
Jane, whose mass is 50.0 kg, needs to swing across a river (having width D) filled with person-eating crocodiles to save Tarzan from danger. She must swing into a wind exerting constant horizontal force
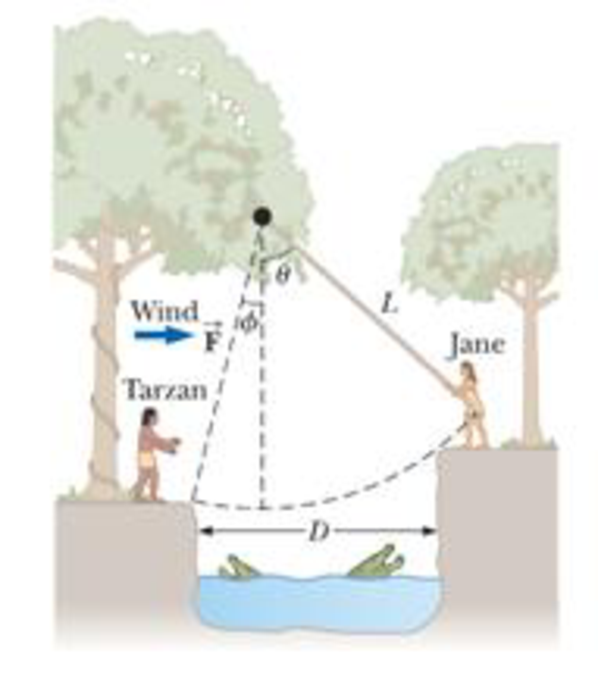
(a)
Minimum speed to reach the opposite side.
Answer to Problem 81P
The speed is
Explanation of Solution
This system has to be solved using spherical polar coordinates with
Considering the geometry, write the equation to determine
Here
Write the equation for energy conservation of the system
Here
Write the equation for initial and final kinetic energy.
Here
Write the expression for gravitational potential energy at A, B and C.
Here
Write down the equation for change in internal energy.
Here
Substitute (III), (IV) and (V) in (II)
Rearrange (VI) in terms of
Conclusion:
Substitute
Substitute
The speed is
(b)
Minimum speed for combined swing.
Answer to Problem 81P
The speed is
Explanation of Solution
Write down the equation for energy conservation
Here
Write down the equation for mechanical energy
Here
Substitute (III), (IV) and (IX) in (VIII)
Here
Rearrange (X) in terms of
Conclusion:
Substitute
The speed is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 7 Solutions
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
- Lab 8 Part 3 PHET Wave Interface simulation. I am having trouble with this part of the lab.arrow_forwardMick and Rick are twins born on Earth in the year 2175. Rick grows up to be an Earth-bound robotics technician while Mick becomes an intergalactic astronaut. Mick leaves the Earth on his first space mission in the year 2200 and travels, according to his clock, for 10 years at a speed of 0.75c. Unfortunately, at this point in his journey, the structure of his ship undergoes mechanical breakdown and the ship explodes. How old is Rick when his brother dies?arrow_forwardHi, I have canceled, why did you charge me again?arrow_forward
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning





