
Concept explainers
Waves in the Earth and the Ocean
In December 2004, a large earthquake off the coast of Indonesia produced a devastating water wave, called a tsunami, that caused tremendous destruction thousands of miles away from the earthquake's epicenter. The tsunami was a dramatic illustration of the energy carried by waves.
It was also a call to action. Many of the communities hardest hit by the tsunami were struck hours after the waves were generated, long after seismic waves from the earthquake that passed through the earth had been detected al distant recording stations, long after the possibility of a tsunami was first discussed. With better detection and more accurate models of how a tsunami is formed and how a tsunami propagates, the affected communities could have received advance warning. The study of physics may seem an abstract undertaking with few practical applications, but on this day a better scientific understanding of these waves could have averted tragedy.
Let’s use our knowledge of waves to explore the properties of a tsunami. In Chapter 15, we saw that a vigorous shake of one end of a rope causes a pulse to travel
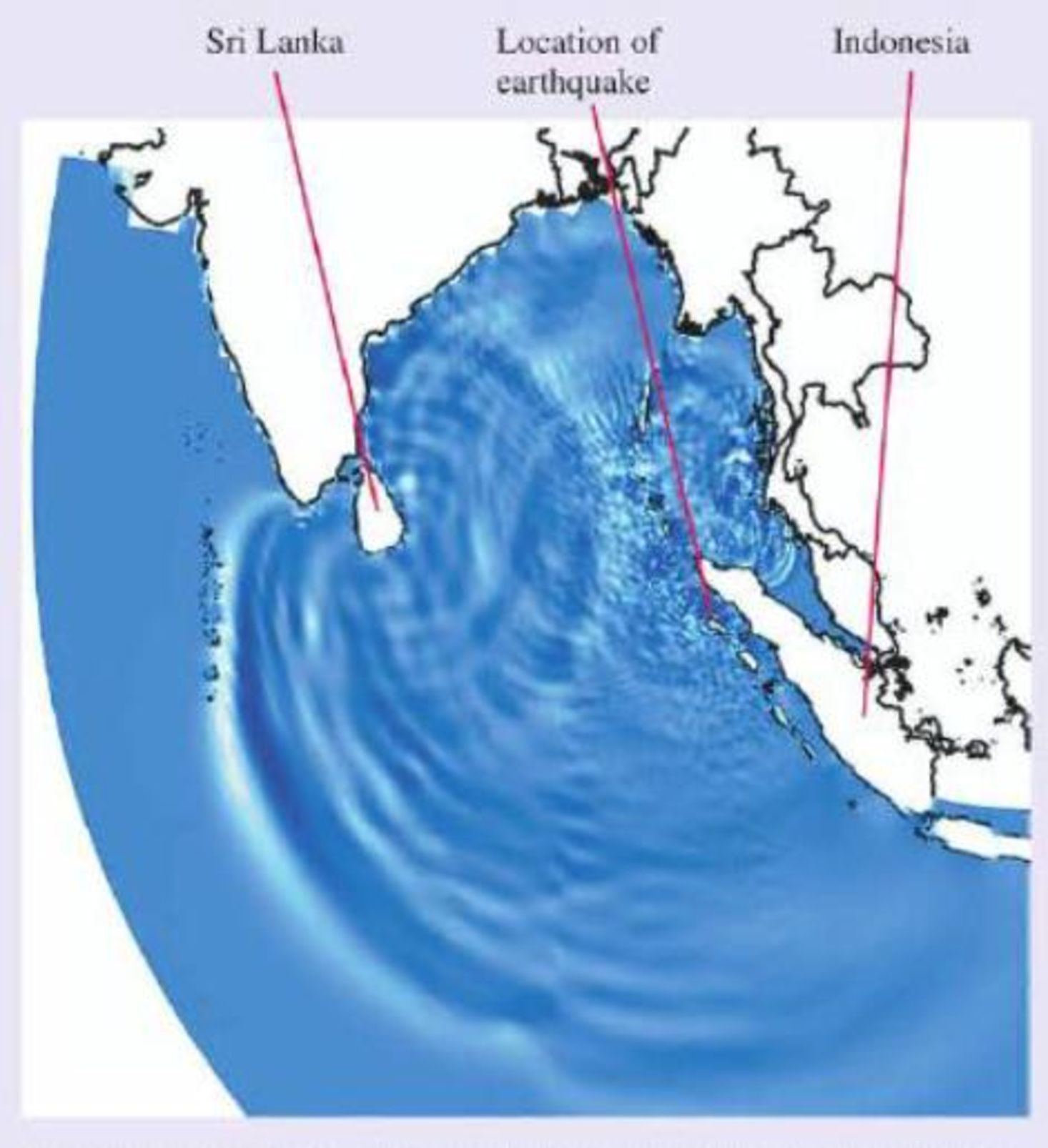
One frame from a computer simulation of the Indian Ocean tsunami three hours after the earthquake that produced it. The disturbance propagating outward from the earthquake is clearly seen, as are wave reflections from the island of Sri Lanka.
along it, carrying energy as it goes. The earthquake that produced the Indian Ocean tsunami of 2004 caused a sudden upward displacement of the seafloor that produced a corresponding rise in the surface of the ocean. This was the disturbance that produced the tsunami, very much like a quick shake on the end of a rope. The resulting wave propagated through the ocean, as we see in the figure.
This simulation of the tsunami looks much like the ripples that spread when you drop a pebble into a pond. But there is a big difference—the scale. The fact that you can see the individual waves on this diagram that spans 5000 km is quite revealing. To show up so clearly, the individual wave pulses must be very wide—up to hundreds of kilometers from front to back.
A tsunami is actually a “shallow water wave,” even in the deep ocean, because the depth of the ocean is much less than the width of the wave. Consequently, a tsunami travels differently than normal ocean waves. In Chapter 15 we learned that wave speeds are fixed by the properties of the medium. That is true for normal ocean waves, but the great width of the wave causes a tsunami to “feel the bottom.” Its wave speed is determined by the depth of the ocean: The greater the depth, the greater the speed. In the deep ocean, a tsunami travels at hundreds of kilometers per hour, much faster than a typical ocean wave. Near shore, as the ocean depth decreases, so docs the speed of the wave.
The height of the tsunami in the open ocean was about half a meter. Why should such a small wave—one that ships didn't even notice as it passed—be so fearsome? Again, it's the width of the wave that matters. Because a tsunami is the wave motion of a considerable mass of water, great energy is involved. As the front of a tsunami wave nears shore, its speed decreases, and the back of the wave moves faster than the front. Consequently, the width decreases. The water begins to pile up, and the wave dramatically increases in height.
The Indian Ocean tsunami had a height of up to 15 m when it reached shore, with a width of up to several kilometers. This tremendous mass of water was still moving at high speed, giving it a great deal of energy. A tsunami reaching the shore isn’t like a typical wave that breaks and crashes. It is a kilometers-wide wall of water that moves onto the shore and just keeps on coming. In many places, the water reached 2 km inland.
The impact of the Indian Ocean tsunami was devastating, but it was the first tsunami for which scientists were able to use satellites and ocean sensors to make planet-wide measurements. An analysis of the data has helped us better understand the physics of these ocean waves. We won’t be able to stop future tsunamis, but with a better knowledge of how they are formed and how they travel, we will be better able to warn people to get out of their way.
The following questions are related to the passage “Waves in the Earth and the Ocean” on the previous page.
In the middle of the Indian Ocean, the tsunami referred to in the passage was a train of pulses approximating a sinusoidal wave with speed 200 m/s and wavelength 150 km. What was the approximate period of these pulses?
A. 1 min
B. 3 min
B. 5min
D. 15 min
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter P Solutions
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Microbiology with Diseases by Body System (5th Edition)
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
Chemistry: An Introduction to General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry (13th Edition)
Human Anatomy & Physiology (2nd Edition)
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach, Vol. 1 (Chs 1-21) (4th Edition)
Applications and Investigations in Earth Science (9th Edition)
- In order for Jane to return to base camp, she needs to swing across a river of width D that is filled with alligators. She must swing into a wind exerting constant horizontal force F, F = 110 N, L = 40.0 m, 0 = 50.0°, and her mass to be 50.0 kg. Wind →F Tarzan! Jane (a) with what minimum speed (in m/s) must Jane begin her swing to just make it to the other side? (If Jane can make it across with zero initial velocity, enter 0.) m/s on a vine having length L and initially making an angle with the vertical (see below figure). Take D = 48.0 m, (b) Shortly after Jane's arrival, Tarzan and Jane decide to swing back across the river (simultaneously). With what minimum speed (in m/s) must they begin their swing? Assume that Tarzan has a mass of 80.0 kg. m/sarrow_forwardR=2.00 12V 2.00 4.00 4.002 What is the current in one of the 4.0 Q resistors? An isolated point charge q is located at point X. Two other points Y and Z are such that YZ2 XY. Y X What is (electric field at Y)/(electric field at Z)?arrow_forwardTwo objects (m₁ = 4.75 kg and m₂ 2.80 kg) are connected by a light string passing over a light, frictionless pulley as in the figure below. The 4.75-kg object is released from rest at a point h = 4.00 m above the table mg m (a) Determine the speed of each object when the two pass each other. m/s (b) Determine the speed of each object at the moment the 4.75-kg object hits the table. m/s (c) How much higher does the 2.80-kg object travel after the 4.75-kg object hits the table? marrow_forward
- A cell of negligible internal resistance is connected to three identical resistors. The current in the cell is 3.0 A. The resistors are now arranged in series. What is the new current in the cell?arrow_forwardA negatively charged sphere is falling through a magnetic field. north pole of magnet direction of motion south pole of magnet What is the direction of the magnetic force acting on the sphere?arrow_forwardElectrons in a conductor are moving down the page. A proton outside the wire is moving to the right. What is the direction of the magnetic force acting on the proton?arrow_forward
- What is the resistance of an ideal voltmeter and the resistance of an ideal ammeter? Resistance of an ideal voltmeter Resistance of an ideal ammeter infinite A. zero B. zero zero C. infinite infinite D. infinite zeroarrow_forwardvariable resistor with a resistance range of 0 to 6.0 KQ is connected in series with two resistors of fixed value 6.0 KQ. The cell in the circuit has an emf of 18 V and a negligible internal resistance. 18 V X Y 6.0 ΚΩ 6.0 ΚΩ 0 - 6.0 ΚΩ What is the maximum range of potential difference that can be observed between X and Y?arrow_forwardA positive point charge of magnitude 1.0 μC and a point charge q are separated by a distance d. electron 1.0 με An electron is placed at a distance d from the +1.0 μC charge. The electric force on the electron is zero. What is q?arrow_forward
- Two point charges of +4q and -q are placed a fixed distance apart. Where is the electric field strength equal to zero? B. +49 D. A network of three resistors is connected to a cell of emf 12V and internal resistance R of 2.0 Q as shown.arrow_forwardThree point charges of equal magnitude are placed at the vertices of an equilateral triangle. The signs of the charges are shown. Point P is equidistant from the vertices of the triangle. What is the direction of the resultant electric field at P? B.arrow_forwardA magnetic force per unit length F acts on P due to Q. The distance between the wires is increased to 2d and the current in Q is decreased to 1/2. P Q P 12 2d What is the magnetic force per unit length that acts on P due to Q after the changes?arrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College An Introduction to Physical SciencePhysicsISBN:9781305079137Author:James Shipman, Jerry D. Wilson, Charles A. Higgins, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
An Introduction to Physical SciencePhysicsISBN:9781305079137Author:James Shipman, Jerry D. Wilson, Charles A. Higgins, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning





