
Concept explainers
Draw a Lewis structure for each of the following species:
- a. H2CO3
- b. CO32−
- c. CH2O
- d. CO2
(a)
Interpretation:
Lewis structure of
Concept Introduction:
A Lewis dot structure for an atom consists of a symbol for the element and one dot for each valence electron.
Steps in drawing a Lewis dot structure,
- Total number of valence electron has to be known.
- Atoms has to be distributed by the knowing the valency of each atom.
- Form bonds and fill the octet with lone pair of electrons.
- Formal charge if present has to be assigned.
Explanation of Solution
Given compound is
Number of valence electron of each atoms is identified and drawn as below,
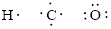
Hydrogen can form only one bond, carbon can form four bonds and oxygen has six valence electrons.
Atoms have to be distributed by putting hydrogen on outside the molecule.
Here, there are two oxygen atoms, so avoiding the oxygen-oxygen single bonds.
The Lewis structure can be,
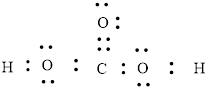 or
or 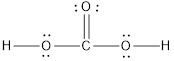
Each atom has to achieve an octet and the existing electron has to be shared.
(b)
Interpretation:
Lewis structure of
Concept Introduction:
A Lewis dot structure for an atom consists of a symbol for the element and one dot for each valence electron.
Steps in drawing a Lewis dot structure,
- Total number of valence electron has to be known.
- Atoms has to be distributed by the knowing the valency of each atom.
- Form bonds and fill the octet with lone pair of electrons.
- Formal charge if present has to be assigned.
Explanation of Solution
Given compound is
Number of valence electron of each atoms is identified and drawn as below,
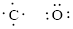
Carbon can form four bonds and oxygen has six valence electrons.
Atoms have to be distributed by putting hydrogen on outside the molecule.
Here, there are two oxygen atoms, so avoiding the oxygen-oxygen single bonds.
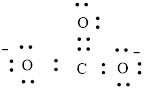 or
or 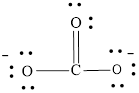
Each atom has to achieve an octet and the existing electron has to be shared.
(c)
Interpretation:
Lewis structure of
Concept Introduction:
A Lewis dot structure for an atom consists of a symbol for the element and one dot for each valence electron.
Steps in drawing a Lewis dot structure,
- Total number of valence electron has to be known.
- Atoms has to be distributed by the knowing the valency of each atom.
- Form bonds and fill the octet with lone pair of electrons.
- Formal charge if present has to be assigned.
Explanation of Solution
Given compound is
Number of valence electron of each atoms is identified and drawn as below,
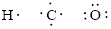
Hydrogen can form only one bond, carbon can form four bonds and oxygen has six valence electrons.
Atoms have to be distributed by putting hydrogen on outside the molecule.
Here, there are two oxygen atoms, so avoiding the oxygen-oxygen single bonds.
The Lewis structure can be,
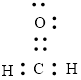 or
or 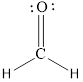
Each atom has to achieve an octet and the existing electron has to be shared.
(d)
Interpretation:
Lewis structure of
Concept Introduction:
A Lewis dot structure for an atom consists of a symbol for the element and one dot for each valence electron.
Steps in drawing a Lewis dot structure,
- Total number of valence electron has to be known.
- Atoms has to be distributed by the knowing the valency of each atom.
- Form bonds and fill the octet with lone pair of electrons.
- Formal charge if present has to be assigned.
Explanation of Solution
Given compound is
Number of valence electron of each atoms is identified and drawn as below,

Carbon can form four bonds and oxygen has six valence electrons.
Atoms have to be distributed by putting hydrogen on outside the molecule.
Here, there are two oxygen atoms, so avoiding the oxygen-oxygen single bonds.
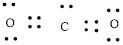 or
or 
Each atom has to achieve an octet and the existing electron has to be shared.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 1 Solutions
Pearson eText for Essential Organic Chemistry -- Instant Access (Pearson+)
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Applications and Investigations in Earth Science (9th Edition)
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
Biology: Life on Earth (11th Edition)
Laboratory Experiments in Microbiology (12th Edition) (What's New in Microbiology)
Organic Chemistry
- b. CH3 H3C 'N' H3C CH3 CN Ph 1. OH N 2. H2O2, Pyridinearrow_forwardFor each of the Followin, moleaks draw all OF The Resonance contributing stuluctures and compare these three molecules in terms of Resonance stabilization 1-C-1 a. b. H A-C+ О 112-1 C. F-C-F Farrow_forwarda. Explain Why electron withdrawing groupe tend to be meta-Directors. Your answer Should lyclude all apropriate. Resonance contributing Structures 6. Explain why -ll is an ortho -pura drccton evon though chlorine has a very High Electronegativityarrow_forward
- Question 1. Please predict the products for each of the following reactions. Clearly show the regiochemistry (Markovnikov vs anti-Markovnikov) and stereochemistry (syn- vs anti- or both). If a mixture of enantiomers is formed, please draw all the enantiomers.arrow_forwardElectrochemistry. Briefly describe the Donnan potential.arrow_forwardIndicate what the Luther equation is used for?arrow_forward
- Indicate one aspect that benefits and another that makes it difficult to use the hydroquinone electrode to measure pH.arrow_forwardAt an electrified interface according to the Gouy-Chapman model, what types of interactions do NOT occur between the ions and the solvent according to this theory?arrow_forwardPlease predict the products for each of the following reactions. Clearly show the regiochemistry (Markovnikov vs anti-Markovnikov) and stereochemistry (syn- vs anti- or both). If a mixture of enantiomers is formed, please draw all the enantiomers. Hint: In this case you must choose the best answer to demonstrate the stereochemistry of H2 addition. 1.03 2. (CH3)2S BIZ CH₂OH 2. DMS KMnO4, NaOH ΖΗ Pd or Pt (catalyst) HBr 20 1 HBr ROOR (peroxide) HO H-SO HC 12 11 10 BH, THE 2. H2O2, NaOH Brz cold HI 19 18 17 16 MCPBA 15 14 13 A Br H₂O BH3⚫THF Brz EtOH Pd or Ni (catalyst) D₂ (deuterium) 1. Os04 2. H2O2 CH3CO3H (peroxyacid) 1. MCPBA 2. H₂O* H B + H H H "H C H H Darrow_forward
 Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax
Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax
