
(a)
Interpretation:
The major product for reaction between
Concept introduction:
Nucleophile: Nucleophiles are electron rich compounds which donates electrons to electrophilic compounds which results in bond formation.
Electrophile: Electrophiles are electron deficient compounds which accepts electrons from nucleophiles that results in bond formation.
Electrophilic addition: It is a type of addition reaction in which the pi bond present in the molecule breaks as the electrophile approaches and results in the formation of product with sigma bond.
Oxidation Reaction: It involves loss of electrons, addition of oxygen atoms or removal of hydrogen atoms.
Reduction Reaction: It is just opposite of oxidation reaction which involves removal of oxygen atoms or addition of hydrogen atoms and addition of electrons.
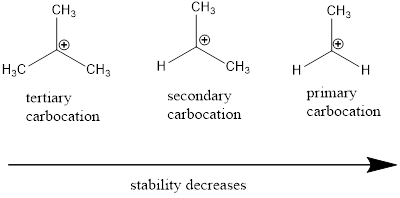
Carbocation: it is carbon ion that bears a positive charge on it.
Carbocation stability order:
(b)
Interpretation:
The major product for reaction between
Concept introduction:
Nucleophile: Nucleophiles are electron rich compounds which donates electrons to electrophilic compounds which results in bond formation.
Electrophile: Electrophiles are electron deficient compounds which accepts electrons from nucleophiles that results in bond formation.
Electrophilic addition: It is a type of addition reaction in which the pi bond present in the molecule breaks as the electrophile approaches and results in the formation of product with sigma bond.
Oxidation Reaction: It involves loss of electrons, addition of oxygen atoms or removal of hydrogen atoms.
Reduction Reaction: It is just opposite of oxidation reaction which involves removal of oxygen atoms or addition of hydrogen atoms and addition of electrons.
Carbocation: it is carbon ion that bears a positive charge on it.
Carbocation stability order:

(c)
Interpretation:
The major product for reaction between
Concept introduction:
Nucleophile: Nucleophiles are electron rich compounds which donates electrons to electrophilic compounds which results in bond formation.
Electrophile: Electrophiles are electron deficient compounds which accepts electrons from nucleophiles that results in bond formation.
Electrophilic addition: It is a type of addition reaction in which the pi bond present in the molecule breaks as the electrophile approaches and results in the formation of product with sigma bond.
Addition of halogen to an
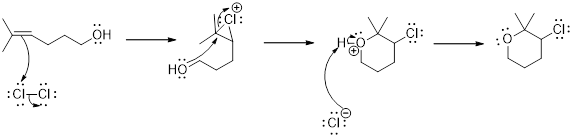
(d)
Interpretation:
The major product for reaction between
Concept introduction:
Nucleophile: Nucleophiles are electron rich compounds which donates electrons to electrophilic compounds which results in bond formation.
Electrophile: Electrophiles are electron deficient compounds which accepts electrons from nucleophiles that results in bond formation.
Electrophilic addition: It is a type of addition reaction in which the pi bond present in the molecule breaks as the electrophile approaches and results in the formation of product with sigma bond.
Oxidation Reaction: It involves loss of electrons, addition of oxygen atoms or removal of hydrogen atoms.
Acid Catalyzed Hydration Reaction: The reaction involves breaking of phi bonds between carbon-carbon multiple bonds and addition of alcohol to more substituted position of carbon in the molecule.
First step is the acid donates proton to the alkene which leads to the formation of more stable carbo cation.
Then, the water is added to the given alkene through acid catalyzed reaction where the water gets added to the carbo cation finally, the removal of one proton from oxonium ion (oxygen with one positive charge) using water results in the formation of product.
Carbocation: it is carbon ion that bears a positive charge on it.
Carbocation stability order:

Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 6 Solutions
Pearson eText for Essential Organic Chemistry -- Instant Access (Pearson+)
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

