
The Greenhouse Effect and Global Warming
Although seasons come and go, on average the earth’s climate is very steady. To maintain this stability, the earth must radiate thermal energy—electromagnetic waves—back into space at exactly the same average rate that it receives energy from the sun. Because the earth is much cooler than the sun, its thermal radiation is long-wavelength infrared radiation that we cannot see. A straightforward calculation using Stefan's law finds that the average temperature of the earth should be –18°C, or 0°F, for the incoming and outgoing radiation to lie in balance.
This result is clearly not correct; at this temperature, the entire earth would be covered in snow and ice. The measured global average temperature is actually a balmier 15°C, or 59°F. The straightforward calculation fails because it neglects to consider the earth’s atmosphere. At visible wavelengths, as the figure shows, the atmosphere has a wide “window” of transparency, but this is not true at the infrared wavelengths of the earth’s thermal radiation. The atmosphere lets in the visible radiation from the sun, but the outgoing thermal radiation from the earth sees a much smaller “window.” Most of this radiation is absorbed in the atmosphere.
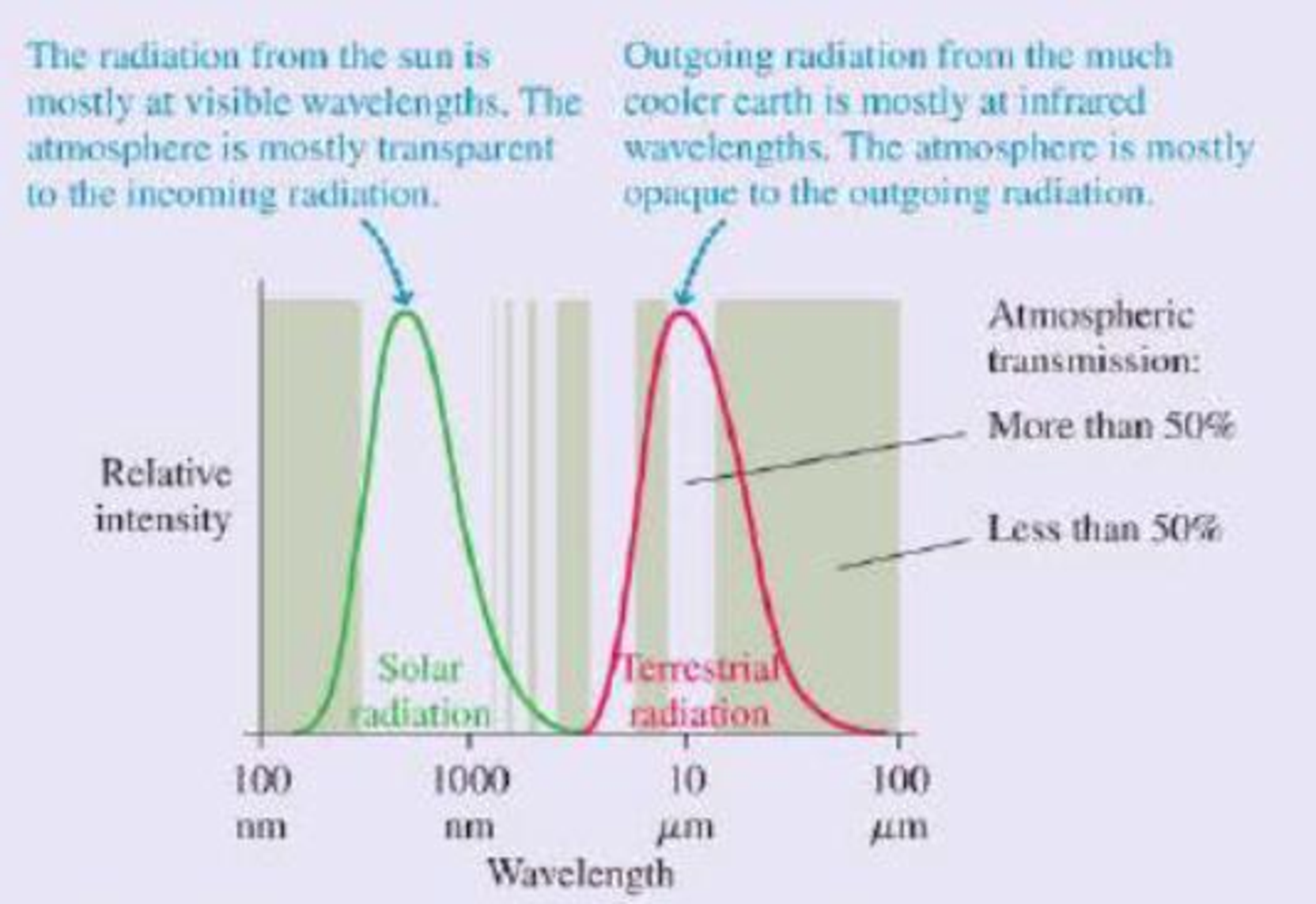
Thermal radiation curves for the sun and the earth. The shaded bands show regions for which the atmosphere is transparent (no shading) or opaque (shaded) to electromagnetic radiation.
Because it’s easier for visible radiant energy to get in than for infrared to get out, the earth is warmer than it would be without the atmosphere. The additional warming of the earth’s surface because of the atmosphere is called the greenhouse effect. The greenhouse effect is a natural part of the earth’s physics; it has nothing to do with human activities, although it’s doubtful any advanced life forms would have evolved without it.
The atmospheric gases most responsible for the greenhouse effect are carbon dioxide and water vapor, both strong absorbers of infrared radiation. These greenhouse gases are of concern today because humans, through the burning of fossil fuels (oil, coal, and natural gas), are rapidly increasing the amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. Preserved air samples show that carbon dioxide made up 0.027% of the atmosphere before the industrial revolution. In the last 150 years, human activities have increased the amount of carbon dioxide by nearly 50%, to about 0.040%. By 2050, the carbon dioxide concentration will likely increase to 0.054%, double the pre-industrial value, unless the use of fossil fuels is substantially reduced.
Carbon dioxide is a powerful absorber of infrared radiation. And good absorbers are also good emitters. The carbon dioxide in the atmosphere radiates energy back to the surface of the earth, warming it. Increasing the concentration of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere means more radiation: this increases the average surface temperature of the earth. The net result is global warming.
There is strong evidence that (he earth has warmed nearly 1°C in the last 100 years because of increased greenhouse gases. What happens next? Climate scientists, using sophisticated models of the earth’s atmosphere and oceans, calculate that a doubling of the carbon dioxide concentration will likely increase the earth’s average temperature by an additional 2°C (≈ 3°F) to 6°C (≈9°F) There is some uncertainty in these calculations; the earth is a large and complex system. Perhaps the earth will get cloudier as the temperature increases, moderating the increase. Or perhaps the arctic ice cap will melt, making the earth less reflective and leading to an even more dramatic
But the basic physics that leads to the greenhouse effect, and to global warming, is quite straightforward. Carbon dioxide in the atmosphere keeps the earth warm; more carbon dioxide will make it warmer. How much warmer? That’s an important question, one that many scientists around the world are attempting to answer with ongoing research. But large or small, change is coming. Global warming is one of the most serious challenges facing scientists, engineers, and all citizens in the 21st century.
The following questions are related to the passage “The Greenhouse Effect and Global Warming” on the previous page.
Averaged over day, night, seasons, and weather conditions, a square meter of the earth’s surface receives an average of 240 W of radiant energy from the sun. The average power radiated back to space is
- A. Less than 240 W.
- B. More than 240 W.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter P Solutions
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
Genetic Analysis: An Integrated Approach (3rd Edition)
Microbiology with Diseases by Body System (5th Edition)
Applications and Investigations in Earth Science (9th Edition)
Human Biology: Concepts and Current Issues (8th Edition)
Anatomy & Physiology (6th Edition)
- A converging lens with a focal length of 6.70 cm forms an image of a 4.60 mm tall real object that is to the left of the lens. The image is 1.50 cm tall and erect. Where are the object and image located? Is the image real or virtual? Please show all stepsarrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwardneed help part earrow_forward
- Critical damping is the case where the mass never actually crosses over equilibrium position, but reaches equilibrium as fast as possible. Experiment with changing c to find the critical damping constant. Use the same initial conditions as in the last problem. Zoom in a bit to make sure you don't allow any oscillations to take place - even small ones.arrow_forwardNASA's KC-135 Reduced Gravity Research aircraft, affectionately known as the "Vomit Comet," is used in training astronauts and testing equipment for microgravity environments. During a typical mission, the aircraft makes approximately 30 to 40 parabolic arcs. During each arc, the aircraft and objects inside it are in free-fall, and passengers float freely in apparent "weightlessness." The figure below shows the altitude of the aircraft during a typical mission. It climbs from 24,000 ft to 30,850 ft, where it begins a parabolic arc with a velocity of 155 m/s at 45.0° nose-high and exits with velocity 155 m/s at 45.0° nose-low. 31 000 45° nose high 45° nose low 24 000 Zero g 65 Maneuver time (s) (a) What is the aircraft's speed (in m/s) at the top of the parabolic arc? 110.0 m/s (b) What is the aircraft's altitude (in ft) at the top of the parabolic arc? 2.04e+04 What is the initial height at the start of the parabolic arc? What is the initial velocity at this point? What is the final…arrow_forward12. What could we conclude if a system has a phase trajectory that sweeps out larger and larger area as time goes by?arrow_forward
- need help part darrow_forwardA cab driver heads south with a steady speed of v₁ = 20.0 m/s for t₁ = 3.00 min, then makes a right turn and travels at v₂ = 25.0 m/s for t₂ = 2.80 min, and then drives northwest at v3 = 30.0 m/s for t3 = 1.00 min. For this 6.80-min trip, calculate the following. Assume +x is in the eastward direction. (a) total vector displacement (Enter the magnitude in m and the direction in degrees south of west.) magnitude direction For each straight-line movement, model the car as a particle under constant velocity, and draw a diagram of the displacements, labeling the distances and angles. Let the starting point be the origin of your coordinate system. Use the relationship speed = distance/time to find the distances traveled during each segment. Write the displacement vector, and calculate its magnitude and direction. Don't forget to convert min to s! m Model the car as a particle under constant velocity, and draw a diagram of the displacements, labeling the distances and angles. Let the…arrow_forwardî A proton is projected in the positive x direction into a region of uniform electric field E = (-5.50 x 105) i N/C at t = 0. The proton travels 7.20 cm as it comes to rest. (a) Determine the acceleration of the proton. magnitude 5.27e13 direction -X m/s² (b) Determine the initial speed of the proton. 8.71e-6 magnitude The electric field is constant, so the force is constant, which means the acceleration will be constant. m/s direction +X (c) Determine the time interval over which the proton comes to rest. 1.65e-7 Review you equations for constant accelerated motion. sarrow_forward
- Three charged particles are at the corners of an equilateral triangle as shown in the figure below. (Let q = 2.00 μC, and L = 0.750 m.) y 7.00 με 60.0° L 9 -4.00 μC x (a) Calculate the electric field at the position of charge q due to the 7.00-μC and -4.00-μC charges. 112 Once you calculate the magnitude of the field contribution from each charge you need to add these as vectors. KN/CI + 64 × Think carefully about the direction of the field due to the 7.00-μC charge. KN/Cĵ (b) Use your answer to part (a) to determine the force on charge q. 240.0 If you know the electric field at a particular point, how do you find the force that acts on a charge at that point? mN Î + 194.0 × If you know the electric field at a particular point, how do you find the force that acts on a charge at that point? mNarrow_forwardIn the Donkey Kong Country video games you often get around by shooting yourself out of barrel cannons. Donkey Kong wants to launch out of one barrel and land in a different one that is a distance in x of 9.28 m away. To do so he launches himself at a velocity of 22.6 m/s at an angle of 30.0°. At what height does the 2nd barrel need to be for Donkey Kong to land in it? (measure from the height of barrel 1, aka y0=0)arrow_forwardFor which value of θ is the range of a projectile fired from ground level a maximum? 90° above the horizontal 45° above the horizontal 55° above the horizontal 30° above the horizontal 60° above the horizontalarrow_forward
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9781938168284Author:Andrew Fraknoi; David Morrison; Sidney C. WolffPublisher:OpenStax
AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9781938168284Author:Andrew Fraknoi; David Morrison; Sidney C. WolffPublisher:OpenStax





