
Concept explainers
a.
To find: the absolute extrema of f and where they occur.
a.
Answer to Problem 52E
The absolute maximum is
Explanation of Solution
Given information: f is an even function, continuous
| x | 0 | 1 | 2 |
| f | 2 | 0 | −1 |
| f’ | Does not exist | 0 | Does not exist |
| f’’ | Does not exist | 0 | Does not exist |
| x | 0 | 1 | 2 |
| f | + | − | − |
| f’ | − | − | + |
| f’’ | + | − | − |
f is an even function; therefore, the table can be extended for the values of x between −3 and 0. Since it is even the portion on the left will be the mirror image of the portion on the right, that is, the y -coordinates remain same, the slopes have opposite sign and the concavity remains same.
| x | −2 | −1 | 0 | 1 | 2 |
| f | −1 | 0 | 2 | 0 | −1 |
| f’ | Does not exist | 0 | Does not exist | 0 | Does not exist |
| f’’ | Does not exist | 0 | Does not exist | 0 | Does not exist |
| x | −3 | −2 | −1 | 0 | 1 | 2 |
| f | − | − | + | + | − | − |
| f’ | − | + | + | − | − | + |
| f’’ | − | − | + | + | − | − |
Since, f < 0 for −3 < x < −2 and 2
Since, f < 0 for −3
Hence, the absolute maximum is
b.
To find: the points of inflection.
b.
Answer to Problem 52E
The points of inflection are
Explanation of Solution
Given information: f is an even function, continuous
| X | 0 | 1 | 2 |
| F | 2 | 0 | −1 |
| f’ | Does not exist | 0 | Does not exist |
| f’’ | Does not exist | 0 | Does not exist |
| X | 0 | 1 | 2 |
| F | + | − | − |
| f’ | − | − | + |
| f’’ | + | − | − |
Hence, the points of inflection are
c.
To graph: the function f with the provided information.
c.
Explanation of Solution
Given information: f is an even function, continuous
| X | 0 | 1 | 2 |
| F | 2 | 0 | −1 |
| f’ | Does not exist | 0 | Does not exist |
| f’’ | Does not exist | 0 | Does not exist |
| X | 0 | 1 | 2 |
| F | + | − | − |
| f’ | − | − | + |
| f’’ | + | − | − |
Graph:
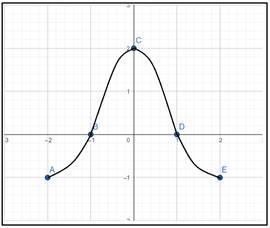
Interpretation:
Hence, this is the probable graph for function f with the provided information.
Chapter 5 Solutions
Calculus 2012 Student Edition (by Finney/Demana/Waits/Kennedy)
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
University Calculus: Early Transcendentals (4th Edition)
Calculus for Business, Economics, Life Sciences, and Social Sciences (14th Edition)
Intro Stats, Books a la Carte Edition (5th Edition)
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th Edition)
Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)
A First Course in Probability (10th Edition)
- Can you solve this 6 questions numerical method and teach me how to solve it and what we use.arrow_forward9Wire of length 20m is divided into two pieces and the pieces are bent into a square and a circle. How should this be done in order to minimize the sum of their areas? Round your answer to the nearest hundredth.arrow_forwardUse Laplace transform to solve the initial value problem y' + y = tsin(t), y(0) = 0arrow_forward
- The function g is defined by g(x) = sec² x + tan x. What are all solutions to g(x) = 1 on the interval 0 ≤ x ≤ 2π ? A x = = 0, x == = 3, x = π, x = 7 4 , 4 and x 2π only = B x = 4' 1, x = 1, x = 57 and x = 3 only C x = πk and x = - +πk D , where is any integer П x = +πk and П x = +πk, where k is any integerarrow_forwardVector v = PQ has initial point P (2, 14) and terminal point Q (7, 3). Vector v = RS has initial point R (29, 8) and terminal point S (12, 17). Part A: Write u and v in linear form. Show all necessary work. Part B: Write u and v in trigonometric form. Show all necessary work. Part C: Find 7u − 4v. Show all necessary calculations.arrow_forwardAn object is suspended by two cables attached at a single point. The force applied on one cable has a magnitude of 125 pounds and acts at an angle of 37°. The force on the other cable is 75 pounds at an angle of 150°.Part A: Write each vector in component form. Show all necessary work.Part B: Find the dot product of the vectors. Show all necessary calculations Part C: Use the dot product to find the angle between the cables. Round the answer to the nearest degree. Show all necessary calculations.arrow_forward
- An airplane flies at 500 mph with a direction of 135° relative to the air. The plane experiences a wind that blows 60 mph with a direction of 60°.Part A: Write each of the vectors in linear form. Show all necessary calculations.Part B: Find the sum of the vectors. Show all necessary calculations. Part C: Find the true speed and direction of the airplane. Round the speed to the thousandths place and the direction to the nearest degree. Show all necessary calculations.arrow_forwardUse sigma notation to write the sum. Σ EM i=1 - n 2 4n + n narrow_forwardVectors t = 3i + 7j, u = 2i − 5j, and v = −21i + 9j are given.Part A: Find the angle between vectors t and u. Show all necessary calculations. Part B: Choose a value for c, such that c > 1. Find w = cv. Show all necessary work.Part C: Use the dot product to determine if t and w are parallel, orthogonal, or neither. Justify your answer.arrow_forward
- A small company of science writers found that its rate of profit (in thousands of dollars) after t years of operation is given by P'(t) = (5t + 15) (t² + 6t+9) ³. (a) Find the total profit in the first three years. (b) Find the profit in the sixth year of operation. (c) What is happening to the annual profit over the long run? (a) The total profit in the first three years is $ (Round to the nearest dollar as needed.)arrow_forwardFind the area between the curves. x= -2, x = 7, y=2x² +3, y=0 Set up the integral (or integrals) needed to compute this area. Use the smallest possible number of integrals. Select the correct choice below and fill in the answer boxes to complete your choice. A. 7 [[2x² +3] dx -2 B. [[ ] dx+ -2 7 S [ ] dx The area between the curves is (Simplify your answer.)arrow_forwardThe rate at which a substance grows is given by R'(x) = 105e0.3x, where x is the time (in days). What is the total accumulated growth during the first 2.5 days? Set up the definite integral that determines the accumulated growth during the first 2.5 days. 2.5 Growth = (105e0.3x) dx 0 (Type exact answers in terms of e.) Evaluate the definite integral. Growth= (Do not round until the final answer. Then round to one decimal place as needed.)arrow_forward
 Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON
Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
 Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning





