
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
9th Edition
ISBN: 9781337093347
Author: Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 6, Problem 6.5.10P
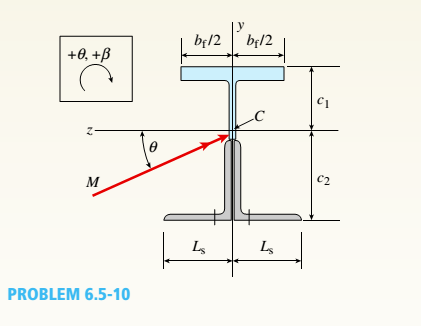
.10 A built-up bourn supporting a condominium balcony is made up of a structural T (one half of a W 200 x 31.3) for the top flange and web and two angles (2 L 2 / b / 6.4. long legal back-lo-backl lot the bottom flange and web. as shown. The beam is subjected to a bending moment .1/ having its
Determine the or ion ta I ion of the neutral axis and calculate the maximum tensile stress ir, and maximum compressive stress tr. in ".he beam. .Assume that 9 = 30°andM = 15 kN · m.
Use the numerical properties: c =4.111mm, c2 =4.169 mm, of = 134 mm, I, = 76 mm, A = 4144 mm 3 =3.88 X 106 mm 4, and = 34.18 X 10 mm 4.

Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Qu 5 Determine the carburizing time necessary to achieve a carbon concentration of 0.30 wt% at a position 4 mm into an iron carbon alloy that initially contains 0.10 wt% C. The surface concentration is to be maintained at 0.90 wt% C, and the treatment is to be conducted at 1100°C. Use the data for the diffusion of
carbon into y-iron: Do = 2.3 x10-5 m2/s and Qd = 148,000 J/mol. Express your answer in hours to three significant figures.
show all work step by step problems formula material science
(Read Question)
In figure A, the homogeneous rod of constant cross section is attached to unyielding supports. In figure B, a homogeneous bar with a cross-sectional area of 600 mm2 is attached to rigid supports. The bar carries the axial loads P1 = 20 kN and P2 = 60 kN, as shown.1. In figure A, derive the expression that calculates the reaction R1 in terms of P, and the given dimensions.2. In figure B, calculate the reaction (kN) at A.3. In figure B, calculate the maximum axial stress (MPa) in the rod.
Chapter 6 Solutions
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Ch. 6 - A composite beam is constructed using a steel...Ch. 6 - A wood beam is strengthened using two steel plates...Ch. 6 - A composite beam consisting of fiberglass faces...Ch. 6 - A wood beam with cross-sectional dimensions 200 mm...Ch. 6 - A hollow box beam is constructed with webs of...Ch. 6 - A r o lukI f/frm f «m t ub e of ou t sid e d ia...Ch. 6 - A beam with a guided support and 10-ft span...Ch. 6 - A plastic-lined steel pipe has the cross-sectional...Ch. 6 - The cross section of a sand wie h beam consisting...Ch. 6 - The cross section of a sandwich beam consisting of...
Ch. 6 - A bimetallic beam used in a temperature-control...Ch. 6 - A simply supported composite beam 3 m long carries...Ch. 6 - A simply supported wooden I-beam with a 12-ft span...Ch. 6 - -14 A simply supported composite beam with a 3.6 m...Ch. 6 - -15 A composite beam is constructed froma wood...Ch. 6 - A wood beam in a historic theater is reinforced...Ch. 6 - Repeat Problem 6.2-1 but now assume that the steel...Ch. 6 - Repeat Problem 6.2-17 but now use a...Ch. 6 - A sandwich beam having steel faces enclosing a...Ch. 6 - A wood beam 8 in. wide and 12 in. deep (nominal...Ch. 6 - A simple beam of span length 3.2 m carries a...Ch. 6 - A simple beam that is 18 ft long supports a...Ch. 6 - The composite beam shown in the figure is simply...Ch. 6 - The cross section of a beam made of thin strips of...Ch. 6 - Consider the preceding problem if the beam has...Ch. 6 - A simple beam thai is IS ft long supports a...Ch. 6 - The cross section of a composite beam made of...Ch. 6 - A beam is constructed of two angle sections, each...Ch. 6 - The cross section of a bimetallic strip is shown...Ch. 6 - A W 12 x 50 steel wide-flange beam and a segment...Ch. 6 - A reinforced concrete beam (see figure) is acted...Ch. 6 - A reinforced concrete T-beam (see figure) is acted...Ch. 6 - A reinforced concrete slab (see figure) is...Ch. 6 - A wood beam reinforced using two channels is...Ch. 6 - A wood beam reinforced by an aluminum channel...Ch. 6 - A beam with a rectangular cross section supports...Ch. 6 - A wood beam with a rectangular cross section (see...Ch. 6 - Solve the preceding problem for the following...Ch. 6 - A simply supported wide-flange beam of span length...Ch. 6 - Solve the preceding problem using the fol...Ch. 6 - A wood cantilever beam with a rectangular cross...Ch. 6 - Solve the preceding problem for a cantilever beam...Ch. 6 - A 2-m-long cantilever beam is constructed using a...Ch. 6 - A wood beam AB with a rectangular cross section (4...Ch. 6 - A steel beam of I-section (see figure) is simply...Ch. 6 - A cantilever beam with a wide-flange cross section...Ch. 6 - Solve the preceding problem using a W 310 x 129...Ch. 6 - A cantilever beam of W 12 × 14 section and length...Ch. 6 - A cantilever beam built up from two channel...Ch. 6 - A built-Lip I-section steel beam with channels...Ch. 6 - Repeat Problem 6.4-14 but use the configuration of...Ch. 6 - A beam with a channel section is subjected to a...Ch. 6 - A beam with a channel section is subjected to a...Ch. 6 - An angle section with equal legs is subjected to a...Ch. 6 - An angle section with equal legs is subjected to a...Ch. 6 - A beam made up all woun equal leg angles is...Ch. 6 - The Z-section of Example D-7 is subjected to M = 5...Ch. 6 - The cross section of a steel beam is constructed...Ch. 6 - The cross section of a steel beam is shown in the...Ch. 6 - A beam with a semicircular cross section of radius...Ch. 6 - .10 A built-up bourn supporting a condominium...Ch. 6 - Asteelpost (E = 30 × 106 psi) having thickness t =...Ch. 6 - A C 200 x 17.1 channel section has an angle with...Ch. 6 - A cold-formed steel section is made by folding a...Ch. 6 - A simple beam with a W 10 x 30 wide-flange cross...Ch. 6 - Solve the preceding problem for a W 250 × 44.8...Ch. 6 - A beam of wide-flange shape, W 8 x 28, has the...Ch. 6 - Solve the preceding problem for a W 200 × 41,7...Ch. 6 - Calculate the distance e from the cent crime of...Ch. 6 - Calculate the distance e from the centerline of...Ch. 6 - The cross section of an unbalanced wide-flange...Ch. 6 - The cross section of an unbalanced wide-flange...Ch. 6 - The cross section of a channel beam with double...Ch. 6 - The cross section of a slit circular tube of...Ch. 6 - The cross section of a slit square tube of...Ch. 6 - The cross section of a slit rectangular tube of...Ch. 6 - A U-shaped cross section of constant thickness is...Ch. 6 - Derive the following formula for the distance e...Ch. 6 - Derive the following formula for the distance e...Ch. 6 - The cross section of a sign post of constant...Ch. 6 - A cross section in the shape of a circular arc of...Ch. 6 - Determine the shape factor f for a cross section...Ch. 6 - (a) Determine the shape factor/for a hollow...Ch. 6 - A propped cantilever beam of length L = 54 in....Ch. 6 - A steel beam of rectangular cross section is 40 mm...Ch. 6 - .5 Calculate the shape factor j for the...Ch. 6 - Solve the preceding problem for a wide-flange beam...Ch. 6 - Determine the plastic modulus Z and shape...Ch. 6 - Prob. 6.10.8PCh. 6 - Prob. 6.10.9PCh. 6 - Prob. 6.10.10PCh. 6 - A hollow box beam with height h = 16 in,, width h...Ch. 6 - Solve the preceding problem for a box beam with...Ch. 6 - A hollow box beam with height h = 9.5 in., inside...Ch. 6 - Solve the preceding problem for a box beam with...Ch. 6 - The hollow box beam shown in the figure is...Ch. 6 - Prob. 6.10.16PCh. 6 - Prob. 6.10.17PCh. 6 - A singly symmetric beam with a T-section (see...Ch. 6 - A wide-flange beam with an unbalanced cross...Ch. 6 - .20 Determine the plastic moment Mpfor beam having...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- (Read image)arrow_forward(Read Image)arrow_forwardM16x2 grade 8.8 bolts No. 25 C1- Q.2. The figure is a cross section of a grade 25 cast-iron pressure vessel. A total of N, M16x2.0 grade 8.8 bolts are to be used to resist a separating force of 160 kN. (a) Determine ks, km, and C. (b) Find the number of bolts required for a load factor of 2 where the bolts may be reused when the joint 19 mm is taken apart. (c) with the number of bolts obtained in (b), determine the realized load factor for overload, the yielding factor of safety, and the separation factor of safety. 19 mmarrow_forward
- Problem4. The thin uniform disk of mass m = 1-kg and radius R = 0.1m spins about the bent shaft OG with the angular speed w2 = 20 rad/s. At the same time, the shaft rotates about the z-axis with the angular speed 001 = 10 rad/s. The angle between the bent portion of the shaft and the z-axis is ẞ = 35°. The mass of the shaft is negligible compared to the mass of the disk. a. Find the angular momentum of the disk with respect to point G, based on the axis orientation as shown. Include an MVD in your solution. b. Find the angular momentum of the disk with respect to point O, based on the axis orientation as shown. (Note: O is NOT the center of fixed-point rotation.) c. Find the kinetic energy of the assembly. z R R 002 2R x Answer: H = -0.046ĵ-0.040 kg-m²/sec Ho=-0.146-0.015 kg-m²/sec T 0.518 N-m =arrow_forwardProblem 3. The assembly shown consists of a solid sphere of mass m and the uniform slender rod of the same mass, both of which are welded to the shaft. The assembly is rotating with angular velocity w at a particular moment. Find the angular momentum with respect to point O, in terms of the axes shown. Answer: Ñ。 = ½mc²wcosßsinßĵ + (}{mr²w + 2mb²w + ½ mc²wcos²ß) k 3 m r b 2 C لا marrow_forwardOnly question 2arrow_forward
- Only question 1arrow_forwardOnly question 3arrow_forwardI have Euler parameters that describe the orientation of N relative to Q, e = -0.7071*n3, e4 = 0.7071. I have Euler parameters that describe the orientation of U relative to N, e = -1/sqrt(3)*n1, e4 = sqrt(2/3). After using euler parameter rule of successive rotations, I get euler parameters that describe the orientation of U relative to Q, e = -0.4082*n1 - 0.4082*n2 - 0.5774*n3. I need euler parameters that describe the orientation of U relative to Q in vector basis of q instead of n. How do I get that?arrow_forward
- Describe at least 4 processes in engineering where control charts are (or should be) appliedarrow_forwardDescribe at least two (2) processes where control charts are (or should be) applied.arrow_forwardProblem 3: A cube-shaped spacecraft is in a circular Earth orbit. Let N (n,) be inertial and the spacecraft is denoted S (ŝ₁). The spacecraft is described such that ¯½º = J ŝ₁ŝ₁ + J ŝ₂§₂ + J §¸Ŝ3 Location of the spacecraft in the orbit is determined by the orbit-fixed unit vectors ê, that are oriented by the angle (Qt), where is a constant angular rate. 52 €3 3> 2t 55 Λ Из At the instant when Qt = 90°, the spacecraft S is oriented relative to the orbit such that 8₁ = 0° Space-three 1-2-3 angles 0₂ = 60° and ES = $₂ rad/s 0₁ = 135° (a) At this instant, determine the direction cosine matrix that describes the orientation of the spacecraft with respect to the inertial frame N.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Everything About COMBINED LOADING in 10 Minutes! Mechanics of Materials; Author: Less Boring Lectures;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=N-PlI900hSg;License: Standard youtube license