
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
9th Edition
ISBN: 9781337093347
Author: Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 6, Problem 6.10.11P
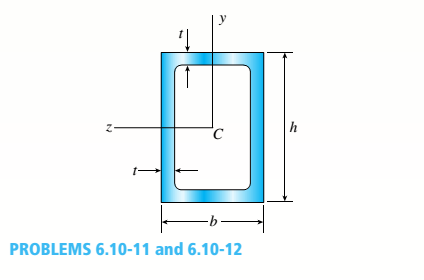
A hollow box beam with height h = 16 in,, width h = 8 in,, and constant wall thickness r = 0.75 LiL is shown in the figure. The beam is constructed of steel with yield stress ty = 32 ksi.
Determine the yield moment My, plastic moment A/p, and shape factor.
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
Pearson eText
Study Area
Access Pearson
mylabmastering.pearson.com
P Pearson MyLab and Mastering
Problem 15.79
P Course Home
b Answered: HW_02.pdf EE 213-01 > Assignments HW_#...
6 of 8
>
Document Sharing
User Settings
The two disks A and B have a mass of 4 kg and 5 kg,
respectively. They collide with the initial velocities shown.
The coefficient of restitution is e = 0.65. Suppose that
(VA)1 = 6 m/s, (VB)1 = 8 m/s. (Figure 1)
Part A
Determine the magnitude of the velocity of A just after impact.
Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units.
Figure
1 of 1
μÅ
(VA)2 =
Value
Units
Submit
Request Answer
Part B
?
Review
Determine the angle between the x axis and the velocity of A just after impact, measured clockwise from the negative x axis.
Express your answer in degrees to three significant figures.
ΕΠΙ ΑΣΦ
vec
01
Submit
Request Answer
Part C
?
Determine the magnitude of the velocity of B just after impact.
Express your answer to three significant…
Pearson eText
Study Area
mylabmastering.pearson.com
Access Pearson
P Pearson MyLab and Mastering
Problem 14.78
P Course Home
b Answered: HW_02.pdf EE 213-01 > Assignments HW_#...
2 of 8
Document Sharing
User Settings
The spring has a stiffness k = 200 N/m and an
unstretched length of 0.5 m. It is attached to the 4.6-kg
smooth collar and the collar is released from rest at A.
Neglect the size of the collar. (Figure 1)
Part A
Determine the speed of the collar when it reaches B.
Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units.
Figure
1 of 1
με
VB = Value
Units
Submit
Request Answer
Provide Feedback
?
Review
Next >
Pearson eText
Study Area
Document Sharing
User Settings
mylabmastering.pearson.com
Access Pearson
P Pearson MyLab and Mastering
Problem 15.96
Part A
In (Figure 1), take m₁ = 3.4 kg and m =
4.8 kg.
Figure
1 of 1
P Course Home
b Answered: HW_02.pdf EE 213-01 > Assignments HW_#...
7 of 8
Determine the component of the angular momentum Ho of particle A about point O.
Express your answer in kilogram-meters squared per second to three significant figures.
(Ho) z
=
-ΜΕ ΑΣΦ
vec
Submit
Request Answer
Part B
?
kg m2/s
Determine the component of the angular momentum Ho of particle B about point O. Suppose that
Express your answer in kilogram-meters squared per second to three significant figures.
ΜΕ ΑΣΦ
vec
Symbols
(Ho)z =
Submit
Request Answer
Provide Feedback
?
kg m2/s
Review
Next >
Chapter 6 Solutions
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Ch. 6 - A composite beam is constructed using a steel...Ch. 6 - A wood beam is strengthened using two steel plates...Ch. 6 - A composite beam consisting of fiberglass faces...Ch. 6 - A wood beam with cross-sectional dimensions 200 mm...Ch. 6 - A hollow box beam is constructed with webs of...Ch. 6 - A r o lukI f/frm f «m t ub e of ou t sid e d ia...Ch. 6 - A beam with a guided support and 10-ft span...Ch. 6 - A plastic-lined steel pipe has the cross-sectional...Ch. 6 - The cross section of a sand wie h beam consisting...Ch. 6 - The cross section of a sandwich beam consisting of...
