
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
9th Edition
ISBN: 9781337093347
Author: Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 6, Problem 6.2.11P
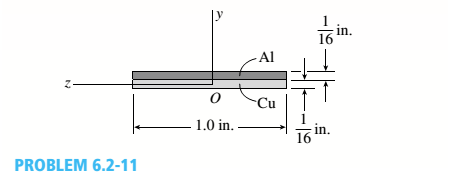
A bimetallic beam used in a temperature-control switch consists of strips of aluminum and copper bonded together as shown in the figure, which is a cross-sectional view. The width of the beam is LO in,, and each strip has a thickness of 1/16 in.
Under the action of a bending moment M = 12 lb-in, acting about the z axis, what are the maximum stresses aaand ecin the aluminum and copper, respectively? (Assume fA, = 10,5 x l0 psi and ecu= 16,8 × 106 psi,)
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 6 Solutions
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Ch. 6 - A composite beam is constructed using a steel...Ch. 6 - A wood beam is strengthened using two steel plates...Ch. 6 - A composite beam consisting of fiberglass faces...Ch. 6 - A wood beam with cross-sectional dimensions 200 mm...Ch. 6 - A hollow box beam is constructed with webs of...Ch. 6 - A r o lukI f/frm f «m t ub e of ou t sid e d ia...Ch. 6 - A beam with a guided support and 10-ft span...Ch. 6 - A plastic-lined steel pipe has the cross-sectional...Ch. 6 - The cross section of a sand wie h beam consisting...Ch. 6 - The cross section of a sandwich beam consisting of...
Ch. 6 - A bimetallic beam used in a temperature-control...Ch. 6 - A simply supported composite beam 3 m long carries...Ch. 6 - A simply supported wooden I-beam with a 12-ft span...Ch. 6 - -14 A simply supported composite beam with a 3.6 m...Ch. 6 - -15 A composite beam is constructed froma wood...Ch. 6 - A wood beam in a historic theater is reinforced...Ch. 6 - Repeat Problem 6.2-1 but now assume that the steel...Ch. 6 - Repeat Problem 6.2-17 but now use a...Ch. 6 - A sandwich beam having steel faces enclosing a...Ch. 6 - A wood beam 8 in. wide and 12 in. deep (nominal...Ch. 6 - A simple beam of span length 3.2 m carries a...Ch. 6 - A simple beam that is 18 ft long supports a...Ch. 6 - The composite beam shown in the figure is simply...Ch. 6 - The cross section of a beam made of thin strips of...Ch. 6 - Consider the preceding problem if the beam has...Ch. 6 - A simple beam thai is IS ft long supports a...Ch. 6 - The cross section of a composite beam made of...Ch. 6 - A beam is constructed of two angle sections, each...Ch. 6 - The cross section of a bimetallic strip is shown...Ch. 6 - A W 12 x 50 steel wide-flange beam and a segment...Ch. 6 - A reinforced concrete beam (see figure) is acted...Ch. 6 - A reinforced concrete T-beam (see figure) is acted...Ch. 6 - A reinforced concrete slab (see figure) is...Ch. 6 - A wood beam reinforced using two channels is...Ch. 6 - A wood beam reinforced by an aluminum channel...Ch. 6 - A beam with a rectangular cross section supports...Ch. 6 - A wood beam with a rectangular cross section (see...Ch. 6 - Solve the preceding problem for the following...Ch. 6 - A simply supported wide-flange beam of span length...Ch. 6 - Solve the preceding problem using the fol...Ch. 6 - A wood cantilever beam with a rectangular cross...Ch. 6 - Solve the preceding problem for a cantilever beam...Ch. 6 - A 2-m-long cantilever beam is constructed using a...Ch. 6 - A wood beam AB with a rectangular cross section (4...Ch. 6 - A steel beam of I-section (see figure) is simply...Ch. 6 - A cantilever beam with a wide-flange cross section...Ch. 6 - Solve the preceding problem using a W 310 x 129...Ch. 6 - A cantilever beam of W 12 × 14 section and length...Ch. 6 - A cantilever beam built up from two channel...Ch. 6 - A built-Lip I-section steel beam with channels...Ch. 6 - Repeat Problem 6.4-14 but use the configuration of...Ch. 6 - A beam with a channel section is subjected to a...Ch. 6 - A beam with a channel section is subjected to a...Ch. 6 - An angle section with equal legs is subjected to a...Ch. 6 - An angle section with equal legs is subjected to a...Ch. 6 - A beam made up all woun equal leg angles is...Ch. 6 - The Z-section of Example D-7 is subjected to M = 5...Ch. 6 - The cross section of a steel beam is constructed...Ch. 6 - The cross section of a steel beam is shown in the...Ch. 6 - A beam with a semicircular cross section of radius...Ch. 6 - .10 A built-up bourn supporting a condominium...Ch. 6 - Asteelpost (E = 30 × 106 psi) having thickness t =...Ch. 6 - A C 200 x 17.1 channel section has an angle with...Ch. 6 - A cold-formed steel section is made by folding a...Ch. 6 - A simple beam with a W 10 x 30 wide-flange cross...Ch. 6 - Solve the preceding problem for a W 250 × 44.8...Ch. 6 - A beam of wide-flange shape, W 8 x 28, has the...Ch. 6 - Solve the preceding problem for a W 200 × 41,7...Ch. 6 - Calculate the distance e from the cent crime of...Ch. 6 - Calculate the distance e from the centerline of...Ch. 6 - The cross section of an unbalanced wide-flange...Ch. 6 - The cross section of an unbalanced wide-flange...Ch. 6 - The cross section of a channel beam with double...Ch. 6 - The cross section of a slit circular tube of...Ch. 6 - The cross section of a slit square tube of...Ch. 6 - The cross section of a slit rectangular tube of...Ch. 6 - A U-shaped cross section of constant thickness is...Ch. 6 - Derive the following formula for the distance e...Ch. 6 - Derive the following formula for the distance e...Ch. 6 - The cross section of a sign post of constant...Ch. 6 - A cross section in the shape of a circular arc of...Ch. 6 - Determine the shape factor f for a cross section...Ch. 6 - (a) Determine the shape factor/for a hollow...Ch. 6 - A propped cantilever beam of length L = 54 in....Ch. 6 - A steel beam of rectangular cross section is 40 mm...Ch. 6 - .5 Calculate the shape factor j for the...Ch. 6 - Solve the preceding problem for a wide-flange beam...Ch. 6 - Determine the plastic modulus Z and shape...Ch. 6 - Prob. 6.10.8PCh. 6 - Prob. 6.10.9PCh. 6 - Prob. 6.10.10PCh. 6 - A hollow box beam with height h = 16 in,, width h...Ch. 6 - Solve the preceding problem for a box beam with...Ch. 6 - A hollow box beam with height h = 9.5 in., inside...Ch. 6 - Solve the preceding problem for a box beam with...Ch. 6 - The hollow box beam shown in the figure is...Ch. 6 - Prob. 6.10.16PCh. 6 - Prob. 6.10.17PCh. 6 - A singly symmetric beam with a T-section (see...Ch. 6 - A wide-flange beam with an unbalanced cross...Ch. 6 - .20 Determine the plastic moment Mpfor beam having...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A r o lukI f/frm f «m t ub e of ou t sid e d ia met er ^ and a copper core of diameter dxare bonded to form a composite beam, as shown in the figure, (a) Derive formulas for the allowable bending moment M that can be carried by the beam based upon an allowable stress <7Ti in the titanium and an allowable stress (u in the copper (Assume that the moduli of elasticity for the titanium and copper are Er- and £Cu, respectively.) (b) If d1= 40 mm, d{= 36 mm, ETl= 120 GPa, ECu= 110 GPa, o-Ti = 840 MPa, and ctqj = 700 MPa, what is the maximum bending moment Ml (c) What new value of copper diameter dtwill result in a balanced design? (i.e., a balanced design is that in which titanium and copper reach allow- able stress values at the same time).arrow_forwardA copper wire having a diameter ofd = 4 mm is bent into a circle and held with the ends just touching (see figure), If the maximum permissible strain in the copper is = 0.0024, what is the shortest length L of wire that can be used? If L = 5.5 m, what is the maximum acceptable diameter of the wire if the maximum normal strain must remain below yield? Assume E = 120 GPa and(7K= 300 MPa.arrow_forwardSegments A B and BCD of beam A BCD are pin connected at x = 4 m. The beam is supported by a sliding support at A and roller supports at C and D (see figure). A triangularly distributed load with peak intensity of SO N/m acts on EC. A concentrated moment is applied at joint D. (a) Find reactions at supports A, C, and D. (b) Find internal stress resultants N, Y, and Mat x = 5m. (c) Repeat parts (a) and (b) for die case of the roller support at C replaced by a linear spring of stiffness kr™ 200 kN/m (see figure).arrow_forward
- The cross section of a composite beam made of aluminum and steel is shown in the figure. The moduli of elasticity are TA= 75 GPa and Es= 200 GPa. Under the action of a bending moment that produces a maximum stress of 50 M Pa in the aluminum, what is the maximum stress xs in the steel? If the height of the beam remains at 120 mm and allowable stresses in steel and aluminum are defined as 94 M Pa and 40 M Pa, respectively, what heights h and h. arc required for aluminum and steel, respectively, so that both steel and aluminum reach their allowable stress values under the maximum moment?arrow_forwardA cantilever beam(Z, = 6 ft) with a rectangular cross section (/> = 3.5 in., h = 12 in.) supports an upward load P = 35 kips at its free end. (a) Find the state of stress ((7T, o^., and r in ksi) on a plane-stress element at L/2 that is i/ = 8 in. up from the bottom of the beam. Find the principal normal stresses and maximum shear stress. Show these stresses on sketches of properly oriented elements. (b) Repeat part (a) if an axial compressive centroidal load N = 40 kips is added at Barrow_forwardA simple beam of span length 3.2 m carries a uniform load of intensity 48 kN/m, The cross section of the beam is a hollow box with wood flanges and steel side plates, as shown in the figure. The wood flanges are 75 mm x 100 mm in cross section, and the steel plates are 300 mm deep. What is the required thickness t of the steel plates if the allowable stresses are 120 M Pa for the steel and 6,5 M Pa for the wood? (Assume that the moduli of elasticity for the steel and wood are 210 GPa and 10 GPa, respectively, and disregard the weight of the beam.)arrow_forward
- A reinforced concrete beam (see figure) is acted on by a positive bending moment of M = 160 kN · m. Steel reinforcement consists of 4 bars of 28 mm diameter. The modulus of elasticity for the concrete is Ec= 25 GPa while that of the steel is Es= 200 GPa. Find the maximum stresses in steel and concrete. If allowable stresses for concrete and steel are T2= 9.2 MPa and t1= 135 MPa, respectively, what is the maximum permissible positive bending moment? What is the required area of steel reinforcement, A$ if a balanced condition must be achieved? What is the allowable positive bending moment? (Recall that in a balanced design, both steel and concrete reach allowable stress values simultaneously under the design moment.)arrow_forwardA simple beam that is 18 ft long supports a uniform load of intensity q. The beam is constructed of two C8 x 11.5 sections (channel sections or C-shapes) on either side of a 4 × 8 (actual dimensions) wood beam (see the cross section shown in the figure part a). The modulus of elasticity of the steel (E; = 30,000 ksi) is 20 times that of the wood (Ew). (a) If the allowable stresses in the steel and wood are 12,000 psi and 900 psi, respectively, what is the allowable load qmax Note: Disregard the weight of the beam, and see Table F-3(a) of Appendix F for the dimensions and properties of the C-shape beam. (b) If the beam is rotated 90° to bend about its v axis (see figure part b) and uniform load q = 250 lb/ft is applied, find the maximum stresses trs and crw in the steel and wood, respectively Include the weight of the beam. (Assume weight densities of 35 lb/ft3 and 490 lb/ft3 for the wood and steel, respectively.)arrow_forwardThe length of the end segments of the bar (see figure) is 20 in. and the length of the prismatic middle segment is 50 in. Also, the diameters at cross sections A. B, C, and D are 0.5, 1.0, 1.0, and 0.5 in., respectively, and the modulus of elasticity is 18 ,000 ksi. (a) Calculate the elongation of a copper bar of solid circular cross section with tapered ends when it is stretched by axial loads of magnitude 3.0 kips (see figure). (b) If the total elongation of the bar cannot exceed 0.025 in., what are the required diameters at B and C? Assume that diameters at A and D remain at 0.5 in.arrow_forward
- A vertical pole of solid, circular cross section is twisted by horizontal forces P = 1100 lb acting at the ends of a rigid horizontal arm AB (see figure part a). The distance from the outside of the pole to the line of action of each force is c = 5.0 in. (see figure part b) and the pole height is L = 14in. (a) If the allowable shear stress in the pole is 4500 psi, what is the minimum required diameter dminof the pole? Find the torsional stiffness of the pole (kip-in./rad). Assume that G = 10,800 ksi. If two translational springs, each with stiffness k = 33 kips/in., are added at 2(75 from A and B (see figure part c), repeat part (a) to find dmin. Hint: Consider the pole and pair of springs as "springs in parallel."arrow_forwardA wood beam with cross-sectional dimensions 200 mm x 300 mm is reinforced on its sides by steel plates 12 mm thick (see figure). The moduli of elasticity for the steel and wood are E±= 190 GPa and Ew= 11 GPa, respectively. Also, the corresponding allowable stresses are eS= 110 MPa and ew = 7.5 MPa, (a) Calculate the maximum permissible bending moment Mmaxwhen the beam is bent about the- axis. Repeat part (a) if the beam is now bent about its y axis. Find the required thickness of the steel plates on the beam bent about the y axis so that Mmaxis the same for both beam orientations.arrow_forwardA retaining wall 6 ft high is constructed of horizontal wood planks 2.5 in. thick (actual dimension) that are supported by vertical wood piles of a 12 in, diameter (actual dimension), as shown in the figure. The lateral earth pressure is pt=125 lb/ft2 at the top of the wall and p2= 425 lb/ft2 at the bottom. Assuming that the allowable stress in the wood is 1175 psi, calculate the maximum permissible spacing s of the piles. Find the required diameter of the wood piles so that piles and planks (f = 2.5 in.) reach the allowable stress at the same time. Hint: Observe that the spacing of the piles may be governed by the load-carrying capacity of either the planks or the piles. Consider the piles to act as cantilever beams subjected to a trapezoidal distribution of load, and consider the planks to act as simple beams between the piles. To be on the safe side, assume that the pressure on the bottom plank is uniform and equal to the maximum pressure.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials Lecture: Beam Design; Author: UWMC Engineering;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-wVs5pvQPm4;License: Standard Youtube License