an important question, one that many scientists around the world are attempting to answer with ongoing research. But large or small, change is coming. Global warming is one of the most serious challenges facing scientists, engineers, and all citizens in the 21st century.
The following questions are related to the passage “The Greenhouse Effect and Global Warming” on the previous page.
The thermal radiation from the earth’s surface peaks at a wavelength of approximately 10 μm. What is the energy of a photon at this wavelength?
- A. 2.4 eV
- B. 1.2 eV
- C. 0.24 eV
- D. 0.12eV
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter P Solutions
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Biology: Life on Earth (11th Edition)
Applications and Investigations in Earth Science (9th Edition)
Chemistry: An Introduction to General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry (13th Edition)
Human Anatomy & Physiology (2nd Edition)
Anatomy & Physiology (6th Edition)
- Solve and answer the problem correctly and be sure to check your work. Thank you!!arrow_forwardThe spring in the figure has a spring constant of 1300 N/m. It is compressed 17.0 cm, then launches a 200 g block. The horizontal surface is frictionless, but the block’s coefficient of kinetic friction on the incline is 0.200. What distance d does the block sail through the air?arrow_forwardSolve and answer the problem correctly and be sure to check your work. Thank you!!arrow_forward
- Solve and answer the problem correctly and be sure to check your work. Thank you!!arrow_forwardA 10-m-long glider with a mass of 680 kg (including the passengers) is gliding horizontally through the air at 28 m/s when a 60 kg skydiver drops out by releasing his grip on the glider. What is the glider's speed just after the skydiver lets go?arrow_forwardPROBLEM 2 A cube of mass m is placed in a rotating funnel. (The funnel is rotating around the vertical axis shown in the diagram.) There is no friction between the cube and the funnel but the funnel is rotating at just the right speed needed to keep the cube rotating with the funnel. The cube travels in a circular path of radius r, and the angle between the vertical and the wall of the funnel is 0. Express your answers to parts (b) and (c) in terms of m, r, g, and/or 0. (a) Sketch a free-body diagram for the cube. Show all the forces acting on it, and show the appropriate coordinate system to use for this problem. (b) What is the normal force acting on the cube? FN=mg58 (c) What is the speed v of the cube? (d) If the speed of the cube is different from what you determined in part (c), a force of friction is necessary to keep the cube from slipping in the funnel. If the funnel is rotating slower than it was above, draw a new free-body diagram for the cube to show which way friction…arrow_forward
- Circular turns of radius r in a race track are often banked at an angle θ to allow the cars to achieve higher speeds around the turns. Assume friction is not present. Write an expression for the tan(θ) of a car going around the banked turn in terms of the car's speed v, the radius of the turn r, and g so that the car will not move up or down the incline of the turn. tan(θ) =arrow_forwardThe character Min Min from Arms was a DLC character added to Super Smash Bros. Min Min’s arms are large springs, with a spring constant of 8.53 ⋅ 10^3 N/m, which she uses to punch and fling away her opponents. Min Min pushes her spring arm against Steve, who is not moving, compressing it 1.20 m as shown in figure A. Steve has a mass of 81.6 kg. Assuming she uses only the spring to launch Steve, how fast is Steve moving when the spring is no longer compressed? As Steve goes flying away he goes over the edge of the level, as shown in figure C. What is the magnitude of Steve’s velocity when he is 2.00 m below where he started?arrow_forwardSlinky dog whose middle section is a giant spring with a spring constant of 10.9 N/m. Woody, who has a mass of 0.412 kg, grabs onto the tail end of Slink and steps off the bed with no initial velocity and reaches the floor right as his velocity hits zero again. How high is the bed? What is Woody’s velocity halfway down? Enter just the magnitude of velocity.arrow_forward
- No chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwardA positive charge of 91 is located 5.11 m to the left of a negative charge 92. The charges have different magnitudes. On the line through the charges, the net electric field is zero at a spot 2.90 m to the right of the negative charge. On this line there are also two spots where the potential is zero. (a) How far to the left of the negative charge is one spot? (b) How far to the right of the negative charge is the other?arrow_forwardA charge of -3.99 μC is fixed in place. From a horizontal distance of 0.0423 m, a particle of mass 7.31 x 103 kg and charge -9.76 µC is fired with an initial speed of 84.1 m/s directly toward the fixed charge. How far does the particle travel before its speed is zero?arrow_forward
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9781938168284Author:Andrew Fraknoi; David Morrison; Sidney C. WolffPublisher:OpenStax
AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9781938168284Author:Andrew Fraknoi; David Morrison; Sidney C. WolffPublisher:OpenStax





