
Concept explainers
a.
To calculate the coefficients
a.
Answer to Problem 66E
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Quadratic approximation to
With the properties
Calculation :
Write the function and get the values at
Therefore,
b.
To find the quadratic approximation to
b.
Answer to Problem 66E
The quadratic approximation is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The given statement is that find the quadratic approximation to
Calculation :
Substitute the values in
Therefore,
The quadratic approximation is
c.
To graph:
c.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
ZOOM IN on the two graphs at point
Graph:
The graph of
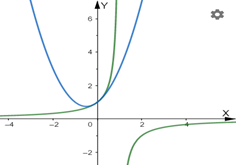
The image of ZOOM IN at point
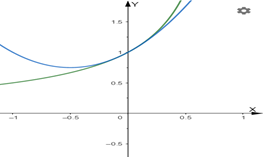
Interpretation:
At the point
d.
To find the quadratic approximation to
d.
Answer to Problem 66E
The quadratic approximation is
The function and its approximation behave similar around
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The given statement is that find the quadratic approximation to
Calculation :
Substitute the values in quadratic approximation equation
Therefore,
The quadratic approximation is
The graph of g and its quadratic approximation together.
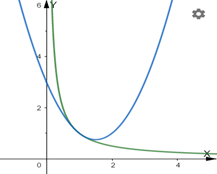
The function and its approximation behave similar around
e.
To find the quadratic approximation to
e.
Answer to Problem 66E
The quadratic approximation is
The function and its approximation behave similar around
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The given statement is that find the quadratic approximation to
Calculation :
Substitute the values in quadratic approximation equation
Therefore,
The quadratic approximation is
The graph of h and its quadratic approximation together.
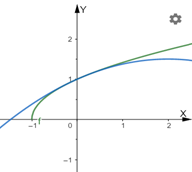
The function and its approximation behave similar around
f.
To write the linearization of f , g , and h at the respective points.
f.
Answer to Problem 66E
Linearization of f , g , and h are
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Functions are given in parts (b), (d), and (e)
Formula used:
Linearization.
Calculation :
For f
Linearization.
For g
Linearization.
For h
Linearization.
Therefore,
Linearization of f , g , and h are
Chapter 5 Solutions
Calculus 2012 Student Edition (by Finney/Demana/Waits/Kennedy)
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th Edition)
A Problem Solving Approach To Mathematics For Elementary School Teachers (13th Edition)
Elementary Statistics
University Calculus: Early Transcendentals (4th Edition)
College Algebra (7th Edition)
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (2nd Edition)
 Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON
Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
 Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning





