
Concept explainers
Name the following
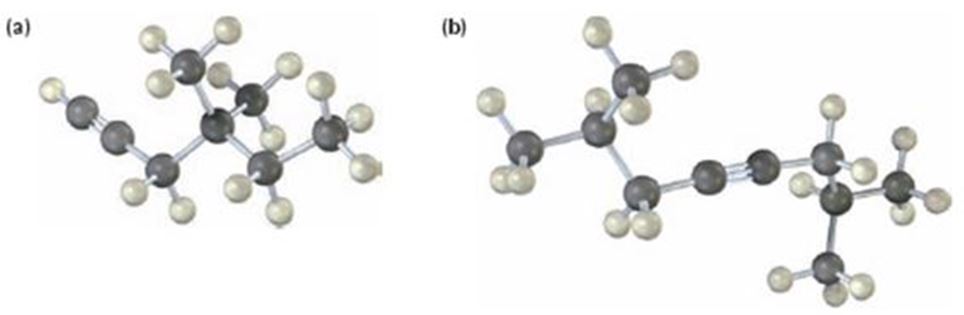
a)
Interpretation:
The alkyne shown is to be named and the products formed when it reacts with 1) H2 in the presence of Lindlar catalyst and 2) H3O+ in the presence of HgSO4 is to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
The longest carbon chain which contains the carbon-carbon triple bond is chosen. The chain is numbered from the end that gives the lowest number to the carbon in triple bond. Compounds with more than one triple bond are called diynes, triynes and so forth. The substituents present, if any are written in the alphabetical order.
When reduced with Hydrogen in the presence of Lindlar catalyst the reduction of alkynes stops in the alkene stage. When treated with H3O+ in the presence of HgSO4, alkynes undergo hydration following Markovnikov regiochemistry to give an enols which will tautomerize to yield aldehydes (terminal alkynes) or ketones (internal alkynes).
To give:
The name of the alkyne shown and to predict the products formed when it reacts with 1) H2 in the presence of Lindlar catalyst and 2) H3O+ in the presence of HgSO4.
Answer to Problem 14VC
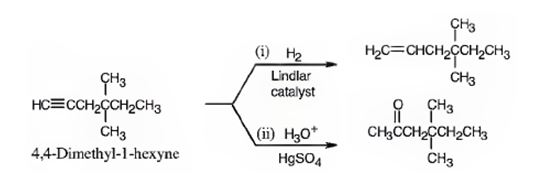
The name of the alkyne shown is 4,4-dimethyl-1-hexyne.
The product formed when it reacts with H2 in the presence of Lindlar catalyst is 4,4-dimethyl-1-hexene.
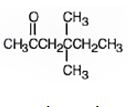
The product formed when it reacts with H3O+ in the presence of HgSO4 is 4,4-dimethyl-2-hexanone.
Explanation of Solution
The compound has a six carbon straight chain with two methyl groups on C4 with a triple bond between C1 & C2. Hence it’s name is 4,4-dimethyl-1-hexyne.
When reduced with hydrogen in the presence of Lindlar catalyst, the triple bond becomes a double bond as each of the two carbons in the triple bond gets attached to a hydrogen and an alkene, 4,4-dimethyl-1-hexene,is thus produced.
When treated with H3O+ in the presence of HgSO4, the addition of water takes place in the triple bond following Markovnikov regiochemistry. The OH group adds to more highly substituted carbon and H adds to the less highly substituted carbon in triple bond resulting in the formation of an enol which undergoes tautomerization to yield the ketone, 4,4-dimethyl-2-hexanone.
The name of the alkyne shown is 4,4-dimethyl-1-hexyne.

The product formed when it reacts with H2 in the presence of Lindlar catalyst is 4,4-dimethyl-1-hexene.

The product formed when it reacts with H3O+ in the presence of HgSO4 is 4,4-dimethyl-2-hexanone.

