
Concept explainers
(a)
Draw free body diagram of each block.
(a)
Answer to Problem 53P
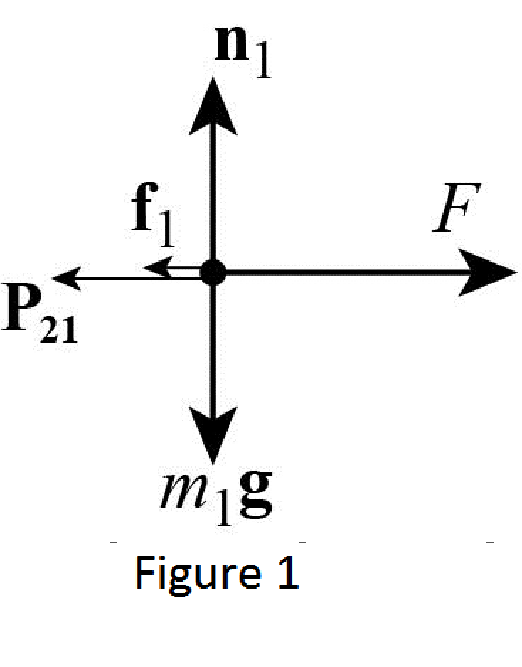
The free body diagram of mass
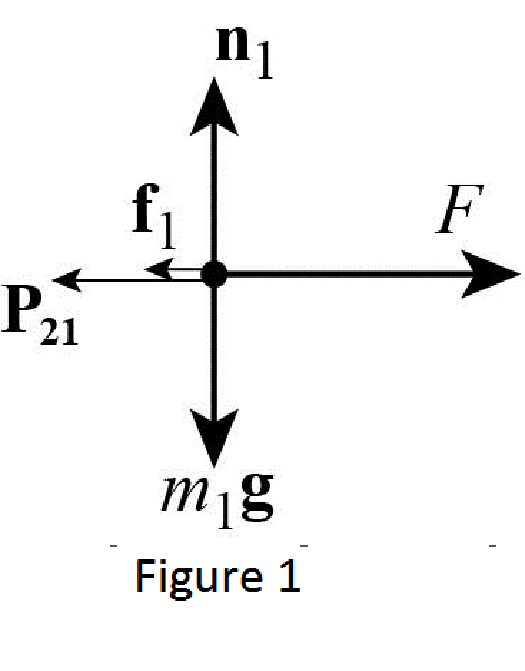
The free body diagram of mass
Explanation of Solution
The free body diagram is the graphical illustration used to visualize the movements and forces applied on a body.
Let
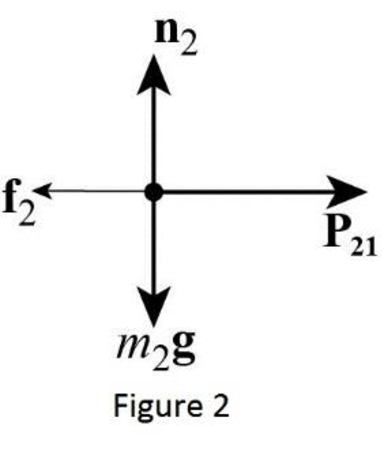
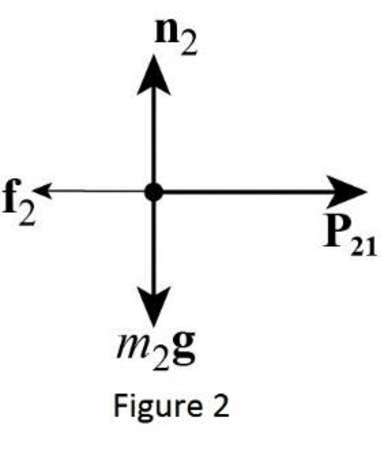
The free body diagram of mass
The free body diagram of mass
Conclusion:
Therefore, the free body diagram of mass
(b)
The net force on the system of two blocks.
(b)
Answer to Problem 53P
The net force on the system of two blocks is
Explanation of Solution
From the Figure 1, write the expression for net force action on the mass
Here,
From the Figure 2, write the expression for net force action on the mass
Here,
So the net force on the system is the sum of net force on the each block.
Since contact force acting on each mass is equal.
The net force on the system of block is equal to the magnitude of force
Conclusion:
Therefore, the net force on the system of two blocks is
(c)
The net force on the mass
(c)
Answer to Problem 53P
The net force on the mass
Explanation of Solution
From the Figure 1, write the expression for net force action on the mass
The net force on the mass
Conclusion:
Therefore, the net force on the mass
(d)
The net force acting on the
(d)
Answer to Problem 53P
The net force acting on the
Explanation of Solution
From the Figure 2, write the expression for net force action on the mass
The net force acting on the
Conclusion:
Therefore, the net force acting on the
(e)
Newton’s second law in the
(e)
Answer to Problem 53P
Newton’s second law in the
Explanation of Solution
The blocks are pushed to the right, the acceleration on each block is same and the block exerts equal and opposite forces on each other, so these forces have the same magnitude.
Write the expression for Newton’s second law in the
Here,
Write the expression for frictional force.
Here,
Use equation (III) and (IV) in (I).
Use equation (III) and (IV) in (II).
Conclusion:
Therefore, Newton’s second law in the
(f)
Acceleration of the blocks.
(f)
Answer to Problem 53P
Acceleration of the blocks is
Explanation of Solution
Add equation (V), and (VI), and solve for
Conclusion:
Therefore, the acceleration of the blocks is
(g)
The magnitude of contact force
(g)
Answer to Problem 53P
The magnitude of contact force
Explanation of Solution
Solve equation (IV) for
Use equation (VII) in (VIII).
Simplify the equation (IX).
Conclusion:
Therefore, the magnitude of contact force
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
- 8. With the aid of a diagram draw the following electric circuit and use the resistor as the load, (a) Closed circuit (b) Open circuitarrow_forwardLab 8 Part 3 PHET Wave Interface simulation. I am having trouble with this part of the lab.arrow_forwardMick and Rick are twins born on Earth in the year 2175. Rick grows up to be an Earth-bound robotics technician while Mick becomes an intergalactic astronaut. Mick leaves the Earth on his first space mission in the year 2200 and travels, according to his clock, for 10 years at a speed of 0.75c. Unfortunately, at this point in his journey, the structure of his ship undergoes mechanical breakdown and the ship explodes. How old is Rick when his brother dies?arrow_forward
- No chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwardYou are standing a distance x = 1.75 m away from this mirror. The object you are looking at is y = 0.29 m from the mirror. The angle of incidence is θ = 30°. What is the exact distance from you to the image?arrow_forwardFor each of the actions depicted below, a magnet and/or metal loop moves with velocity v→ (v→ is constant and has the same magnitude in all parts). Determine whether a current is induced in the metal loop. If so, indicate the direction of the current in the loop, either clockwise or counterclockwise when seen from the right of the loop. The axis of the magnet is lined up with the center of the loop. For the action depicted in (Figure 5), indicate the direction of the induced current in the loop (clockwise, counterclockwise or zero, when seen from the right of the loop). I know that the current is clockwise, I just dont understand why. Please fully explain why it's clockwise, Thank youarrow_forward
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning
Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning





