
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The Lewis dot structure of
Concept introduction:
Lewis structure represents the valence shell electrons in a compound. It shows the distribution of electrons around each atom in a molecule.
(a)
Explanation of Solution
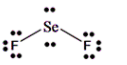
Selenium is a 16th group element which has 6 valence electrons and fluorine is a 17th group element which has 7 valence electrons.
Total valence electrons = 6 + 2×7
= 6 + 14
= 20
Therefore; the total valence electron is 20.
The Lewis dot structure of SeF2 is shown below:
(b)
Interpretation:
The Lewis dot structure of
Concept introduction:
Lewis structure represents the valence shell electrons in a compound. It shows the distribution of electrons around each atom in a molecule.
(b)
Explanation of Solution
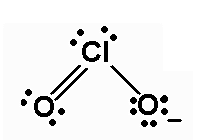
Chlorine is a 17th group element which has 7 valence electrons and oxygen is a 16th group element which has 6 valence electrons.
Total valence electrons = 7 + 2×6 + 1
= 20
Therefore; the total valence electrons is 20.
The Lewis dot structure is shown below:
(c)
Interpretation:
The Lewis dot structure of
Concept introduction:
Lewis structure represents the valence shell electrons in a compound. It shows the distribution of electrons around each atom in a molecule.
(c)
Explanation of Solution
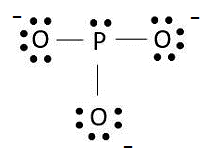
Phosphorus is a 15th group element which has 5 valence electrons and oxygen is a 16th group element which has 6 valence electrons.
The total number of valence electrons = 5 + 3(6) + 3 = 26
Therefore; the total valence electron is 20
The Lewis dot structure is shown below:
(d)
Interpretation:
The Lewis dot structure of
Concept introduction:
Lewis structure represents the valence shell electrons in a compound. It shows the distribution of electrons around each atom in a molecule.
(d)
Explanation of Solution
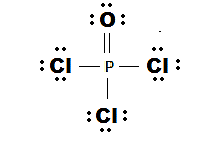
Phosphorus is a 15th group element which has 5 valence electrons and oxygen is a 16th group element which has 6 valence electron and chlorine is a 17th group element which has 7 valence electrons.
Total number of valence electrons = 5 + 6 + 3(7)
= 5+ 6+ 21
= 32
Therefore; the total valence electron is 32
The Lewis dot structure is shown below:
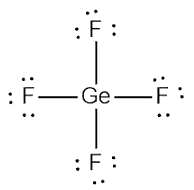
(e)
Interpretation:
The Lewis dot structure of
Concept introduction:
Lewis structure represents the valence shell electrons in a compound. It shows the distribution of electrons around each atom in a molecule.
(e)
Explanation of Solution
Germanium is a 14th group element which has 4 valence electrons and fluorine is a 17th group element which has 7 valence electrons.
The total valence electron = 4+ 4(7)
= 4 + 28
= 32
Therefore; the total valence electron is 32
The Lewis dot structure is shown below:
Chapter 8 Solutions
Glencoe Chemistry: Matter and Change, Student Edition
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Introductory Chemistry (6th Edition)
Human Physiology: An Integrated Approach (8th Edition)
Human Anatomy & Physiology (2nd Edition)
Campbell Biology in Focus (2nd Edition)
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
Campbell Biology: Concepts & Connections (9th Edition)
- N Classify each of the following molecules as aromatic, antiaromatic, or nonaromatic. NH O aromatic O antiaromatic O nonaromatic O aromatic O antiaromatic O nonaromatic O aromatic O antiaromatic O nonaromatic Garrow_forwardThe conjugate base of alkanes is called alkides. Correct?.arrow_forwardName these organic compounds: structure Br name CH3 CH3 ☐ ☐arrow_forward
- HH H-C H -C-H HH Draw the Skeletal Structures & H Name the molecules HH H H H H-C-C-C-C-C-C-H HHH HHH H H HHHHHHH H-C-C-C-C-C-C-C-C-C-H HHHHH H H H Harrow_forwarddont provide AI solution .... otherwise i will give you dislikearrow_forwardName these organic compounds: structure name CH3 CH3 ☐ F F CH3 ☐ O Explanation Check 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms ofarrow_forward
- Classify each of the following molecules as aromatic, antiaromatic, or nonaromatic. ZI NH Explanation Check O aromatic O antiaromatic O nonaromatic O aromatic O antiaromatic H O nonaromatic O aromatic O antiaromatic O nonaromatic ×arrow_forwardPart I. Draw the stepwise reaction mechanism of each product (a, b, c, d, e, f) HO HO OH НОН,С HO OH Sucrose HO CH₂OH H N N HO -H H -OH KMnO4, Heat H OH CH₂OH (d) Phenyl Osatriazole OH НОН,С HO HO + Glacial HOAC HO- HO CH₂OH OH HO Fructose (a) Glucose OH (b) H₂N HN (c) CuSO4-5H2O, ethanol H N N N HO ·H H OH H OH N CH₂OH OH (f) Phenyl Osazone H (e) Carboxy phenyl osatriazole Figure 2.1. Reaction Scheme for the Total Synthesis of Fine Chemicalsarrow_forwardWhich molecule is the most stable? Please explain.arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