Ch. 6 - A bimetallic beam used in a temperature-control...Ch. 6 - A simply supported composite beam 3 m long carries...Ch. 6 - A simply supported wooden I-beam with a 12-ft span...Ch. 6 - -14 A simply supported composite beam with a 3.6 m...Ch. 6 - -15 A composite beam is constructed froma wood...Ch. 6 - A wood beam in a historic theater is reinforced...Ch. 6 - Repeat Problem 6.2-1 but now assume that the steel...Ch. 6 - Repeat Problem 6.2-17 but now use a...Ch. 6 - A sandwich beam having steel faces enclosing a...Ch. 6 - A wood beam 8 in. wide and 12 in. deep (nominal...Ch. 6 - A simple beam of span length 3.2 m carries a...Ch. 6 - A simple beam that is 18 ft long supports a...Ch. 6 - The composite beam shown in the figure is simply...Ch. 6 - The cross section of a beam made of thin strips of...Ch. 6 - Consider the preceding problem if the beam has...Ch. 6 - A simple beam thai is IS ft long supports a...Ch. 6 - The cross section of a composite beam made of...Ch. 6 - A beam is constructed of two angle sections, each...Ch. 6 - The cross section of a bimetallic strip is shown...Ch. 6 - A W 12 x 50 steel wide-flange beam and a segment...Ch. 6 - A reinforced concrete beam (see figure) is acted...Ch. 6 - A reinforced concrete T-beam (see figure) is acted...Ch. 6 - A reinforced concrete slab (see figure) is...Ch. 6 - A wood beam reinforced using two channels is...Ch. 6 - A wood beam reinforced by an aluminum channel...Ch. 6 - A beam with a rectangular cross section supports...Ch. 6 - A wood beam with a rectangular cross section (see...Ch. 6 - Solve the preceding problem for the following...Ch. 6 - A simply supported wide-flange beam of span length...Ch. 6 - Solve the preceding problem using the fol...Ch. 6 - A wood cantilever beam with a rectangular cross...Ch. 6 - Solve the preceding problem for a cantilever beam...Ch. 6 - A 2-m-long cantilever beam is constructed using a...Ch. 6 - A wood beam AB with a rectangular cross section (4...Ch. 6 - A steel beam of I-section (see figure) is simply...Ch. 6 - A cantilever beam with a wide-flange cross section...Ch. 6 - Solve the preceding problem using a W 310 x 129...Ch. 6 - A cantilever beam of W 12 × 14 section and length...Ch. 6 - A cantilever beam built up from two channel...Ch. 6 - A built-Lip I-section steel beam with channels...Ch. 6 - Repeat Problem 6.4-14 but use the configuration of...Ch. 6 - A beam with a channel section is subjected to a...Ch. 6 - A beam with a channel section is subjected to a...Ch. 6 - An angle section with equal legs is subjected to a...Ch. 6 - An angle section with equal legs is subjected to a...Ch. 6 - A beam made up all woun equal leg angles is...Ch. 6 - The Z-section of Example D-7 is subjected to M = 5...Ch. 6 - The cross section of a steel beam is constructed...Ch. 6 - The cross section of a steel beam is shown in the...Ch. 6 - A beam with a semicircular cross section of radius...Ch. 6 - .10 A built-up bourn supporting a condominium...Ch. 6 - Asteelpost (E = 30 × 106 psi) having thickness t =...Ch. 6 - A C 200 x 17.1 channel section has an angle with...Ch. 6 - A cold-formed steel section is made by folding a...Ch. 6 - A simple beam with a W 10 x 30 wide-flange cross...Ch. 6 - Solve the preceding problem for a W 250 × 44.8...Ch. 6 - A beam of wide-flange shape, W 8 x 28, has the...Ch. 6 - Solve the preceding problem for a W 200 × 41,7...Ch. 6 - Calculate the distance e from the cent crime of...Ch. 6 - Calculate the distance e from the centerline of...Ch. 6 - The cross section of an unbalanced wide-flange...Ch. 6 - The cross section of an unbalanced wide-flange...Ch. 6 - The cross section of a channel beam with double...Ch. 6 - The cross section of a slit circular tube of...Ch. 6 - The cross section of a slit square tube of...Ch. 6 - The cross section of a slit rectangular tube of...Ch. 6 - A U-shaped cross section of constant thickness is...Ch. 6 - Derive the following formula for the distance e...Ch. 6 - Derive the following formula for the distance e...Ch. 6 - The cross section of a sign post of constant...Ch. 6 - A cross section in the shape of a circular arc of...Ch. 6 - Determine the shape factor f for a cross section...Ch. 6 - (a) Determine the shape factor/for a hollow...Ch. 6 - A propped cantilever beam of length L = 54 in....Ch. 6 - A steel beam of rectangular cross section is 40 mm...Ch. 6 - .5 Calculate the shape factor j for the...Ch. 6 - Solve the preceding problem for a wide-flange beam...Ch. 6 - Determine the plastic modulus Z and shape...Ch. 6 - Prob. 6.10.8PCh. 6 - Prob. 6.10.9PCh. 6 - Prob. 6.10.10PCh. 6 - A hollow box beam with height h = 16 in,, width h...Ch. 6 - Solve the preceding problem for a box beam with...Ch. 6 - A hollow box beam with height h = 9.5 in., inside...Ch. 6 - Solve the preceding problem for a box beam with...Ch. 6 - The hollow box beam shown in the figure is...Ch. 6 - Prob. 6.10.16PCh. 6 - Prob. 6.10.17PCh. 6 - A singly symmetric beam with a T-section (see...Ch. 6 - A wide-flange beam with an unbalanced cross...Ch. 6 - .20 Determine the plastic moment Mpfor beam having...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Pearson eText Study Area Document Sharing User Settings mylabmastering.pearson.com Access Pearson P Pearson MyLab and Mastering Problem 14.69 Part A P Course Home b Answered: HW_02.pdf EE 213-01 > Assignments HW_#... 1 of 8 Review The 5-kg collar has a velocity of 7 m/s to the right when it is at A. It then travels down along the smooth guide shown in (Figure 1). The spring has an unstretched length of 100 mm and B is located just before the end of the curved portion of the rod. Determine the speed of the collar when it reaches point B, which is located just before the end of the curved portion of the rod. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. Figure 1 of 1 με v = Value Units Submit Request Answer Part B ? What is the normal force on the collar at this instant? Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. ☐ μÅ ? N = Value Units Submit Request Answer Provide Feedback Next >arrow_forwardPearson eText Study Area mylabmastering.pearson.com Access Pearson P Pearson MyLab and Mastering Problem 15.106 P Course Home b Answered: HW_02.pdf EE 213-01 > Assignments HW_#... 8 of 8 Document Sharing User Settings The two spheres A and B each have a mass of 400 g. The spheres are fixed to the horizontal rods as shown in (Figure 1) and their initial velocity is 2 m/s. The mass of the supporting frame is negligible and it is free to rotate. Neglect the size of the spheres. Part A If a couple moment of M = 0.3 N · m is applied to the frame, determine the speed of the spheres in 3 s. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. Figure 1 of 1 ☐ ? v = Value Units Units input for part A Submit Request Answer Return to Assignment Provide Feedback ■Reviewarrow_forwardPearson eText Study Area Access Pearson mylabmastering.pearson.com P Pearson MyLab and Mastering Problem 15.79 P Course Home b Answered: HW_02.pdf EE 213-01 > Assignments HW_#... 6 of 8 > Document Sharing User Settings The two disks A and B have a mass of 4 kg and 5 kg, respectively. They collide with the initial velocities shown. The coefficient of restitution is e = 0.65. Suppose that (VA)1 = 6 m/s, (VB)1 = 8 m/s. (Figure 1) Part A Determine the magnitude of the velocity of A just after impact. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. Figure 1 of 1 μÅ (VA)2 = Value Units Submit Request Answer Part B ? Review Determine the angle between the x axis and the velocity of A just after impact, measured clockwise from the negative x axis. Express your answer in degrees to three significant figures. ΕΠΙ ΑΣΦ vec 01 Submit Request Answer Part C ? Determine the magnitude of the velocity of B just after impact. Express your answer to three significant…arrow_forward
