
Concept explainers
A 1.00-kg object slides to the right on a surface having a coefficient of kinetic friction 0.250 (Fig. P7.68a). The object has a speed of vi = 3.00 m/s when it makes contact with a light spring (Fig. P7.68b) that has a force constant of 50.0 N/m. The object comes to rest after the spring has been compressed a distance d (Fig. P7.68c). The object is then forced toward the left by the spring (Fig. P7.68d) and continues to move in that direction beyond the spring’s unstretched position. Finally, the object comes to rest a distance D to the left of the unstretched spring (Fig. P7.68e). Find (a) the distance of compression d, (b) the speed v at the unstretched position when the object is moving to the left (Fig. P7.68d), and (c) the distance D where the object comes to rest.
Figure P7.68
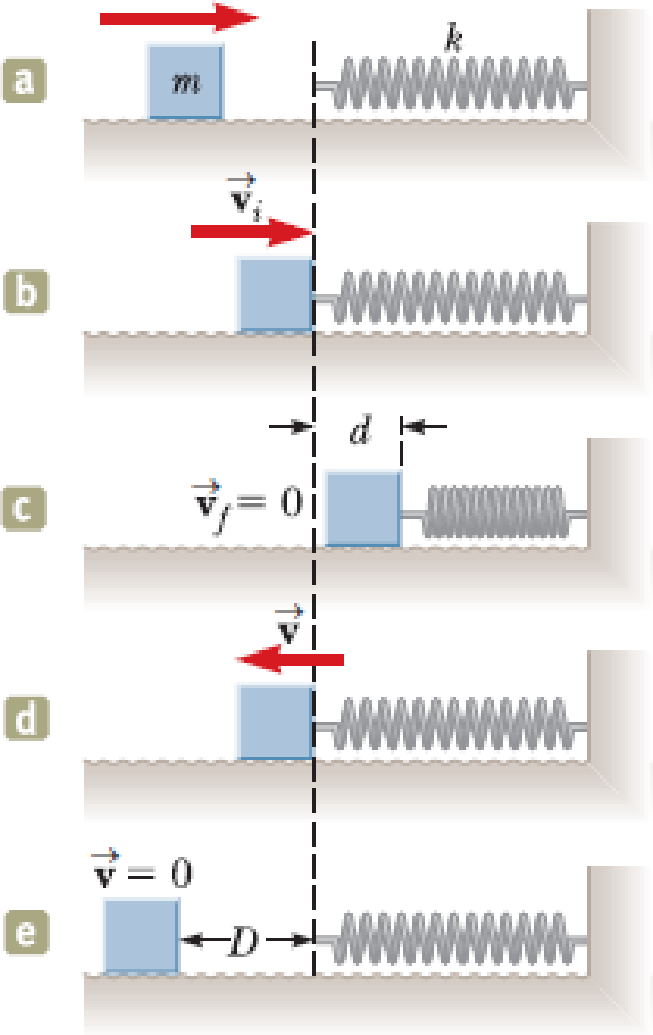
(a)
Distance of compression.
Answer to Problem 68P
The distance of compression is
Explanation of Solution
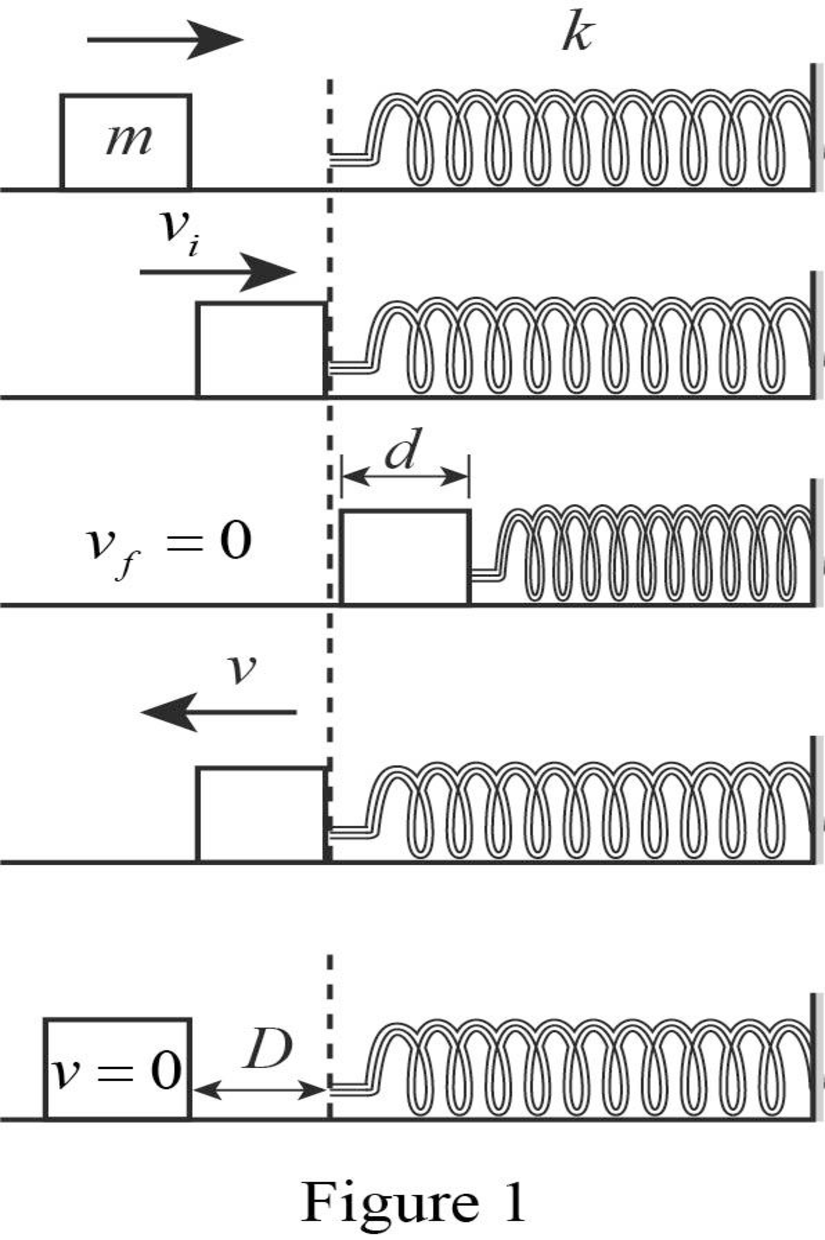
Write the energy conservation equation between second and third picture.
Here
Write the equation for change in kinetic energy,
Here
Write the equation for change in potential energy,
Here
The final kinetic energy zero as the final velocity zero. The initial elastic potential energy is also zero as the spring is not extended initially.
Write the equation for change in internal energy
Here
Substitute (II), (III) and (IV) in (I)
Conclusion:
Substitute
Then,
The distance of compression is
(b)
Speed at the un stretched position when the object is moving left.
Answer to Problem 68P
The speed is
Explanation of Solution
Write the energy conservation equation between picture two and four
Substitute (II) and (IV) in (VI)
Substitute
Rewrite (VIII) for
Conclusion:
Substitute
The speed is
(c)
The distance at which the object comes to rest.
Answer to Problem 68P
The distance is
Explanation of Solution
Consider the motion from picture two to five
Substitute
Rearrange (X) in terms of
Conclusion:
Substitute
The distance is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 7 Solutions
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
- Please solve and answer the problem correctly please. Thank you!!arrow_forwardPlease help explain this. The experiment without the sandpaper had a 5% experimental error, with sandpaper it is 9.4%. Would the explaination be similar to the experiment without sandpaper? Thanks!arrow_forwardA sinusoidal wave with wavelength 0.400 m travels along a string. The maximum transverse speed of a point on the string is 3.00 m/s and the maximum transverse acceleration is 8.10×104m/s2. What is the propagation speed v of the wave? What is the amplitude A of the wave?arrow_forward
- Should the results of your experimental Coefficient of Static Friction for the Wooden Block for the wooden block (Data Table 1) and the wooden block with the added mass (Data Table 2) be similar? Explain why or why not. Determine whether the results of the experiment are within a reasonable experimental error (< 10%) by calculating the % difference. Please help with showing how to calculate and with explaination, I'm not sure. Thanks!arrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvote Alreadyarrow_forwardPlease solve and answer the question correctly please. Thank you!!arrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University





