
Interpretation:
The Lewis structure, molecular shape, bond angle and hybrid orbitals in
Concept introduction:
VSEPR theory stands for Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Theory. It helps to predict the molecular shape or geometry of the molecule with the help of the number of bond pairs or lone pairs present in it.
According to the VSEPR theory, the presence of lone pair on the central atom of a molecule causes deviation from standard molecular geometry. Thus, valence electrons provide a Lewis structure, which gives an idea about electron pair geometry and hybridization.
Answer to Problem 67SSC
| Lewis structure | molecular shape, | bond angle | hybrid orbitals | |
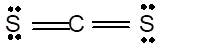 |
Linear | 180° | sp hybrid orbitals | |
 |
Trigonal planer | 120° | sp2 hybrid orbitals | |
 |
Bent | 104° | sp3 hybrid orbitals | |
 |
Tetrahedral | 109° | sp3 hybrid orbitals | |
 |
Pyramid | 107° | sp3 hybrid orbitals |
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
In the
Number of valence electron = Number of atom C (valence electron in C) + Number of atom S (valence electron in S) =
Hence the Lewis structure must be:
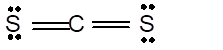
Geometry = Linear, bond angle = 180°
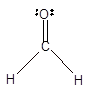
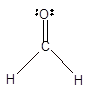
In the
Number of valence electron = Number of atom C (valence electron in C) + Number of atom O (valence electron in O)+ Number of atom H (valence electron in H) =
Hence the Lewis structure must be:
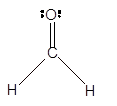
Geometry = Trigonal planer, bond angle = 120°
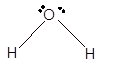
In the
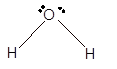
Number of valence electron = Number of atom O (valence electron in O) + Number of atom H (valence electron in H) =
Hence the Lewis structure must be:
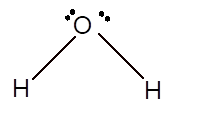
Geometry = bent, bond angle = 104°
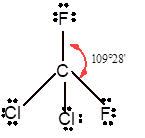
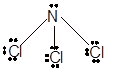
In
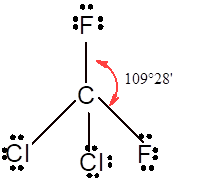
In the
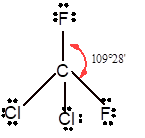
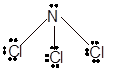
Number of valence electron = Number of atom P (valence electron in P) + Number of atom Cl (valence electron in Cl) =
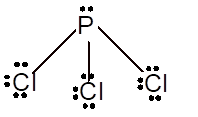
With sp3 hybridization, the geometry must be tetrahedral but the presence of one lone pair on central P atom alters the standard geometry of molecule to pyramid shape due to repulsion between lone pair and bond pair of the molecule.
Thus,
| Lewis structure | molecular shape, | bond angle | hybrid orbitals | |
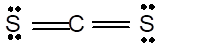 |
Linear | 180° | sp hybrid orbitals | |
 |
Trigonal planer | 120° | sp2 hybrid orbitals | |
 |
Bent | 104° | sp3 hybrid orbitals | |
 |
Tetrahedral | 109° | sp3 hybrid orbitals | |
 |
Pyramid | 107° | sp3 hybrid orbitals |
Chapter 8 Solutions
Glencoe Chemistry: Matter and Change, Student Edition
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Introductory Chemistry (6th Edition)
Chemistry: Structure and Properties (2nd Edition)
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
Microbiology: An Introduction
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
Chemistry: A Molecular Approach (4th Edition)
- Indicate the names of these compounds (if they exist). 0: HỌC—NH CH3CH2-CH2arrow_forwardN Classify each of the following molecules as aromatic, antiaromatic, or nonaromatic. NH O aromatic O antiaromatic O nonaromatic O aromatic O antiaromatic O nonaromatic O aromatic O antiaromatic O nonaromatic Garrow_forwardThe conjugate base of alkanes is called alkides. Correct?.arrow_forward
- Name these organic compounds: structure Br name CH3 CH3 ☐ ☐arrow_forwardHH H-C H -C-H HH Draw the Skeletal Structures & H Name the molecules HH H H H H-C-C-C-C-C-C-H HHH HHH H H HHHHHHH H-C-C-C-C-C-C-C-C-C-H HHHHH H H H Harrow_forwarddont provide AI solution .... otherwise i will give you dislikearrow_forward
- Name these organic compounds: structure name CH3 CH3 ☐ F F CH3 ☐ O Explanation Check 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms ofarrow_forwardClassify each of the following molecules as aromatic, antiaromatic, or nonaromatic. ZI NH Explanation Check O aromatic O antiaromatic O nonaromatic O aromatic O antiaromatic H O nonaromatic O aromatic O antiaromatic O nonaromatic ×arrow_forwardPart I. Draw the stepwise reaction mechanism of each product (a, b, c, d, e, f) HO HO OH НОН,С HO OH Sucrose HO CH₂OH H N N HO -H H -OH KMnO4, Heat H OH CH₂OH (d) Phenyl Osatriazole OH НОН,С HO HO + Glacial HOAC HO- HO CH₂OH OH HO Fructose (a) Glucose OH (b) H₂N HN (c) CuSO4-5H2O, ethanol H N N N HO ·H H OH H OH N CH₂OH OH (f) Phenyl Osazone H (e) Carboxy phenyl osatriazole Figure 2.1. Reaction Scheme for the Total Synthesis of Fine Chemicalsarrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