- 40.00 30.00 100.00- 100.00 P = 1000 N A=167 d=140.00 100.00- -b 20.00 200.00 Weld Strength P = 273 N/mm^2 Electrod E60 Safety factor S₁ = 3 Force P = 1000 N Using by SOLIDWORKSarrow_forwardWhat are the reaction forces in A and B?arrow_forwardPearson eText Study Area Access Pearson mylabmastering.pearson.com P Pearson MyLab and Mastering Problem 15.6 P Course Home b Answered: HW_02.pdf EE 213-01 > Assignments HW_#... 3 of 8 ■ Review Document Sharing User Settings The jet plane has a mass of 250 Mg and a horizontal velocity of 100 m/s when t = 0. Part A If both engines provide a horizontal thrust which varies as shown in the graph in (Figure 1), determine the plane's velocity in 5 s. Neglect air resistance and the loss of fuel during the motion. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. Figure 1 of 1 > ☐ μÅ ? v = Value Units Submit Request Answer Provide Feedback Next >arrow_forward
- Access Pearson mylabmastering.pearson.com P Pearson MyLab and Mastering Problem 15.43 P Course Home b Answered: HW_02.pdf EE 213-01 > Assignments HW_#... Pearson eText Study Area Document Sharing User Settings The 20-g bullet is travelling at 400 m/s when it becomes embedded in the 2-kg stationary block. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and the plane is μk = 0.2. (Figure 1) Part A Determine the distance the block will slide before it stops. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. Figure 1 of 1 με S = Value Units Submit Request Answer Provide Feedback ? 4 of 8 Review Next >arrow_forwardAccess Pearson mylabmastering.pearson.com P Pearson MyLab and Mastering Problem 15.64 P Course Home b Answered: HW_02.pdf EE 213-01 > Assignments HW_#... 5 of 8 Pearson eText Study Area Document Sharing User Settings Ball A has a mass of 3 kg and is moving with a velocity of (VA)1 = 8 m/s when it makes a direct collision with ball B, which has a mass of 2.5 kg and is moving with a velocity of (VB) 1 = 4 m/s. Suppose that e = 0.7. Neglect the size of the balls. (Figure 1) Part A Determine the velocity of A just after the collision. ■Review Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. Assume the positive direction is to the right. Figure 1 of 1 ◎ на ? (VA)2= Value Units Submit Request Answer Part B Determine the velocity of B just after the collision. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. Assume the positive direction is to the right. μÅ ? (VB)2= = Value Units Submit Request Answer Provide Feedback Next…arrow_forwardI only need help with number 3, actually just the theta dot portion. Thanks! I have Vr = 10.39 ft/sarrow_forward
- Only 100% sure experts solve it correct complete solutions okk don't use guidelines or ai answers okk will dislike okkk. Only human experts solved itarrow_forwardAirplanes A and B, flying at constant velocity and at the same altitude, are tracking the eye of hurricane C. The relative velocity of C with respect to A is 300 kph 65.0° South of West, and the relative velocity of C with respect to B is 375 kph 50.0° South of East. A 120.0 km B 1N 1. Determine the relative velocity of B with respect to A. A ground-based radar indicates that hurricane C is moving at a speed of 40.0 kph due north. 2. Determine the velocity of airplane A. 3. Determine the velocity of airplane B. Consider that at the start of the tracking expedition, the distance between the planes is 120.0 km and their initial positions are horizontally collinear. 4. Given the velocities obtained in items 2 and 3, should the pilots of planes A and B be concerned whether the planes will collide at any given time? Prove using pertinent calculations. (Hint: x = x + vt) 0arrow_forwardOnly 100% sure experts solve it correct complete solutions okk don't use guidelines or ai answers okk will dislike okkk.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials Lecture: Beam Design; Author: UWMC Engineering;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-wVs5pvQPm4;License: Standard Youtube License