
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
For the given set of species the available
Concept introduction:
Nucleophile: Nucleophiles are electron rich compounds which donates electrons to electrophilic compounds which results in bond formation.
Nucleophilic nature depends on the negative charge present in the molecule, the solvent in which it present and the electronegativity of the atom.
Electrophile: Electrophiles are electron deficient compounds which accepts electrons from nucleophiles that results in bond formation.
Leaving group: it is a fragment that leaves substrate with a pair of electrons via heterolytic bond cleavage.
Cation: The positively charged chemical species is referred as cation.
(b)
Interpretation:
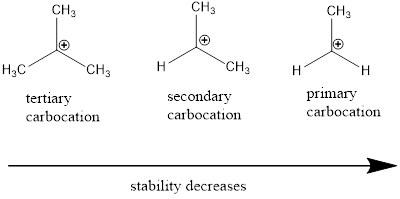
From the given carbocation the most stable one has to be identified.
Concept introduction:
Nucleophile: Nucleophiles are electron rich compounds which donates electrons to electrophilic compounds which results in bond formation.
Nucleophilic nature depends on the negative charge present in the molecule, the solvent in which it present and the electronegativity of the atom.
Electrophile: Electrophiles are electron deficient compounds which accepts electrons from nucleophiles that results in bond formation.
Cation: The positively charged chemical species is referred as cation.
Carbocation stability order:
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 6 Solutions
Pearson eText for Essential Organic Chemistry -- Instant Access (Pearson+)
- Assign all the protonsarrow_forwardAssign all the carbonsarrow_forward9 7 8 C 9 8 200 190 B 5 A -197.72 9 8 7 15 4 3 0: ང་ 200 190 180 147.52 134.98 170 160 150 140 130 120 110 100 90 90 OH 10 4 3 1 2 -143.04 140. 180 170 160 150 140 130 120 110 100 90 CI 3 5 1 2 141.89 140.07 200 190 180 170 160 150 140 130 120 110 100 ៖- 90 129. 126.25 80 70 60 -60 50 40 10 125.19 -129.21 80 70 3.0 20 20 -8 60 50 10 ppm -20 40 128.31 80 80 70 60 50 40 40 -70.27 3.0 20 10 ppm 00˚0-- 77.17 30 20 20 -45.36 10 ppm -0.00 26.48 22.32 ―30.10 ―-0.00arrow_forward
- Assign all the carbonsarrow_forwardC 5 4 3 CI 2 the Righ B A 5 4 3 The Lich. OH 10 4 5 3 1 LOOP- -147.52 T 77.17 -45.36 200 190 180 170 160 150 140 130 120 110 100 90 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 ppm B -126.25 77.03 200 190 180 170 160 150 140 130 120 110 100 90 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 ppm 200 190 180 170 160 150 140 130 120 110 100 90 80 TO LL <-50.00 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 ppm 45.06 30.18 -26.45 22.36 --0.00 45.07 7.5 1.93 2.05 -30.24 -22.36 C A 7 8 5 ° 4 3 7.5 7.0 6.5 6.0 5.5 5.0 4.5 4.0 3.5 3.0 2.5 2.0 1.5 1.0 ppm 9 8 5 4 3 ཡི་ OH 10 2 7.5 7.0 6.5 6.0 5.5 5.0 4.5 4.0 3.5 3.0 2.5 2.0 1.5 5 4 3 2 that th 7 I 7.0 6.5 6.0 5.5 5.0 4.5 4.0 3.5 3.0 2.5 2.0 1.5 115 2.21 4.00 1.0 ppm 6.96 2.76 5.01 1.0 ppm 6.30 1.00arrow_forwardCurved arrows were used to generate the significant resonance structure and labeled the most significant contribute. What are the errors in these resonance mechanisms. Draw out the correct resonance mechanisms with an brief explanation.arrow_forward
- What are the: нсе * Moles of Hice while given: a) 10.0 ml 2.7M ? 6) 10.ome 12M ?arrow_forwardYou are asked to use curved arrows to generate the significant resonance structures for the following series of compounds and to label the most significant contributor. Identify the errors that would occur if you do not expand the Lewis structures or double-check the mechanisms. Also provide the correct answers.arrow_forwardhow to get limiting reactant and % yield based off this data Compound Mass 6) Volume(mL Ben zaphone-5008 ne Acetic Acid 1. Sam L 2-propanot 8.00 Benzopin- a col 030445 Benzopin a Colone 0.06743 Results Compound Melting Point (°c) Benzopin acol 172°c - 175.8 °c Benzoping to lone 1797-180.9arrow_forward
- Assign ALL signals for the proton and carbon NMR spectra on the following pages.arrow_forward7.5 1.93 2.05 C B A 4 3 5 The Joh. 9 7 8 1 2 7.5 7.0 6.5 6.0 5.5 5.0 4.5 4.0 3.5 3.0 2.5 2.0 1.5 1.0 ppm 9 7 8 0.86 OH 10 4 3 5 1 2 7.5 7.0 6.5 6.0 5.5 5.0 4.5 4.0 3.5 3.0 2.5 2.0 1.5 1.0 ppm 9 7 8 CI 4 3 5 1 2 7.0 6.5 6.0 5.5 5.0 4.5 4.0 3.5 3.0 2.5 2.0 2.21 4.00 1.5 2.00 2.07 1.0 ppm 2.76arrow_forwardAssign the functional group bands on the IR spectra.arrow_forward
