
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
9th Edition
ISBN: 9781337093347
Author: Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 6, Problem 6.10.1P
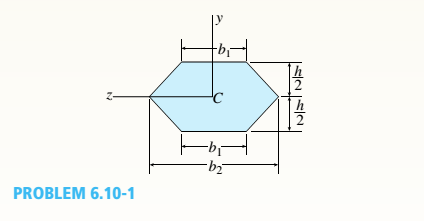
Determine the shape factor f for a cross section in the shape of a double trapezoid having the dimensions shown in the figure.
Also, check your result for the special cases of a rhombus (b1= 0) and a rectangle (b1= b2).
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
please explain each method used, thank you
Determine the resultant loadings acting on the cross sections at points D and E of the frame.
A spring of stiffness factor 98 N/m is pulled through 20 cm. Find the restoring force and compute the mass which should be attached so as to stretch in spring by same amount.
Chapter 6 Solutions
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Ch. 6 - A composite beam is constructed using a steel...Ch. 6 - A wood beam is strengthened using two steel plates...Ch. 6 - A composite beam consisting of fiberglass faces...Ch. 6 - A wood beam with cross-sectional dimensions 200 mm...Ch. 6 - A hollow box beam is constructed with webs of...Ch. 6 - A r o lukI f/frm f «m t ub e of ou t sid e d ia...Ch. 6 - A beam with a guided support and 10-ft span...Ch. 6 - A plastic-lined steel pipe has the cross-sectional...Ch. 6 - The cross section of a sand wie h beam consisting...Ch. 6 - The cross section of a sandwich beam consisting of...
Ch. 6 - A bimetallic beam used in a temperature-control...Ch. 6 - A simply supported composite beam 3 m long carries...Ch. 6 - A simply supported wooden I-beam with a 12-ft span...Ch. 6 - -14 A simply supported composite beam with a 3.6 m...Ch. 6 - -15 A composite beam is constructed froma wood...Ch. 6 - A wood beam in a historic theater is reinforced...Ch. 6 - Repeat Problem 6.2-1 but now assume that the steel...Ch. 6 - Repeat Problem 6.2-17 but now use a...Ch. 6 - A sandwich beam having steel faces enclosing a...Ch. 6 - A wood beam 8 in. wide and 12 in. deep (nominal...Ch. 6 - A simple beam of span length 3.2 m carries a...Ch. 6 - A simple beam that is 18 ft long supports a...Ch. 6 - The composite beam shown in the figure is simply...Ch. 6 - The cross section of a beam made of thin strips of...Ch. 6 - Consider the preceding problem if the beam has...Ch. 6 - A simple beam thai is IS ft long supports a...Ch. 6 - The cross section of a composite beam made of...Ch. 6 - A beam is constructed of two angle sections, each...Ch. 6 - The cross section of a bimetallic strip is shown...Ch. 6 - A W 12 x 50 steel wide-flange beam and a segment...Ch. 6 - A reinforced concrete beam (see figure) is acted...Ch. 6 - A reinforced concrete T-beam (see figure) is acted...Ch. 6 - A reinforced concrete slab (see figure) is...Ch. 6 - A wood beam reinforced using two channels is...Ch. 6 - A wood beam reinforced by an aluminum channel...Ch. 6 - A beam with a rectangular cross section supports...Ch. 6 - A wood beam with a rectangular cross section (see...Ch. 6 - Solve the preceding problem for the following...Ch. 6 - A simply supported wide-flange beam of span length...Ch. 6 - Solve the preceding problem using the fol...Ch. 6 - A wood cantilever beam with a rectangular cross...Ch. 6 - Solve the preceding problem for a cantilever beam...Ch. 6 - A 2-m-long cantilever beam is constructed using a...Ch. 6 - A wood beam AB with a rectangular cross section (4...Ch. 6 - A steel beam of I-section (see figure) is simply...Ch. 6 - A cantilever beam with a wide-flange cross section...Ch. 6 - Solve the preceding problem using a W 310 x 129...Ch. 6 - A cantilever beam of W 12 × 14 section and length...Ch. 6 - A cantilever beam built up from two channel...Ch. 6 - A built-Lip I-section steel beam with channels...Ch. 6 - Repeat Problem 6.4-14 but use the configuration of...Ch. 6 - A beam with a channel section is subjected to a...Ch. 6 - A beam with a channel section is subjected to a...Ch. 6 - An angle section with equal legs is subjected to a...Ch. 6 - An angle section with equal legs is subjected to a...Ch. 6 - A beam made up all woun equal leg angles is...Ch. 6 - The Z-section of Example D-7 is subjected to M = 5...Ch. 6 - The cross section of a steel beam is constructed...Ch. 6 - The cross section of a steel beam is shown in the...Ch. 6 - A beam with a semicircular cross section of radius...Ch. 6 - .10 A built-up bourn supporting a condominium...Ch. 6 - Asteelpost (E = 30 × 106 psi) having thickness t =...Ch. 6 - A C 200 x 17.1 channel section has an angle with...Ch. 6 - A cold-formed steel section is made by folding a...Ch. 6 - A simple beam with a W 10 x 30 wide-flange cross...Ch. 6 - Solve the preceding problem for a W 250 × 44.8...Ch. 6 - A beam of wide-flange shape, W 8 x 28, has the...Ch. 6 - Solve the preceding problem for a W 200 × 41,7...Ch. 6 - Calculate the distance e from the cent crime of...Ch. 6 - Calculate the distance e from the centerline of...Ch. 6 - The cross section of an unbalanced wide-flange...Ch. 6 - The cross section of an unbalanced wide-flange...Ch. 6 - The cross section of a channel beam with double...Ch. 6 - The cross section of a slit circular tube of...Ch. 6 - The cross section of a slit square tube of...Ch. 6 - The cross section of a slit rectangular tube of...Ch. 6 - A U-shaped cross section of constant thickness is...Ch. 6 - Derive the following formula for the distance e...Ch. 6 - Derive the following formula for the distance e...Ch. 6 - The cross section of a sign post of constant...Ch. 6 - A cross section in the shape of a circular arc of...Ch. 6 - Determine the shape factor f for a cross section...Ch. 6 - (a) Determine the shape factor/for a hollow...Ch. 6 - A propped cantilever beam of length L = 54 in....Ch. 6 - A steel beam of rectangular cross section is 40 mm...Ch. 6 - .5 Calculate the shape factor j for the...Ch. 6 - Solve the preceding problem for a wide-flange beam...Ch. 6 - Determine the plastic modulus Z and shape...Ch. 6 - Prob. 6.10.8PCh. 6 - Prob. 6.10.9PCh. 6 - Prob. 6.10.10PCh. 6 - A hollow box beam with height h = 16 in,, width h...Ch. 6 - Solve the preceding problem for a box beam with...Ch. 6 - A hollow box beam with height h = 9.5 in., inside...Ch. 6 - Solve the preceding problem for a box beam with...Ch. 6 - The hollow box beam shown in the figure is...Ch. 6 - Prob. 6.10.16PCh. 6 - Prob. 6.10.17PCh. 6 - A singly symmetric beam with a T-section (see...Ch. 6 - A wide-flange beam with an unbalanced cross...Ch. 6 - .20 Determine the plastic moment Mpfor beam having...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- please box out or highlight all the answersarrow_forwardWhat are some ways Historical Data can be used and applied to an estimate?arrow_forwardProblem 1. Rod OAB is rotating counterclockwise with the constant angular velocity of 5 rad/s. In the position shown, collar P is sliding toward A with the constant speed of 0.8 m/s relative to the rod. Find the velocity of P and the acceleration of P. y B 3 P 300 mm A - Answer: Up = -0.861 − 0.48ĵ™; ā₂ = 4.8î −1.1ĵ marrow_forward
- A bent tube is attached to a wall with brackets as shown. . A force of F = 980 lb is applied to the end of the tube with direction indicated by the dimensions in the figure. a.) Determine the force vector F in Cartesian components. → → b.) Resolve the force vector F into vector components parallel and perpendicular to the position vector rDA. Express each of these vectors in Cartesian components. 2013 Michael Swanbom cc 10 BY NC SA g x B A א Z FK с кая b Values for dimensions on the figure are given in the table below. Note the figure may not be to scale. Be sure to align your cartesian unit vectors with the coordinate axes shown in the figure. Variable Value a 8 in 12 in с 15 in 36 in h 23 in g 28 in a. F = b. FDA = = ( + k) lb k) lb FIDA = 2 + k) lbarrow_forwardProblem 4. Part 1 100 mm C @ PROBLEM 15.160 Pin P slides in the circular slot cut in the plate shown at a constant relative speed u = 500 mm/s. Assuming that at the instant shown the angular velocity of the plate is 6 rad/s and is increasing at the rate of 20 rad/s², determine the acceleration of pin P when = 90°. 150 mm is NOT zero. Answer: a = 3.4î −15.1ĵ m/s² ) P (Hint: u is a constant number, which means that the tangential component of F is zero. However, the normal component of Part2. When 0 = 120°, u = 600 mm/s and is increasing at the rate of 30mm/s², determine the acceleration of pin P.arrow_forwardProblem 5. Disk D of the Geneva mechanism rotates with constant counterclockwise angular velocity wD = 10 rad/s. At the instant when & = 150º, determine (a) the angular velocity of disk S, and (b) the velocity of pin P relative to disk S. (c). the angular acceleration of S. Disk S R=50 mm =135° |1=√ER- Disk D Partial answers: Ō = -4.08 Â rad/s ā¸ = -233 k rad/s²arrow_forward
- Problem 3. In the figure below, point A protrudes from link AB and slides in the rod OC. Rod OC is rotating with angular velocity woc = 2 rad/s and aoc = 3 rad/s² in the directions shown. Find the following, remembering to clearly define your axes and the rate of rotation of the frame. a. The angular velocity of link AB and the velocity of A relative to rod OC. m (Answers: @AB is 2.9 rad/s CCW, rxy = .58! toward C) S b. The angular acceleration of link AB and the acceleration of A relative to rod OC. Answers: αAB = 7.12 rad/s² CCW, r = 6.3 m ܐܨ toward C. B C A 30° Фос 400 mm OA=500 mm docarrow_forwardProblem 2. 6 m 30° B PROBLEM 15.164 At the instant shown the length of the boom AB is being decreased at the constant rate of 0.2 m/s and the boom is being lowered at the constant rate of 0.08 rad/s. Determine (a) the velocity of Point B, (b) the acceleration of Point B. Partial answer: a = −0.049î +0.009ĵ m/s²arrow_forwardA crate is hung by three ropes attached to a steel ring at A such that the top surface is parallel to the xy plane. Point A is located at a height of h = 121.92 cm above the top of the crate directly over the geometric center of the top surface. Use the given dimensions from the table below to perform the following calculations: →> a.) Determine the position vector IAD that describes rope AD. b.) Compute the unit vector cд that points from point C to point A. c.) If rope AB carries a tension force of magnitude FT = 760 → N, determine the force vector FT that expresses how this force acts on point A. Express each vector in Cartesian components to three significant figures. 2013 Michael Swanbom ↑z BY NC SA b x B У a D Values for dimensions on the figure are given in the following table. Note the figure may not be to scale. Be sure to align your cartesian unit vectors with the coordinate axes shown in the figure. Variable Value a 101.6 cm b 124.46 cm с 38.71 cm a. rдD = + b. ÛCA c. FT= =…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L
International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781305501607
Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan Kiusalaas
Publisher:CENGAGE L
EVERYTHING on Axial Loading Normal Stress in 10 MINUTES - Mechanics of Materials; Author: Less Boring Lectures;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=jQ-fNqZWrNg;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY