
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The Lewis electron dot structure for
Concept Introduction:
- Lewis structures are diagrams that represent the
chemical bonding of covalently bonded molecules and coordination compounds. - It is also known as Lewis dot structures which represent the bonding between atoms of a molecule and the lone pairs of electrons that may exist in the molecule.
- The Lewis structure is based on the concept of the octet rule so that the electrons shared in each atom should have 8 electrons in its outer shell.
Lewis structure for any molecule is drawn by using the following steps,
First the skeletal structure for the given molecule is drawn then the total number of valence electrons for all atoms present in the molecule is determined.
The next step is to subtract the electrons present in the total number of bonds present in the skeletal structure of the molecule with the total valence electrons such that considering each bond contains two electrons with it.
Finally, the electrons which got after subtractions have to be equally distributed such that each atom contains eight electrons in its valence shell.
(a)
Explanation of Solution
Given molecule is
The Lewis electron dot structure for given molecule can be determined by first drawing the skeletal structure. Then, the total number of valence electrons for all atoms present in the molecule is determined.
The next step is to subtract the electrons present in the total number of bonds present in the skeletal structure of the molecule with the total valence electrons such that considering each bond contains two electrons with it.
Finally, the electrons which got after subtractions have to be equally distributed considering each atom contains eight electrons in its valence shell.
 .
.
Total number of valence electrons is given below:
Total number of electrons in bonds present is given below:
The eight electrons remaining will be distributing in such a way that each atom should have 8 electrons in its outer shell.
Therefore, the Lewis structure is given below:
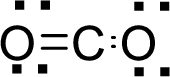 .
.
The molecular geometry will be linear because of the presence of two bond pairs around the central atom.
There will be two electron regions in the molecule and hence the electron-region geometry will also be linear.
(b)
Interpretation:
The Lewis electron dot structure for
Concept Introduction:
Refer to (a).
(b)
Explanation of Solution
Given molecule is
The Lewis electron dot structure for given molecule can be determined by first drawing the skeletal structure. Then, the total number of valence electrons for all atoms present in the molecule is determined.
The next step is to subtract the electrons present in the total number of bonds present in the skeletal structure of the molecule with the total valence electrons such that considering each bond contains two electrons with it.
Finally, the electrons which got after subtractions have to be equally distributed considering each atom contains eight electrons in its valence shell.
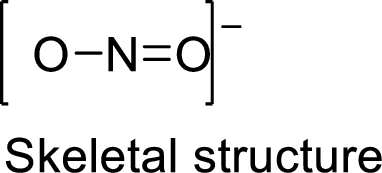 .
.
Total number of valence electrons is given below:
Total number of electrons in bonds present is given below:
The twelve electrons remaining will be distributing in such a way that each atom should have 8 electrons in its outer shell.
Therefore, the Lewis structure is given below:
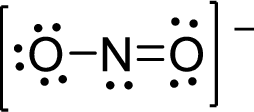 .
.
The molecular geometry will be angular because of the presence of two bond pairs and one lone pair around the central atom.
There will be three electron regions in the molecule and hence the electron-region geometry will also be triangular planar.
(c)
Interpretation:
The Lewis electron dot structure for
Concept Introduction:
Refer to (a).
(c)
Explanation of Solution
Given molecule is
The Lewis electron dot structure for given molecule can be determined by first drawing the skeletal structure. Then, the total number of valence electrons for all atoms present in the molecule is determined.
The next step is to subtract the electrons present in the total number of bonds present in the skeletal structure of the molecule with the total valence electrons such that considering each bond contains two electrons with it.
Finally, the electrons which got after subtractions have to be equally distributed considering each atom contains eight electrons in its valence shell.
 .
.
Total number of valence electrons is given below:
Total number of electrons in bonds present is given below:
The twelve electrons remaining will be distributing in such a way that each atom should have 8 electrons in its outer shell.
Therefore, the Lewis structure is given below:
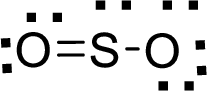
The molecular geometry will be angular because of the presence of two bond pairs and one lone pair around the central atom.
There will be three electron regions in the molecule and hence the electron-region geometry will also be triangular planar.
(d)
Interpretation:
The Lewis electron dot structure for
Concept Introduction:
Refer to (a).
(d)
Explanation of Solution
Given molecule is
The Lewis electron dot structure for given molecule can be determined by first drawing the skeletal structure. Then, the total number of valence electrons for all atoms present in the molecule is determined.
The next step is to subtract the electrons present in the total number of bonds present in the skeletal structure of the molecule with the total valence electrons such that considering each bond contains two electrons with it.
Finally, the electrons which got after subtractions have to be equally distributed considering each atom contains eight electrons in its valence shell.
 .
.
Total number of valence electrons is given below:
Total number of electrons in bonds present is given below:
The twelve electrons remaining will be distributing in such a way that each atom should have 8 electrons in its outer shell.
Therefore, the Lewis structure is given below:
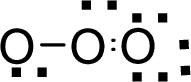 .
.
The molecular geometry will be angular because of the presence of two bond pairs and one lone pair around the central atom.
There will be three electron regions in the molecule and hence the electron-region geometry will also be triangular planar.
(e)
Interpretation:
The Lewis electron dot structure for
Concept Introduction:
Refer to (a).
(e)
Explanation of Solution
Given molecule is
The Lewis electron dot structure for given molecule can be determined by first drawing the skeletal structure. Then, the total number of valence electrons for all atoms present in the molecule is determined.
The next step is to subtract the electrons present in the total number of bonds present in the skeletal structure of the molecule with the total valence electrons such that considering each bond contains two electrons with it.
Finally, the electrons which got after subtractions have to be equally distributed considering each atom contains eight electrons in its valence shell.
 .
.
Total number of valence electrons is given below:
Total number of electrons in bonds present is given below:
The sixteen electrons remaining will be distributing in such a way that each atom should have 8 electrons in its outer shell.
Therefore, the Lewis structure is given below:
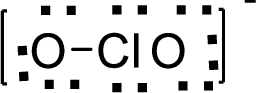 .
.
The molecular geometry will be angular because of the presence of two bond pairs and one lone pair around the central atom.
There will be four electron regions in the molecule and hence the electron-region geometry will be tetrahedral.
The similarity is that two oxygen atoms are bonded to the central atom in all these molecules. But, there are differences in the geometry of the molecules because of the differences in lone pair of electrons around the central atom.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 7 Solutions
Chemistry: The Molecular Science
- What is the name of the following compound? SiMe3arrow_forwardK Draw the starting structure that would lead to the major product shown under the provided conditions. Drawing 1. NaNH2 2. PhCH2Br 4 57°F Sunny Q Searcharrow_forward7 Draw the starting alkyl bromide that would produce this alkyne under these conditions. F Drawing 1. NaNH2, A 2. H3O+ £ 4 Temps to rise Tomorrow Q Search H2arrow_forward
 Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning

