
Concept explainers
Size and Life
Physicists look for simple models and general principles that underlie and explain diverse physical phenomena. In the first 13 chapters of this textbook, you’ve seen that just a handful of general principles and laws can be used to solve a wide range of problems. Can this approach have any relevance to a subject like biology? It may seem surprising, but there are general 'laws of biology“’ that apply, with quantitative accuracy, to organisms as diverse as elephants and mice.
Let’s look at an example. An elephant uses more metabolic power than a mouse. This is not surprising, as an elephant is much bigger. But recasting the data shows an interesting trend. When we looked at the energy required to raise the temperature of different substances, we considered specific heat. The “specific” meant that we considered the heat required for 1 kilogram. For animals, rather than metabolic rate, we can look at the specific metabolic rate, the metabolic power used per kilogram of tissue. If we factor out the mass difference between a mouse and an elephant, are their specific metabolic powers the same?
In fact, the specific metabolic rate varies quite a bit among mammals, as the graph of specific metabolic rate versus mass shows. But there is an interesting trend: All of the data points lie on a single smooth curve. In other words, there really is a biological law we can use to predict a mammal’s metabolic rate knowing only its mass M. In particular, the specific metabolic rate is proportional to M –0.25. Because a 4000 kg elephant is 160,000 times more massive than a 25 g mouse, the mouse’s specific metabolic power is (160,000)0.25 = 20 times that of the elephant. A law that shows how a property scales with the size of a system is called a scaling law.
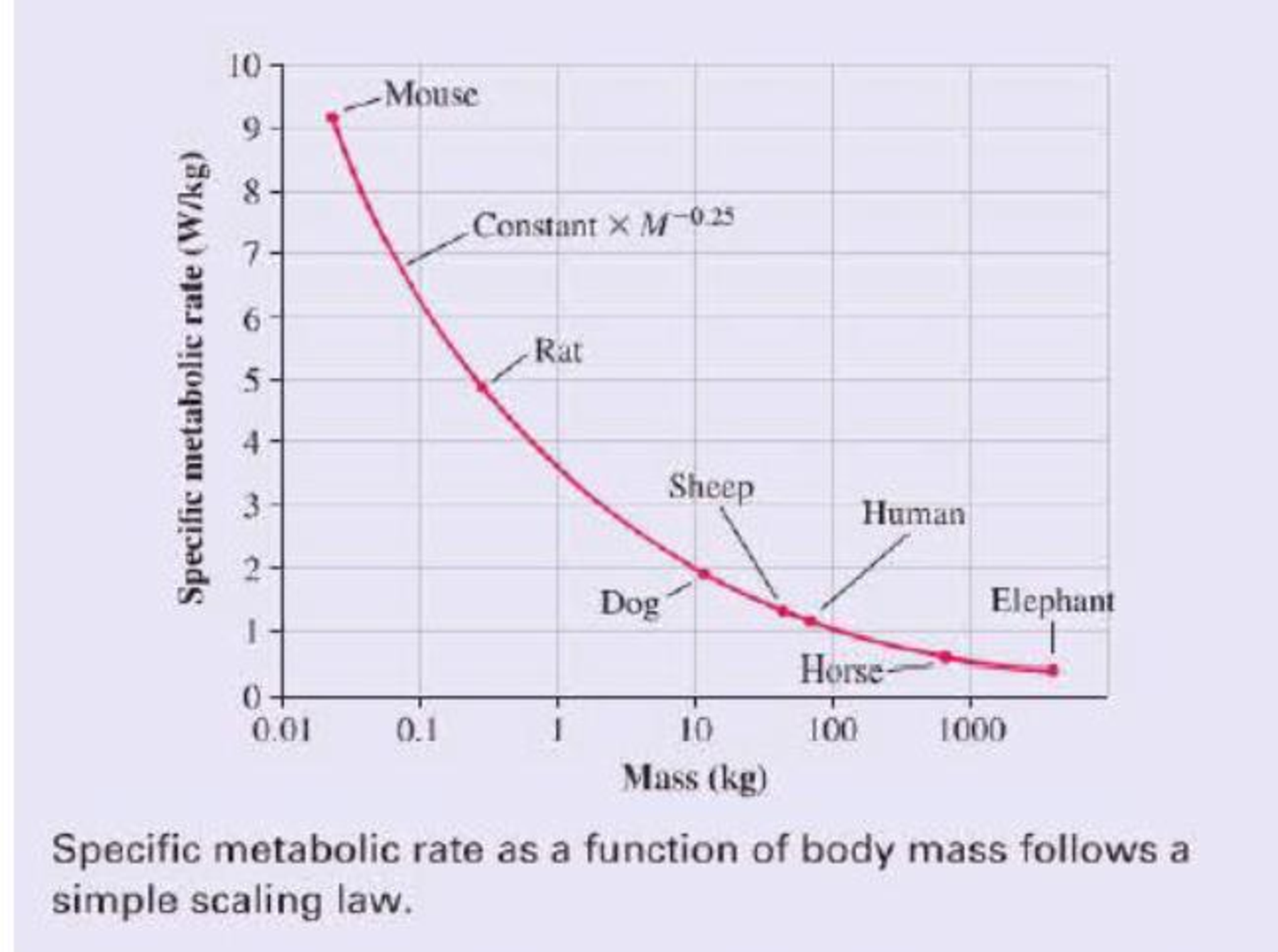
A similar scaling law holds for birds, reptiles, and even bacteria. Why should a single simple relationship hold true for organisms that range in size from a single cell to a 100 ton blue whale? Interestingly, no one knows for sure. It is a matter of current research to find out just what this and other scaling laws tell us about the nature of life.
Perhaps the metabolic-power scaling law is a result of
If heat dissipation were the only factor limiting metabolism, we can show that the specific metabolic rate should scale as M–0.33quite different from the M–0.25 scaling observed. Clearly, another factor is at work. Exactly what underlies the M–0.25 scaling is still a matter of debate, but some recent analysis suggests the scaling is due to limitations not of heat transfer but of fluid flow. Cells in mice, elephants, and all mammals receive nutrients and oxygen for metabolism from the bloodstream. Because the minimum size of a capillary is about the same for all mammals, the structure of the circulatory system must vary from animal to animal. The human aorta has a diameter of about 1 inch; in a mouse, the diameter is approximately l/20th of this. Thus a mouse has fewer levels of branching to smaller and smaller blood vessels as we move from the aorta to the capillaries. The smaller blood vessels in mice mean that viscosity is more of a factor throughout the circulatory system. The circulatory system of a mouse is quite different from that of ail elephant.
A model of specific metabolic rate based on blood-flow limitations predicts a M–0.25 law, exactly as observed. The model also makes other testable predictions. For example, the model predicts that the smallest possible mammal should have a body mass of about 1 gram—exactly the size of the smallest shrew. Even smaller animals have different types of circulatory' systems; in the smallest animals, nutrient transport is by diffusion alone. But the model can be extended to predict that the specific metabolic rate for these animals will follow a scaling law similar to that for mammals, exactly as observed. It is too soon to know if this model will ultimately prove to be correct, but it’s indisputable that there are large-scale regularities in biology that follow mathematical relationships based on the laws of physics.
The following questions are related to the passage "Size and Life" on the previous page.
Given the data of the graph, approximately how much energy, in Calories, would a 200 g rat use during the course of a day?
- A. 10
- B. 20
- C. 100
- D. 200
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter P Solutions
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
Campbell Biology in Focus (2nd Edition)
Campbell Biology: Concepts & Connections (9th Edition)
Chemistry: An Introduction to General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry (13th Edition)
Campbell Essential Biology with Physiology (5th Edition)
Chemistry: A Molecular Approach (4th Edition)
- A particular water pipe has a radius of 0.28 meters. If the pipe is completely filled with water, moving with average velocity 0.45 m/s, what is the flow rate of water through the pipe with units of cubic meters of water per second?arrow_forwardWater is flowing through a horizontal pipe with two segments. In one segment, the water flows at a speed v1 = 4.52 m/s. In the second segment the speed of the water is v2 = 2.38 m/s. Based on Bernoulli's Principle, what is the difference in pressure (P2 - P1) between the two segments? Assume that the density of the water is 997 kg/m3 and give your answer as the number of Pascals (i.e. N/m2).arrow_forwardWater from the faucet is supplied to the hose at a rate of 0.00057 m3/s. At what speed (number of meters per second) does the water exit the nozzle if the cross sectional area of the narrow nozzle is 2.1 x 10-6 m2?arrow_forward
- Jason Fruits/Indiana University Research Communications Silver/ silver oxide Zinc zinc/oxidearrow_forwardCar P moves to the west with constant speed v0 along a straight road. Car Q starts from rest at instant 1, and moves to the west with increasing speed. At instant 5, car Q has speed w0 relative to the road (w0 < v0). Instants 1-5 are separated by equal time intervals. At instant 3, cars P and Q are adjacent to one another (i.e., they have the same position). In the reference frame o f the road, at instant 3 i s the speed o f car Q greater than, less than, or equal to the speed of car P? Explain.arrow_forwardCar P moves to the west with constant speed v0 along a straight road. Car Q starts from rest at instant 1, and moves to the west with increasing speed. At instant 5, car Q has speed w0 relative to the road (w0 < v0). Instants 1-5 are separated by equal time intervals.arrow_forward
- Car P moves to the west with constant speed v0 along a straight road. Car Q starts from rest at instant 1, and moves to the west with increasing speed. At instant 5, car Q has speed w0 relative to the road (w0 < v0). Instants 1-5 are separated by equal time intervals. Sketch and label a vector diagram illustrating the Galilean transformation of velocities that relates velocity of car P relative to the road, velocity of car Q relative to road, and velocity of car Q relative to car P at instant 3. In the frame of car P, at instant 3 is car Q moving to the west, moving to the east, or at rest? Explain.arrow_forwardJust 5 and 6 don't mind 7arrow_forwardIn an electron gun, electrons are accelerated through a region with an electric field of magnitude 1.5 × 104 N/C for a distance of 2.5 cm. If the electrons start from rest, how fast are they moving after traversing the gun?arrow_forward
- Please solve and answer this problem correctly please. Thank you!!arrow_forwardPlease solve and answer this problem correctly please. Thank you!!arrow_forwarda) Use the node-voltage method to find v1, v2, and v3 in the circuit in Fig. P4.14. b) How much power does the 40 V voltage source deliver to the circuit? Figure P4.14 302 202 w w + + + 40 V V1 80 Ω 02 ΣΑΩ 28 A V3 + w w 102 202arrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College





