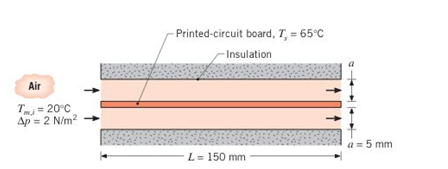
Problem 8.1P: Fully developed conditions are known to exist for water flowing through a 25-nim-diameer tube at... Problem 8.2P: What is the pressure drop associated with water at 27C flowing with a mean velocity of 0.2m/s... Problem 8.3P: Water at 27C flows with a mean velocity of 1 m/s through a l-km-long pipe of 0.25-m inside diameter.... Problem 8.4P: An engine oil cooler consists of a bundle of 25 smooth tubes, each of length L=2.5m and diameter... Problem 8.5P: For fully developed laminar flow through a parallel-plate channel, the x-momentum equation has the... Problem 8.6P: Consider pressurized water, engine oil (unused), and NaK (22/78) flowing in a 20-mm-diameter tube.... Problem 8.7P: Velocity and temperature profiles for laminar flow in a tube of radius r0=10 mm have the form... Problem 8.8P: At a particular axial station, velocity and temperature profiles for laminar flow in a parallel... Problem 8.9P: In Chapter 1, it was stated that for incompressible liquids, flow work could usually be neglected in... Problem 8.10P: When viscous dissipation is included. Equation 8.48 (multiplied by cp ) becomes cpuTx=krr(rTr)+( du... Problem 8.11P: Consider a circular tube of diameter D and length L, with a mass flow rate of m. (a) For constant... Problem 8.13P: Consider flow in a circular tube. Within the test section length (between 1 and 2) a constant heat... Problem 8.14P: Consider a cylindrical nuclear fuel rod of length L and diameter D that is encased in a concentric... Problem 8.15P: Consider the laminar thermal boundary layer development near the entrance of the tube shown in... Problem 8.16P: In a particular application involving fluid flow at a rate m through a circular tube of length L and... Problem 8.17P: A flat-plate solar collector is used w heat atmospheric air flowing through a rectangular channel.... Problem 8.18P: Atmospheric air enters the heated section of a circular tube at a flow rate of 0.005 kg/s and a... Problem 8.19P: Fluid enters a tube with a flow rate of 0.015kg/s and an inlet temperature of 20C . The tube, which... Problem 8.20P: Water at 300 K and a flow rate of 5kg/s enters a black, thin-walled tube, which passes through a... Problem 8.21P: Slug flow is an idealized tube flow condition for which the velocity is assumed to be uniform over... Problem 8.22P: Superimposing a control volume that is differential in x on the tube flow conditions of Figure 8.8,... Problem 8.23P: An experimental nuclear core simulation apparatus consists of a long thin-walled metallic tube of... Problem 8.24P: Water at 20°C and a flow rate of 0.1kg/s enters a heated, thin-walled tube with a diameter of 15 mm... Problem 8.25P: Engine oil is heated by flowing through a circular tube of diameter D=50mm and length L=25m and... Problem 8.26P: Engine oil flows through a 25mm -diameter tube at a rate of 0.5kg/s . The oil enters the tube at a... Problem 8.27P: In the final stages of production, a pharmaceutical is sterilized by heating it from 25 to 75C as it... Problem 8.28P: An oil preheater consists of a single tube of 10mm diameter and 5m length, with its surface... Problem 8.29P: Engine oil flows at a rate of 1kg/s through a 5mm diameter straight tube. The oil has an inlet... Problem 8.30P: Air at p=1atm enters a thin-walled ( D=5-mm diameter) long tube (L=2m) at an inlet temperature of... Problem 8.31P: To cool a summer home without using a vapor compression refrigeration cycle, air is routed through a... Problem 8.32P: Batch processes are often used in chemical and pharmaceutical operations to achieve a desired... Problem 8.33P: The evaporator section of a heat pump is installed in a large tank of water, which is used as a heat... Problem 8.35P: Water flowing at 2kg/s through a 40mm diameter tube is to be heated from 25 to 75C by maintaining... Problem 8.36P: Consider the conditions associated with the hot water pipe of Problem 7.56, but now account for the... Problem 8.37P: A thick-walled, stainless steel (AISI 316) pipe of inside and outside diameters Di=20 mm and Do=40... Problem 8.38P: An air heater for an industrial application consists of an insulated, concentric tube annulus, for... Problem 8.39P: Consider fully developed conditions in a circular tube with constant surface temperature TsTm .... Problem 8.40P: Consider the encased pipe of Problem 4.29, but now allow tor the difference between the mean... Problem 8.41P: Water flows through a thick-wailed tube with an innerdiameter of 12 mm and a length of 8 in. The... Problem 8.42P: Atmospheric air enters a 10m -long. 150mm -diameter uninsulated heating duct at 60C and 0.04kg/s .... Problem 8.43P: NaK (45%/55). which is an alloy of sodium and potassium. is used to cool fast neutron nuclear... Problem 8.44P: The products of combustion from a burner are routed to an industrial application through a... Problem 8.45P: Liquid mercury at 0.5kg/s is lo be heated from 300 to 400 K by passing it through a 50mm -diameter... Problem 8.46P: The surface of a 50-mm-diameter. thin-walled tube is maintained at 100C . In one case air is in... Problem 8.47P: Consider a horizontal, thin-walled circular tube of diameter D=0.025m submerged in a container of... Problem 8.48P: Consider pressurized liquid water flowing at m=0.1kg/s in a circular tube of diameter D=0.1m and... Problem 8.49P: Cooling water flows through the 25.4-mm -diameter thin-walled tubes of a steam condenser at 1 m/s.... Problem 8.50P: The air passage for cooling a gas turbine vane can be approximated as a lube of 3-mm diameter and... Problem 8.51P: The core of a high-temperature, gas-cooled nuclear reactor has coolant tubes of 20-mm diameter and... Problem 8.52P: Air at 200kPa enters a 2-m -long, thin-walled tube of 25-mm diameter at 150C and 6m/s . Steam aft 20... Problem 8.53P: Heated air required for a food-drying process is generated by passing ambient air at 20C through... Problem 8.54P: Consider laminar flow of a fluid with Pr=4 that undergoes a combined entrance process within a... Problem 8.55P: A common procedure for cooling a high-performance computer chip involves joining the chip to a heat... Problem 8.56P: One way to cool chips mounted on the circuit boards ofa computer is to encapsulate the boards in... Problem 8.57P: Refrigerant- 134a is being transported a 0.1 kg/s through a Teflon tube of inside diameter D0=28 mm... Problem 8.58P: Oil at 150°C flows slowly through a long, thin-walled pipe of 30-mm inner diameter. The pipe is... Problem 8.59P: Exhaust gases from a wire processing oven are discharged into a tall stack, and the gas and stack... Problem 8.60P: A hot fluid passes through a thin-walled tube of 10-mm diameter and 1-m length, and a coolant at... Problem 8.61P: Consider a thin-walled tube of 10mm diameter and 2m length. Water enters the tube from a large... Problem 8.62P: Water at a flow rate of m =0.215kg/s is cooled from 70°C to 30°C by passing it through a thin-walled... Problem 8.64P: To maintain pump power requirements per unit flow rate below an acceptable level, operation of (he... Problem 8.65P: Consider a thin-walled, metallic tube of length L=1m and inside diameter Di=3mm . Water enters the... Problem 8.66P: A circular tube of diameter D=0.2mm and length L=100mm in1poes a constant heat flux of qn=20103W/m2... Problem 8.67P: Repeat Problem 8.66 for a circular tube of diameter D=2mm . an applied heat flux of qn=200,000W/m2 .... Problem 8.68P: Heat is to be removed from a reaction vessel operating at 75C by supplying water at 27C and 0.12... Problem 8.69P: A healing contractor must heat 0.2kg/s of water from 15C to 35C using hot gases in cross flow over a... Problem 8.70P: A thin-walled tube with a diameter of 6 mm and length of 20m is used to carry exhaust gas from a... Problem 8.71P: A 50mm -diameter, thin—walled metal pipe covered with a 25mm -thick layer of insulation (0.085W/m.K)... Problem 8.72P: A thin-walled, uninsulated 0.3m -diameter duct is used to route chilled air at 0.05kg/s through the... Problem 8.73P: Pressurized water at Tm,i=200C is pumped at m=2kg/s from a power plant to a nearby industrial user... Problem 8.74P: Water at 290K and 0.2kg/s flows through a Teflon tube (k=0.35W/mK) of inner and outer radii equal to... Problem 8.75P: The temperature of flue gases flowing through the large stack of a boiler is measured by means of a... Problem 8.76P: In a biomedical supplies manufacturing process, a requirement exists for a large platen that is to... Problem 8.77P: Consider the ground source heat pump of Problem 5.100 under winter conditions for which the liquid... Problem 8.78P: For a sharp-edged inlet and a combined entry region, the average Nusselt number may be computed from... Problem 8.79P: Fluid enters a thin-walled rube of 5-mni diameter and 2-m length with a flow rate of 0.04 kg/s and a... Problem 8.80P: Air at 3104kg/s and 27C enters a rectangular duct that is 1 m long and 4 turn 16mm on a side. A... Problem 8.81P: Air at 25C flows at 30106kg/s within 100mm -long channels used to cool a high thermal conductivity... Problem 8.82P: A cold plate is an active cooling device that is attached to a heat-generating system in order to... Problem 8.83P: The cold plate design of Problem 8.82 has not been optimized with respect to selection of the... Problem 8.84P: A device that recovers heat from high-temperature combustion products involves passing the... Problem 8.85P: Air at 1 atm and 285K enters a 2-m -long rectangular duct with