
Concept explainers
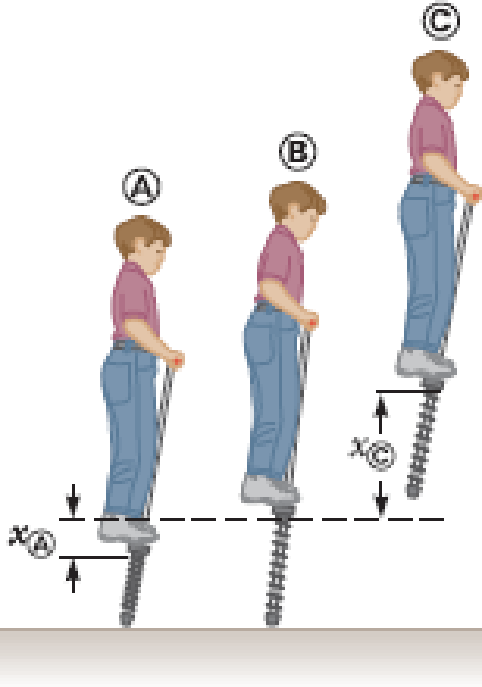
A child’s pogo stick (Fig. P7.69) stores energy in a spring with a force constant of 2.50 × 104 N/m. At position Ⓐ (xⒶ = −0.100 m), the spring compression is a maximum and the child is momentarily at rest. At position Ⓑ (xⒷ = 0), the spring is relaxed and the child is moving upward. At position Ⓒ, the child is again momentarily at rest at the top of the jump. The combined mass of child and pogo stick is 25.0 kg. Although the boy must lean forward to remain balanced, the angle is small, so let’s assume the pogo stick is vertical. Also assume the boy does not bend his legs during the motion. (a) Calculate the total energy of the child–stick–Earth system, taking both gravitational and elastic potential energies as zero for x = 0. (b) Determine xⒸ. (c) Calculate the speed of the child at x = 0. (d) Determine the value of x for which the kinetic energy of the system is a maximum. (e) Calculate the child’s maximum upward speed.
Figure P7.69
(a)
Total energy of the system.
Answer to Problem 69P
Total energy is
Explanation of Solution
Write the equation for total energy of the system
Here
Write the equation for kinetic energy at A, B and C
Here
Write the expression for gravitational potential energy at A, B and C.
Here
Write down the equation for elastic potential energy at A, B and C.
Here
As there is no motion, kinetic energy is zero
Substitute
Conclusion:
Substitute
Total energy is
(b)
Extension at point C.
Answer to Problem 69P
Extension is
Explanation of Solution
Write the energy conservation equation
Substitute for all the terms in (VI)
Kinetic energy is zero as there is no motion
The elastic potential energy is zero at C.
Now rewrite (VII) in terms of
Conclusion:
Substitute
Extension is
(c)
Speed of the child at
Answer to Problem 69P
The speed is
Explanation of Solution
Write the energy conservation equation.
At
Kinetic energy at A is also zero.
Then rewrite (IX) in terms of
Conclusion:
Substitute
The speed is
(d)
Value of
Answer to Problem 69P
Kinetic energy is maximum at
Explanation of Solution
Write the energy of the system when the spring is compressed
Rewrite (XI) in terms of
Rewrite (XII) in terms of
Conclusion:
Substitute
As this the value for compression, the position is below
Therefore,
Kinetic energy is maximum at
(e)
Maximum upward speed.
Answer to Problem 69P
Maximum speed is
Explanation of Solution
Write the equation for maximum kinetic energy
Substitute (III) and (IV) in (XIV)
Rewrite (XV) in terms of
Conclusion:
Substitute
Maximum speed is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 7 Solutions
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning





