
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
5th Edition
ISBN: 9781133104261
Author: Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 5.3, Problem 5.6QQ
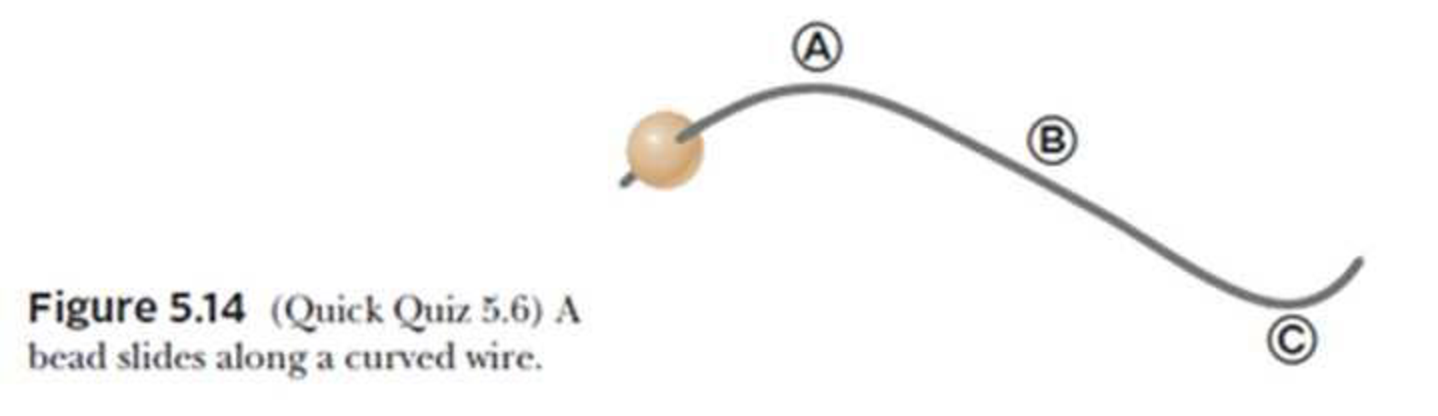
A bead slides freely along a curved wire lying on a horizontal surface at constant speed as shown by Figure 5.14. (a) Draw the vectors representing the force exerted by the wire on the bead at points Ⓐ, Ⓑ, and Ⓒ. (b) Suppose the bead in Figure 5.14 speeds up with constant tangential acceleration as it moves toward the right. Draw the vectors representing the force on the bead at points Ⓐ, Ⓑ, and Ⓒ.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
A spool rests on a horizontal, frictionless surface and you are looking at it from the top view (appears
as a circle).
In the following questions, the spool is pulled by tension forces that are applied at various locations,
directions, and radii.
To solve each problem, draw the spool as a circle on a piece of paper and then draw the given tension
vectors.
REMEMBER that the direction UPWARD points to the TOP of the page and DOWNWARD points to the
BOTTOM of the page.
re 1 The resulting TORQUE will be either OUT OF the page (CCW motion, POSITIVE torque) or INTO the
page (CW motion, NEGATIVE torque).
nen
A rope of tension 1T applies a force at radius 2R on the spool. It is located at 6 o'clock and pulls to
ence the right.
What is the resulting torque in terms of RT?
Remember to check whether the torque is positive (results in CCW motion) or negative (results in CW
motion).
RT
Submit Answer
Tries 0/3
A rope of tension 4T applies a force at radius 4R on the spool. It is located at 9 o'clock…
The "Giant Swing" at a county fair consists of a vertical central shaft with horizontal arms
attached at its upper end. Each arm supports a seat suspended from a cable 5.00 m long, and
the upper end of the cable is fastened to the arm at a point 3.00 m from the central shaft as
seen below.
а.
Find the time of one revolution of the swing if the cable supporting a seat makes an
angle of 30.0° with the vertical.
b. Does the angle depend on the weight of the passenger for a given rate of revolution?
3.00 m-
130.0°
02016 Pearson Ccation, irc.
5.00 m
The tension is growing!Context
At your summer job, your supervisor wants to test your physics skills. A new winch (a cable driven by a motor) is to be used to hoist loads up an inclined ramp. Your supervisor is worried about the packages arriving too quickly at the top of the ramp.
Constraints
The inclined ramp is made up of small cylinders that are free to rotate: there is no friction between the ramp and the load.The angle theta of the ramp from the horizontal is known.The winch cable exerts a known force.The cable is oriented at an angle a from the horizontal.The charge, initially immobile, has a known mass.The length of the ramp is known.
Schematization
Draw a diagram of the object that interests us. Draw your x and y axes. Draw and name each force experienced by the object that interests us.
Modelization
Build a model to calculate the final speed of the load as it arrives at the top of the ramp, given the known parameters. Then test your model with the following values:
Ramp…
Chapter 5 Solutions
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Ch. 5.1 - You press your physics textbook flat against a...Ch. 5.1 - A crate is located in the center of a flatbed...Ch. 5.1 - You are playing with your daughter in the snow....Ch. 5.2 - You are riding on a Ferris wheel (Fig. 5.8) that...Ch. 5.3 - Which of the following is impossible for a car...Ch. 5.3 - A bead slides freely along a curved wire lying on...Ch. 5.4 - Consider a sky surfer falling through air, as in...Ch. 5 - The driver of a speeding empty truck slams on the...Ch. 5 - The manager of a department store is pushing...Ch. 5 - An object of mass m moves with acceleration a down...
Ch. 5 - An office door is given a sharp push and swings...Ch. 5 - Prob. 5OQCh. 5 - A pendulum consists of a small object called a bob...Ch. 5 - A door in a hospital has a pneumatic closer that...Ch. 5 - The driver of a speeding truck slams on the brakes...Ch. 5 - A child is practicing for a BMX race. His speed...Ch. 5 - A large crate of mass m is placed on the flatbed...Ch. 5 - Before takeoff on an airplane, an inquisitive...Ch. 5 - Prob. 12OQCh. 5 - As a raindrop falls through the atmosphere, its...Ch. 5 - An object of mass m is sliding with speed vi at...Ch. 5 - A car is moving forward slowly and is speeding up....Ch. 5 - Prob. 2CQCh. 5 - Prob. 3CQCh. 5 - Prob. 4CQCh. 5 - Prob. 5CQCh. 5 - Prob. 6CQCh. 5 - Prob. 7CQCh. 5 - Prob. 8CQCh. 5 - Prob. 9CQCh. 5 - Prob. 10CQCh. 5 - It has been suggested that rotating cylinders...Ch. 5 - Prob. 12CQCh. 5 - Why does a pilot tend to black out when pulling...Ch. 5 - Prob. 1PCh. 5 - Prob. 2PCh. 5 - Prob. 3PCh. 5 - Prob. 4PCh. 5 - Prob. 5PCh. 5 - The person in Figure P5.6 weighs 170 lb. As seen...Ch. 5 - A 9.00-kg hanging object is connected by a light,...Ch. 5 - Prob. 8PCh. 5 - A 3.00-kg block starts from rest at the top of a...Ch. 5 - Prob. 10PCh. 5 - Prob. 11PCh. 5 - A block of mass 3.00 kg is pushed up against a...Ch. 5 - Two blocks connected by a rope of negligible mass...Ch. 5 - Three objects are connected on a table as shown in...Ch. 5 - Why is the following situation impossible? Your...Ch. 5 - Prob. 16PCh. 5 - A light string can support a stationary hanging...Ch. 5 - Why is the following situation impossible? The...Ch. 5 - A crate of eggs is located in the middle of the...Ch. 5 - Prob. 20PCh. 5 - Prob. 21PCh. 5 - A roller coaster at the Six Flags Great America...Ch. 5 - Prob. 23PCh. 5 - Prob. 24PCh. 5 - Prob. 25PCh. 5 - A pail of water is rotated in a vertical circle of...Ch. 5 - Prob. 27PCh. 5 - A child of mass m swings in a swing supported by...Ch. 5 - Prob. 29PCh. 5 - (a) Estimate the terminal speed of a wooden sphere...Ch. 5 - Prob. 31PCh. 5 - Prob. 32PCh. 5 - Prob. 33PCh. 5 - A 9.00-kg object starting from rest falls through...Ch. 5 - Prob. 35PCh. 5 - Prob. 36PCh. 5 - Prob. 37PCh. 5 - Prob. 38PCh. 5 - Prob. 39PCh. 5 - Prob. 40PCh. 5 - Prob. 41PCh. 5 - Prob. 42PCh. 5 - Consider the three connected objects shown in...Ch. 5 - A car rounds a banked curve as discussed in...Ch. 5 - Prob. 45PCh. 5 - An aluminum block of mass m1 = 2.00 kg and a...Ch. 5 - Figure P5.47 shows a photo of a swing ride at an...Ch. 5 - Why is the following situation impossible? A...Ch. 5 - A space station, in the form of a wheel 120 m in...Ch. 5 - A 5.00-kg block is placed on top of a 10.0-kg...Ch. 5 - In Example 6.5, we investigated the forces a child...Ch. 5 - Prob. 52PCh. 5 - Prob. 53PCh. 5 - Prob. 54PCh. 5 - Prob. 55PCh. 5 - Prob. 56PCh. 5 - Prob. 57PCh. 5 - Why is the following situation impossible? A book...Ch. 5 - A single bead can slide with negligible friction...Ch. 5 - An amusement park ride consists of a large...Ch. 5 - Prob. 61PCh. 5 - Prob. 62PCh. 5 - Prob. 63PCh. 5 - If a single constant force acts on an object that...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The slope of the 5.0 KN force F is specified as shown in the figure. Express F as a vector in terms of the unit vectors i and j. Assume a = 13, b = 6. Answer: F = ( F b i+ j) KNarrow_forwardYou are designing the section of a roller coaster ride shown in the figure. Previous sections of the ride give the train a speed of 11.9 m/s11.9 m/s at the top of the incline, which is ℎ=38.7 mh=38.7 m above the ground. As any good engineer would, you begin your design with safety in mind. Your local government's safety regulations state that the riders' centripetal acceleration should be no more than ?=1.77 gn=1.77 g at the top of the hump and no more than ?=5.69 gN=5.69 g at the bottom of the loop. For this initial phase of your design, you decide to ignore the effects of friction and air resistance. What is the minimum radius you can use for the semi-circular hump? What is the minimum radius you can use for the vertical loop?arrow_forwardProblem 10 : A cord connected at one end to a block which can slide on an inclined plane has its other end wrapped around a cylinder resting in a depression at the top of the plane as shown in (Figure 1). Part A Determine the speed of the block after it has traveled 1.30 m along the plane, starting from rest. Assume there is no friction. Express your answer using two significant figures. Part B Determine the speed of the block after it has traveled 1.30 m along the plane, starting from rest. Assume the coefficient of friction between all surfaces is μ = 0.0280. Since the block is much lighter than the cylinder, ignore tension in the string when calculating the normal force on the cylinder. Do not ignore tension in the string when calculating the net torque (including friction) on the cylinder.arrow_forward
- For the normal force in the drawing to have the same magnitude at all points on the vertical track, the stunt driver must adjust the speed to be different at different points. Suppose, for example, that the track has a radius of 2.23 m and that the driver goes past point 1 at the bottom with a speed of 24.0 m/s. What speed must she have at point 3, so that the normal force at the top has the same magnitude as it did at the bottom?arrow_forwardIn the figure below, a spider is resting after starting to spin its web. The gravitational force on the spider is 0.160 N on the junction of the three strands of silk. The junction is supported by different tension forces in the two strands above it so that the resultant force on the junction is zero. The two sloping strands are perpendicular, and we have chosen the x and y directions to be along them. The tension T, is 0.102 N. T (a) Find the tension T. (b) Find the angle the x axis makes with the horizontal. (c) Find the angle the y axis makes with the horizontal.arrow_forwardI am very confused about how to get the values. If they are computable using a calculator, please explain how to input them.An object set on top of a tripod is supported by the tripod. Assume that the tripod's legs meet at position D(0,7,0), where the object with weight W will be placed, and that the tripod's ends are located at points A(-2,0,-3), B(-3,0,-2), and C(2.5,0,-1). If the the maximum force a tripod leg can support is 500 N; find the answer.1. Solve for the magnitudes of forces AD, BD, and CD in terms of the weight W if the given configuration is in equilibrium.2. What is the maximum weight W that can be placed on the tripod with the given configuration?arrow_forward
- Consider the pendulum shown in the figure. The pendulum is released at point A, swings through its lowest point at point C, and reaches its turning point at point D. You may ignore the effects of air resistance. Answer the following questions: A В D C (a) Draw the free body diagram when the object is located at point B. (b) On your free-body diagram, draw a circle around the force components that contribute to the centripetal acceleration and draw a square around the force components that contribute to the tangential acceleration. (c) Draw the direction of the total acceleration vector when the object is located at point B.arrow_forwardTo determine Cartesian force components from the magnitude and determine the position and resultant vectors by summing Cartesian components. As shown, a 3.1-lb ball is suspended at point D inside a box with dimensions w=9.50 ft, d=6.70 ft, and h=4.10 ft. The ball is held in place by three cables anchored at points A, B, and C on the surface of the box. If point D is the origin of the Cartesian coordinate system, point A is located at (−4.60,−3.50,2.50) ft, point B is located at (2.10,−3.50,1.90) ft, and point C is located at (2.10,6.00,−1.60) ft. 1) The tension in cable DA has a magnitude of TDA=7.66 lb. Find the Cartesian components of tension TDA, which is directed from D to A. so TDA=? 2)If the tensions in cables DA and DB are TDA=7.66 lb and TDB=5.56 lb, respectively, what is the tension in cable DC? so TDC=?arrow_forwardTo get a toolbox up an inclined slope, a student installs a pulley system as in the picture shown. The student uses their body weight to apply a force. The student weighs 81.9kg, and the toolbox weighs 16.3kg. The angle of the slope is 31.2° above the horizontal. The coefficient of friction between the box and the slope is 0.227. Once the student gets the box moving, what will its acceleration be? Activate Windowsarrow_forward
- A box descends a ramp and lands on a surface. The box exits the side of the table as it meets the bottom of the tamp, becoming a horizontal projectile. It lands x metres away from the table. The same ramp may be rolled down by a solid sphere with the same coefficient of friction, mass, and height. Will the sphere land a long way away? fewer than a lot more At a similar size B. Have a paragraph-length description of the logic.arrow_forwardA small ball of mass 740.0 g is placed in a tube that is bent into a circular arc of radius R= 67.5 cm. The friction between the ball and the walls of the tube is negligible. The ball has an iron core. A magnet is used to raise the ball until it makes an angle of 5.00 degrees with the vertical, and then released from rest. What will the ball’s velocity and acceleration be at this time?arrow_forwardA 500 N F force is applied to the vertical rod, as shown in picture below. Write F as a function of the unit vectors i and j, and identify their vector and scalar components.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON
Conservative and Non Conservative Forces; Author: AK LECTURES;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=vFVCluvSrFc;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY