
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The hybridization and approximate bond angle for each carbon atoms in
Concept Introduction:
Hybridization is the mixing of valence atomic orbitals to get equivalent hybridized orbitals that having similar characteristics and energy.
Geometry of different types of molecule with respect to the hybridizations are mentioned are mentioned below,
Bond angle is the angle between two bonds of a molecule and it is determined based on the electron-domain geometry.
(a)
Explanation of Solution
Given molecule is
The Lewis electron dot structure for alanine is given below:
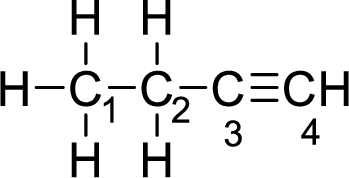 .
.
Consider the first carbon. There will be four electron regions in the molecule and hence the electron-region geometry will be tetrahedral. For a molecule having tetrahedral geometry, the hybridization will be
Consider the second carbon. There will be four electron regions in the molecule and hence the electron-region geometry will be tetrahedral. For a molecule having tetrahedral geometry, the hybridization will be
Consider the third carbon. There will be two electron regions in the molecule and hence the electron-region geometry will be linear. For a molecule having linear geometry, the hybridization will be
Consider the fourth carbon atom. There will be two electron regions in the molecule and hence the electron-region geometry will be linear. For a molecule having linear geometry, the hybridization will be
(b)
Interpretation:
The shortest carbon-to-carbon bond length in molecule has to be identified.
Concept Introduction:
Bond length is the distance between the nuclei in a bond and it is related to the sum of the covalent radii at the bonded atoms.
Higher the bond order, shorter will be the bond length.
(b)
Explanation of Solution
Given molecule is
The Lewis electron dot structure for alanine is given below:
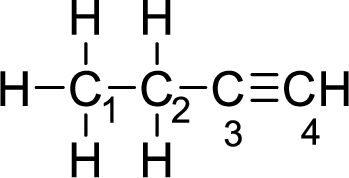 .
.
In the given molecule, the triple bond is present between
(c)
Interpretation:
The strongest carbon-to-carbon bond length in molecule has to be identified.
Concept Introduction:
Comparing triple bond, double bond and single bond, the bond with higher energy is the triple bond.
(c)
Explanation of Solution
Given molecule is
The Lewis electron dot structure for alanine is given below:
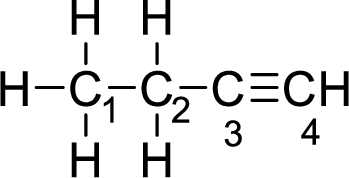 .
.
In the given molecule, the triple bond is present between
The strength of a triple bond is more than the single bond.
Thus, the strongest carbon-to-carbon bond is between
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 7 Solutions
Chemistry: The Molecular Science
- Show the mechanism steps to obtain the lowerenergy intermediate: *see imagearrow_forwardSoap is made by the previous reaction *see image. The main difference between one soap and another soap isthe length (number of carbons) of the carboxylic acid. However, if a soap irritates your skin, they mostlikely used too much lye.Detergents have the same chemical structure as soaps except for the functional group. Detergentshave sulfate (R-SO4H) and phosphate (R-PO4H2) functional groups. Draw the above carboxylic acidcarbon chain but as the two variants of detergents. *see imagearrow_forwardWhat are the reactions or reagents used? *see imagearrow_forward
- The two pKa values of oxalic acid are 1.25 and 3.81. Why are they not the same value? Show the protontransfer as part of your explanation. *see imagearrow_forwardасть Identify all the bonds that gauche interact with C-OMe in the most stable conformation of the above compound.arrow_forwardPredict the reactants used in the formation of the following compounds using Acid-Catalyzed dehydration reactionarrow_forward
- Can I please get help with this?arrow_forward.. Give the major organic product(s) for each of the following reactions or sequences of reactions. Show ll relevant stereochemistry [3 ONLY]. A H Br 1. NaCN 2 NaOH, H₂O, heat 3. H3O+ B. CH₂COOH 19000 1. LiAlH4 THF, heat 2 H₂O* C. CH Br 1. NaCN, acetone 2 H3O+, heat D. Br 1. Mg. ether 3. H₂O+ 2 CO₂ E. CN 1. (CH) CHMgBr, ether 2 H₂O+arrow_forwardAssign this COSY spectrumarrow_forward
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax
Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax