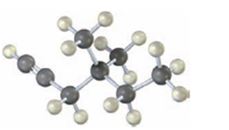
b)
Interpretation:
The alkyne shown is to be named and the products formed when it reacts with 1) H2 in the presence of Lindlar catalyst and 2) H3O+ in the presence of HgSO4 is to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
The longest carbon chain which contains the carbon-carbon triple bond is chosen. The chain is numbered from the end that gives the lowest number to the carbon in triple bond. Compounds with more than one triple bond are called diynes, triynes and so forth. The substituents present, if any are written in the alphabetical order.
When reduced with Hydrogen in the presence of Lindlar catalyst the reduction of alkynes stops in the alkene stage. When treated with H3O+ in the presence of HgSO4, alkynes undergo hydration following Markovnikov regiochemistry to give an enols which will tautomerize to yield aldehydes (terminal alkynes) or ketones (internal alkynes).
To give:
The name of the alkyne shown and to predict the products formed when it reacts with 1) H2 in the presence of Lindlar catalyst and 2) H3O+ in the presence of HgSO4.
Answer to Problem 14VC
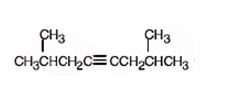
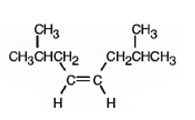
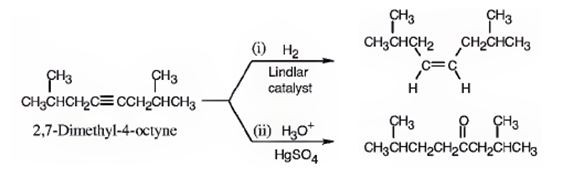
The name of the alkyne shown is 2,7-dimethyl-4-octyne.
The product formed when it reacts with H2 in the presence of Lindlar catalyst is cis-2,7-dimethyl-4-octene.
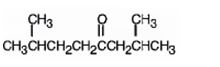
The product formed when it reacts with H3O+ in the presence of HgSO4 is 2,7-dimethyl-4-octanone.
Explanation of Solution
The compound has an eight carbon straight chain with two methyl groups on C2 & C7 with a triple bond between C4 & C5. Hence it’s name is 2,7-dimethyl-4-octyne.
When reduced with hydrogen in the presence of Lindlar catalyst, the triple bond becomes a double bond as each of the two carbons in the triple bond gets attached to a hydrogen and an alkene, cis- 2,7-dimethyl-4-octene.is thus produced.
When treated with H3O+ in the presence of HgSO4, the addition of water takes place in the triple bond. As the alkene is symmetrical the Markovnikov regiochemistry cannot be applied. The OH group adds to one carbon and H adds to the other carbon in triple bond resulting in the formation of an enol which undergoes tautomerization to yield the ketone, 2,7-dimethyl-4-octanone.
The name of the alkyne shown is 2,7-dimethyl-4-octyne.

The product formed when it reacts with H2 in the presence of Lindlar catalyst is cis-2,7-dimethyl-4-octene.

The product formed when it reacts with H3O+ in the presence of HgSO4 is 2,7-dimethyl-4-octanone.

Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 9 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- Write all of Me Possible Products For each Of the Following reactions. In each case identity all pains of enantiomers, all digsterzoners and all Meso compounds 9. 11-60 11-0-11 V-G Η Η H ~ C-11 +HB+ - 1 H b. पन्ना 171-0-11 H-C-H Н C-C=c-call +HBr Perendez ==arrow_forwardHow can i draw the mechanisms for this molecule?arrow_forwarda. Discuss and explain he difference IN Stability between the Chai and Boat Гольцу от судомехане b. For the Following Molecule draw both possible Clain conformations and explain which one is more stable and for what Reason. H. CH₂ CH₂ H "Harrow_forward
- Please provide the mechanism for this reacitonarrow_forwardQuestion 5: Name the following compound in two ways using side chain and using prefix amine (Common name and IUPAC name both) CH3NH2 CH3CH2NHCH3 CH₂CH₂N(CH3)2 Draw the structure of diethyl methyl amine Question 6. Write the balanced combustion reaction for: a. Hexane b. Propyne c. 2-pentene Question 7: Write the following electrophilic substitution reactions of benzene: Hint: Use notes if you get confused a. Halogenation reaction: b. Nitration reaction : c. Sulphonation reaction: d. Alkylation reaction: e. Aceylation reaction:arrow_forwardQuestion 4. Name the following structures ○ CH3-C-N-H H CH3CH2-C-N-H H CH3CH2-C-N-CH3 Harrow_forward

 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