cross section 75mm150mm . The duct is... Problem 8.86P: A double-wall heat exchanger is used to transfer heat between liquids flowing through semicircular... Problem 8.87P: Consider laminar, fully developed flow in a channel of constant surface temperature TS . For a given... Problem 8.88P: You have been asked to perform a feasibility study on the design of a blood warmer to be used during... Problem 8.89P: A coolant flows through a rectangular channel (gallery) within the body of a mold used to form metal... Problem 8.90P: An electronic circuit board dissipating 50W is sandwiched between two ducted, forced-air-cooled heat... Problem 8.91P: To slow down large prime movers like locomotives, a process termed dynamic electric braking is used... Problem 8.92P: A printed circuit board (PCB) is cooled by laminar. fully developed airflow in adjoining,... Problem 8.93P: Water at m=0.02kg/s and Tm,i=20C enters an annular region formed by an inner tube of diameter Di=25... Problem 8.94P: tFor the conditions of Problem 8.93, how tong must the annulus be if the water flow rate is 0.30kg/s... Problem 8.95P: Referring 10 Figure 8.11, consider conditions in an annulus having an outer surface that is... Problem 8.96P: Consider the air healer of Problem 8.38, but now with airflow through the annulus and steam flow... Problem 8.97P: Consider a concentric tube annulus for which the inner and outer diameters are 25 and 50mm . Water... Problem 8.98P: It is common practice (o recover waste heat from an oil-or gas-fired furnace by using the exhaust... Problem 8.99P: A concentric lube arrangement, for which the inner and outer diameters are 80mm and 100mm .... Problem 8.101P: Consider sterilization of the pharmaceutical product of Problem 8.27. To avoid any possibility of... Problem 8.102P: An engineer proposes to insert a solid rod of diameter Di into a circular tube of diameter Do to... Problem 8.103P: An electrical power transformer of diameter 230mm and height 500mm dissipates 1000W . It is desired... Problem 8.104P: A bayonet cooler is used to reduce the temperature of a pharmaceutical fluid. The pharmaceutical... Problem 8.105P: The mold used in an injection molding process consists of a top half and a bottom half. Each half is... Problem 8.107P Problem 8.108P Problem 8.109P: Consider the microchannel cooling arrangement ofProblem 8.107. However, instead of assuming... Problem 8.110P: The onset of turbulence in a gas flowing within a circular tube occurs at ReD,c2300 , while a... Problem 8.111P: Due to its comparatively large thermal conductivity, water is a preferred fluid for convection... Problem 8.113P: A novel scheme for dissipating heat from the chips ofa multichip array involves machining coolant... Problem 8.115P: An experiment is designed to study microscale forced convection. Water at Tm,i=300K is to be heated... Problem 8.116P: Determine the tube diameter that corresponds to a 10 reduction in the convection heat transfer... Problem 8.117P: An experiment is devised to measure liquid flow andconvective heat transfer rates in microscale... Problem 8.118P: In the processing of very long plastic tubes of 2mm inside diameter, air flows inside the tubing... Problem 8.119P: Air at 300K and a flow rate of 3kg/h passes upward through a 30mm tube, as shown in the sketch. A... Problem 8.120P: What is the convection mass transfer coefficient associated with fully developed atmospheric airflow... Problem 8.121P: Air flowing through a tube of 75mm diameter passes over a 150-nuniong roughened Section that is... Problem 8.123P: Consider gas flow of mass density and rate m though a tube whose inner surface is coated with a... Problem 8.124P: Atmospheric air at 25C and 3104kg/s flows through a 10mm -diameter, 1-m-long circular tube whose... Problem 8.125P: Air at 25C and 1atm is in fully developed flow at m=103kg/s through a 10mm -diameter circular tube... Problem 8.126P: A humidifier consists of a bundle of vertical tubes, each of 20mm diameter, through which dry... Problem 8.127P: The final step of a manufacturing process in which a protective coating is applied to the inner... Problem 8.128P: Dry air is inhaled at a rate of lo liter/win through a trachea with a diameter of 20mm and a length... Problem 8.129P: A mass transfer Operation is preceded by laminar flow of a gaseous species B through a circular tube... format_list_bulleted


 Principles of Heat Transfer (Activate Learning wi...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305387102Author:Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Heat Transfer (Activate Learning wi...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305387102Author:Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.Publisher:Cengage Learning