
(a)
Interpretation:
The major product of the given reaction should be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Addition of halides to
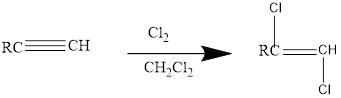
If excess halides are present, a second addition reaction also occurs.
(b)
Interpretation:
The major product of the given reaction should be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Addition of halides to alkynes: Halogens like chlorine and bromine adds to the alkyne compounds. The general form of the reaction is given below.
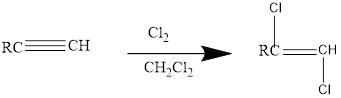
If excess halides are present, a second addition reaction also occurs.
(c)
Interpretation:
The major product of the given reaction should be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Addition of halides to alkynes: Halogens like chlorine and bromine adds to the alkyne compounds. The general form of the reaction is given below.
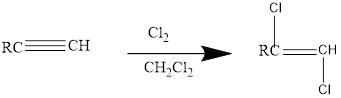
If excess halides are present, a second addition reaction also occurs.
(d)
Interpretation:
The major product of the given reaction should be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Addition of halides to alkynes: Halogens like chlorine and bromine add to the alkyne compounds. The general form of the reaction is given below.
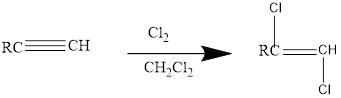
If excess halides are present, a second addition reaction also occurs.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 6 Solutions
Pearson eText for Essential Organic Chemistry -- Instant Access (Pearson+)
- An organic chemistry Teaching Assistant (TA) suggested in your last discussion section that there is only one major organic product of the following reaction and that this reaction builds a ring. If the TA is right, draw the product in the drawing area below. If the TA is wrong, just check the box below the drawing area. NaOH ?arrow_forwardA student suggests that the molecule on the right can be made from a single molecule that doesn't have a ring. If the student is correct, draw the starting material below, otherwise, check the box under the drawing area. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. : ☐ + NaOH टेarrow_forwardRate = k [I]1.7303[S2O82-]0.8502, Based on your rate, write down a mechanism consistent with your results and indicate which step is the rate determining step.arrow_forward
- 36. Give the major product(s) of each of the following reactions. Aqueous work-up steps (when necessary) have been omitted. a. CH3CH=CHCH3 b. CH3CH2CH2CCH3 H,PO₂, H₂O, A (Hint: See Section 2-2.) 1. LIAIH. (CH,CH,),O 2. H', H₂O H NaBH, CH,CH₂OH d. Br LIAIH. (CH,CH,)₂O f. CH3 NaBH, CH,CH,OH (CH3)2CH H NaBH, CH,CH₂OH Harrow_forwardPredict the major products of this reaction: + H excess NaOH Δ ? Note that the second reactant is used in excess, that is, there is much more of the second reactant than the first. If there won't be any products, just check the box under the drawing area instead.arrow_forwardAn organic chemistry Teaching Assistant (TA) suggested in your last discussion section that there is only one major organic product of the following reaction and that this reaction builds a ring. If the TA is right, draw the product in the drawing area below. If the TA is wrong, just check the box below the drawing area. 1. NaOMe CH3O N. OCH3 ? 2. H3O+arrow_forward
- Complete the reaction in the drawing area below by adding the major products to the right-hand side. If there won't be any products, because nothing will happen under these reaction conditions, check the box under the drawing area instead. Note: if the products contain one or more pairs of enantiomers, don't worry about drawing each enantiomer with dash and wedge bonds. Just draw one molecule to represent each pair of enantiomers, using line bonds at the chiral center. + More... ☐ ☐ : ☐ + G 1. NaOMe Click and drag to start drawing a structure. 2. H +arrow_forward6. Ammonia reacts with nitrogen monoxide and oxygen to form nitrogen and water vapor. If the rate of consumption of NO is 4.5 mollitermin) (a) Find the rate of reaction (b) Find the rate of formations of N; and HO (c) Find the rate of consumption of NH, and O 4NH: 4NO 0:4: +60arrow_forward34. Give the expected major product of each of the following reactions. Conc. HI a. CH3CH2CH2OH b. (CH3)2CHCH2CH2OH Conc. HBr H Conc. HI C. OH Conc.HCI d. (CH3CH2)3COHarrow_forward
- 42. Which of the following halogenated compounds can be used successfully to prepare a Grignard reagent for alcohol synthesis by subsequent reaction with an aldehyde or ketone? Which ones cannot and why? H3C CH3 a. Br H OH b. Cl C. I H H d. Cl e. H OCH3 Br Harrow_forwardFor each reaction below, decide if the first stable organic product that forms in solution will create a new CC bond, and check the appropriate box. Next, for each reaction to which you answered "Yes" to in the table, draw this product in the drawing area below. Note for advanced students: for this problem, don't worry if you think this product will continue to react under the current conditions - just focus on the first stable product you expect to form in solution. ? Will the first MgBr product that forms in this reaction create a new CC bond? olo ? OH جمله O Yes Ⓒ No MgCl ? Will the first product that forms in this reaction create a new CC bond? Click and drag to start drawing a structure. Yes No X ☐ : ☐ टे PHarrow_forwardAssign all the protonsarrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
