
Concept explainers
(a)
The value of
(a)
Answer to Problem 8.9EP
The value of the bias current is
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
The given diagram is shown in Figure 1
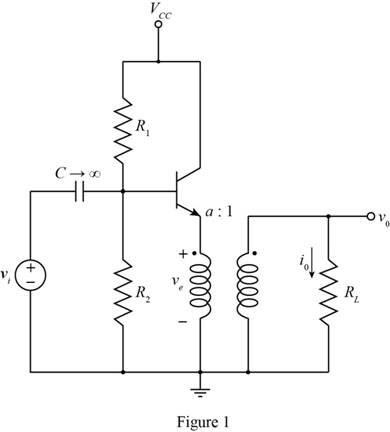
The conversion from
The expression for the value of the base to emitter to voltage is given by,
Substitute
The expression for the bias current is given by,
Substitute
Conclusion:
Therefore, the value of the bias current is
(b)
The value of
(b)
Answer to Problem 8.9EP
The value of current
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
The value of peak voltage and output voltage are equal and the expression for the value of the load current is given by,
Substitute
The expression for the emitter current for3 the
Substitute
The expression for the base current of the
Substitute
The expression for the collector current of
Substitute
The conversion from
The conversion from
The conversion from
The expression to determine the value of the diode current is given by,
Substitute
The value of the collector current for
Substitute
The expression for the base emitter voltage of
Substitute
The expression for the value of
Substitute
The expression for the base emitter voltage of
Substitute
The expression for the collector current
Substitute
Conclusion:
Therefore, the value of current
(c)
The value of
(c)
Answer to Problem 8.9EP
The value of current
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
The value of peak voltage and output voltage are equal and the expression for the value of the load current is given by,
Substitute
The expression for the emitter current for3 the
Substitute
The expression for the base current of the
Substitute
The expression for the collector current of
Substitute
The conversion from
The conversion from
The expression to determine the value of the diode current is given by,
Substitute
The value of the collector current for
Substitute
The expression for the base emitter voltage of
Substitute
The expression for the value of
Substitute
The expression for the base emitter voltage of
Substitute
The expression for the collector current
Substitute
Conclusion:
Therefore, the value of current
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 8 Solutions
Microelectronics: Circuit Analysis and Design
- Find the Thévenin equivalent circuit for the portions of the networks in Figure external to the elements between points a and b. E = 20 VZ0° + R ww 2 ΚΩ Хо XL 000 6ΚΩ 3 ΚΩ b RLarrow_forwardWhat percentage of the full-load current of a thermally protected continuous-duty motor of more than one Hp can the trip current be, if the full-load current is 15 amperes? Ο 122 Ο 140 156 O 170arrow_forwardQ3arrow_forward
- In thinkercad can you make a parallel series circuit with a resistors and a voltage source explain how the voltage and current moves through the circuit, and explaining all the components, and if you were to break the circuit to find the current how would you do that? Please show visuals if possible.arrow_forwardIn thinkercad can you make a series circuit with a resistors and a voltage source explain how the voltage and current moves through the circuit, and explaining all the components, and if you were to break the circuit to find the current how would you do that? Please show visuals if possible.arrow_forwardIn thinkercad can you make a parallel circuit with a resistors and a voltage source explain how the voltage and current moves through the circuit, and explaining all the components, and if you were to break the circuit to find the current how would you do that? Please show visuals if possiblearrow_forward
- Q1arrow_forward2-2 -Draw V-curves for synchronous motor at no load, half load, and full load? 2-List the advantages of damper bars in synchronous machines? 3-Draw phasor diagram for alternator at unity power factor, and derive EMF equation from it?arrow_forwardconduit bending techniques and the most common anglesarrow_forward
- Question 1 Draw and complex CMOS logic and design the width-to-length ratios (W/L) of the transistors needed to implement the CMOS circuit for the following function (asuume Wp: W₁ = 2:1) n f=AB+CD+E+AD Question 2 Implement the following function using CMOS technology. f = x1(x2x3 + x4) Design the width-to-length ratios (W/L) of the transistors needed to implement the CMOS circuuit for the following function (asuume Wp: W₁ = 2:1) n Question 3 Consider the following three-pole feedback amplifier with a loop gain function: 6000× B T (jf) = 1+j f 2×10³ 1+ j f 3×104 f 1+ j 4×105 If ẞ=38.66×10³ determine the phase margin and the gain margin of this system (if it is stable).arrow_forwardhow to bend conduit in exact angles. and bending angles stepsarrow_forward¡ you need to connect a three phase alternator B (incoming generator) in parallel with alternator A which is connected to an infinite bus bar, what are the necessary conditions to make this connection appen properly? Explain how you can use a three lamps to achieve this connection?arrow_forward
 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,





