
Concept explainers
First-stage allocation, time-driven activity-based
| Wages and salaries | $480,000 |
| 60,000 | |
| Rent | 120,000 |
| Other overhead | 240,000 |
| Total overhead costs | $900,000 |
Marshall has established four activity cost pools and the following budgeted activity for each cost pool:
| Activity Cost Pool | Activity Measure | Budgeted Total Activity for the Year |
| Direct manufacturing labor support | Number of direct manufacturing labor-hours | 30,000 direct manufacturing labor-hours |
| Order processing | Number of customer orders | 500 orders |
| Design support | Number of custom design-hours | 2,490 custom design-hours |
| Other | Facility-sustaining costs allocated to orders based on direct manufacturing labor-hours | 30,000 direct manufacturing labor-hours |
Some customer orders require more complex designs, while others need simple designs. Marshall estimates that it will do 120 complex designs during a year, which will each take 11.75 hours for a total of 1,410 design-hours. It estimates it will do 180 simple designs, which will each take 6 hours for a total of 1,080 design-hours.
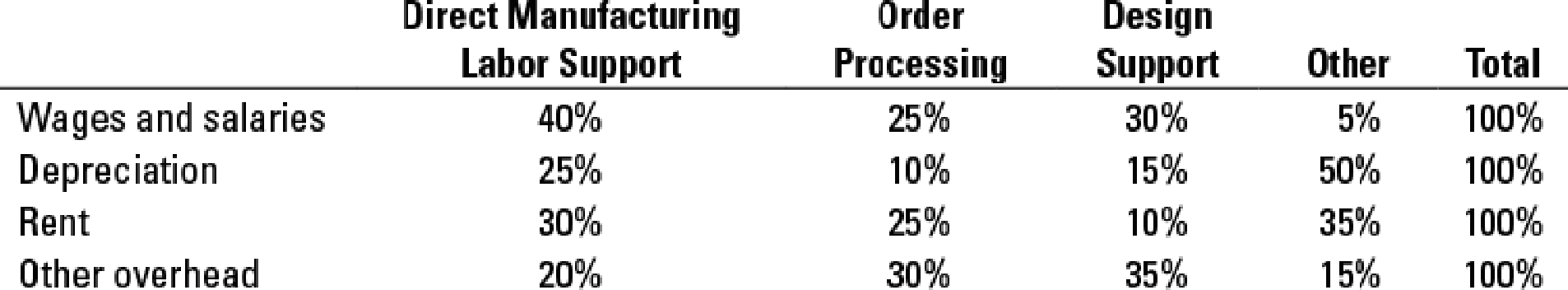
Paul Napoli, Marshall’s controller, has prepared the following estimates for distribution of the overhead costs across the four activity-cost pools:
Order 277100 consists of four different metal products. Three products require a complex design and one requires a simple design. Order 277100 requires $4,550 of direct materials and 80 direct manufacturing labor-hours
- 1. Allocate the overhead costs to each activity cost pool. Calculate the activity rate for each pool
Required
- 2. Determine the cost of Order 277100.
- 3. How does activity-based costing enhance Marshall’s ability to price its orders? Suppose Marshall used a simple costing system to allocate all overhead costs to orders on the basis of direct manufacturing labor-hours. How might this have affected Marshall’s pricing decision for Order 227100?
- 4. When designing its activity-based costing system. Marshall uses time-driven activity-based costing system (TDABC) for its design department. What does this approach allow Marshall to do? How would the cost of Order 277100 have been different if Marshall had used the number of customer designs rather than the number of custom design-hours to allocate costs to different customer orders? Which cost driver do you prefer for design support? Why?
Learn your wayIncludes step-by-step video

Chapter 5 Solutions
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis (16th Edition)
Additional Business Textbook Solutions
Operations Management
Fundamentals of Management (10th Edition)
Intermediate Accounting (2nd Edition)
Principles of Operations Management: Sustainability and Supply Chain Management (10th Edition)
FUNDAMENTALS OF CORPORATE FINANCE
 Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub
Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage Learning Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,Principles of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,Principles of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College





