
Genetic Analysis: An Integrated Approach (3rd Edition)
3rd Edition
ISBN: 9780134605173
Author: Mark F. Sanders, John L. Bowman
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 5, Problem 33P
DNA sequence for
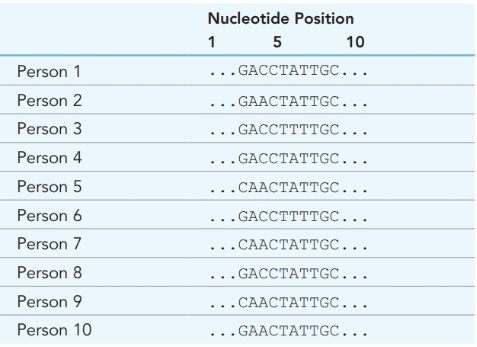
Identify the nucleotide positions of all SNPs ( single nucleotide polymorphisms).
How many different SNP haplotypes are represented in the data?
What is the sequence of each haplotype?
Identify the haplotype carried by each person.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
C
MasteringHealth MasteringNu ×
session.healthandnutrition-mastering.pearson.com/myct/itemView?assignment ProblemID=17396416&attemptNo=1&offset=prev
10. Your instructor will give you 2 amino acids during the activity session (video 2-7.
A. First color all the polar and non-polar covalent bonds in the R groups of your 2 amino acids
using the same colors as in #7. Do not color the bonds in the backbone of each amino acid.
B. Next, color where all the hydrogen bonds, hydrophobic interactions and ionic bonds could
occur in the R group of each amino acid. Use the same colors as in #7. Do not color the bonds
in the backbone of each amino acid.
C. Position the two amino acids on the page below in an orientation where the two R groups
could bond together. Once you are satisfied, staple or tape the amino acids in place and label
the bond that you formed between the two R groups.
- Polar covalent Bond - Red
- Non polar Covalent boND- yellow
- Ionic BonD - PINK
Hydrogen Bonn - Purple
Hydrophobic interaction-green
O=C-N
H
I.
H
HO
H
=O
CH2
C-C-N
HICK
H
HO
H
CH2
OH
H₂N
C = O
Find the dental formula and enter it in the following format:
I3/3 C1/1 P4/4 M2/3 = 42 (this is not the correct number, just the correct format)
Please be aware: the upper jaw is intact (all teeth are present). The bottom jaw/mandible is not intact. The front teeth should include 6 total rectangular teeth (3 on each side) and 2 total large triangular teeth (1 on each side).
Chapter 5 Solutions
Genetic Analysis: An Integrated Approach (3rd Edition)
Ch. 5 - For parts a, b, and c, draw a diagram illustrating...Ch. 5 - 5.2 In a diploid species of plant, the genes for...Ch. 5 - A pure-breeding tall plant producing oval fruit as...Ch. 5 - 5.4 Genes E and H are syntenic in an experimental...Ch. 5 - In tomato plants, purple leaf color is controlled...Ch. 5 - 5.6 In Drosophila, the map positions of genes are...Ch. 5 - 5.7 Genes A, B, and C are linked on a chromosome...Ch. 5 - Gene G recombines with gene T at a frequency of...Ch. 5 - Genes A, B, C, D, and E are linked on a...Ch. 5 - Syntenic genes can assort independently. Explain...
Ch. 5 - 5.11 The recombination frequency between linked...Ch. 5 - On the DrosophilaX chromosome, the dominant allele...Ch. 5 - Researchers cross a corn plant that is pure -...Ch. 5 - 5.14 syndrome is an autosomal disorder affecting...Ch. 5 - 5.15 Three dominant traits of corn seedlings,...Ch. 5 - 5.16 In a diploid plant species, an with the...Ch. 5 - Prob. 17PCh. 5 - The Rh blood group in humans is determined by a...Ch. 5 - 5.19 Genetic linkage mapping for a large number of...Ch. 5 - 5.20 with the genotype form tetrads in the...Ch. 5 -
Gene and gene are genetically linked. Answer...Ch. 5 -
T. H. Morgan’s data on eye color and wing form,...Ch. 5 - Prob. 23PCh. 5 -
The boss in your laboratory has just heard of a...Ch. 5 - In rabbits, chocolate-colored fur (w+) is dominant...Ch. 5 - Prob. 26PCh. 5 - 5.27 In tomatoes, the allele for tall plant height...Ch. 5 - 5.28 Neurofibromatosis is an autosomal dominant...Ch. 5 - A 2006 genetic study of a large American family...Ch. 5 - 5.30 A experiment examining potential genetic...Ch. 5 - A genetic study of an early onset form of heart...Ch. 5 - In experiments published in 1918 that sought to...Ch. 5 - DNA sequence for 10 individuals are Identify the...Ch. 5 - 5.34 The accompanying pedigree below shows a...Ch. 5 - 5.35 Based on previous family studies, an...Ch. 5 - Divide a clean sheet of paper into four quadrant...Ch. 5 - 5.37 For six genes known to be linked on chromosme...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 12. Calculate the area of a circle which has a radius of 1200 μm. Give your answer in mm² in scientific notation with the correct number of significant figures.arrow_forwardDescribe the image quality of the B.megaterium at 1000X before adding oil? What does adding oil do to the quality of the image?arrow_forwardWhich of the follwowing cells from this lab do you expect to have a nucleus and why or why not? Ceratium, Bacillus megaterium and Cheek epithelial cells?arrow_forward
- 14. If you determine there to be debris on your ocular lens, explain what is the best way to clean it off without damaging the lens?arrow_forward11. Write a simple formula for converting mm to μm when the number of mm's is known. Use the variable X to represent the number of mm's in your formula.arrow_forward13. When a smear containing cells is dried, the cells shrink due to the loss of water. What technique could you use to visualize and measure living cells without heat-fixing them? Hint: you did this technique in part I.arrow_forward
- 10. Write a simple formula for converting μm to mm when the number of μm's are known. Use the variable X to represent the number of um's in your formula.arrow_forward8. How many μm² is in one cm²; express the result in scientific notation. Show your calculations. 1 cm = 10 mm; 1 mm = 1000 μmarrow_forwardFind the dental formula and enter it in the following format: I3/3 C1/1 P4/4 M2/3 = 42 (this is not the correct number, just the correct format) Please be aware: the upper jaw is intact (all teeth are present). The bottom jaw/mandible is not intact. The front teeth should include 6 total rectangular teeth (3 on each side) and 2 total large triangular teeth (1 on each side).arrow_forward
- Answer iarrow_forwardAnswerarrow_forwardcalculate the questions showing the solution including variables,unit and equations all the questiosn below using the data a) B1, b) B2, c) hybrid rate constant (1) d) hybrid rate constant (2) e) t1/2,dist f) t1/2,elim g) k10 h) k12 i) k21 j) initial concentration (C0) k) central compartment volume (V1) l) steady-state volume (Vss) m) clearance (CL) AUC (0→10 min) using trapezoidal rule n) AUC (20→30 min) using trapezoidal rule o) AUCtail (AUC360→∞) p) total AUC (using short cut method) q) volume from AUC (VAUC)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles Of Radiographic Imaging: An Art And A ...Health & NutritionISBN:9781337711067Author:Richard R. Carlton, Arlene M. Adler, Vesna BalacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles Of Radiographic Imaging: An Art And A ...Health & NutritionISBN:9781337711067Author:Richard R. Carlton, Arlene M. Adler, Vesna BalacPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax

Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...
Biology
ISBN:9781305251052
Author:Michael Cummings
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles Of Radiographic Imaging: An Art And A ...
Health & Nutrition
ISBN:9781337711067
Author:Richard R. Carlton, Arlene M. Adler, Vesna Balac
Publisher:Cengage Learning




Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:OpenStax
DNA vs RNA (Updated); Author: Amoeba Sisters;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=JQByjprj_mA;License: Standard youtube license