
Concept explainers
Yeast are single-celled eukaryotic organisms that grow in culture as either haploids or diploids. Diploid yeast are generated when two haploid strains fuse together. Seven haploid strains of yeast exhibit similar growth habit: At
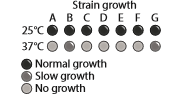
Describe the nature of the mutation affecting each of these mutant yeast strains. Explain why strains B and G display different growth habit at

How many different genes are mutated among these seven yeast strains? Identify the strains that represent each gene mutation.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 4 Solutions
Genetic Analysis: An Integrated Approach (3rd Edition)
- Why are nutrient absorption and dosage levels important when taking multivitamins and vitamin and mineral supplements?arrow_forwardI'm struggling with this topic and would really appreciate your help. I need to hand-draw a diagram and explain the process of sexual differentiation in humans, including structures, hormones, enzymes, and other details. Could you also make sure to include these terms in the explanation? . Gonads . Wolffian ducts • Müllerian ducts . ⚫ Testes . Testosterone • Anti-Müllerian Hormone (AMH) . Epididymis • Vas deferens ⚫ Seminal vesicles ⚫ 5-alpha reductase ⚫ DHT - Penis . Scrotum . Ovaries • Uterus ⚫ Fallopian tubes - Vagina - Clitoris . Labia Thank you so much for your help!arrow_forwardRequisition Exercise A phlebotomist goes to a patient’s room with the following requisition. Hometown Hospital USA 125 Goodcare Avenue Small Town, USAarrow_forward
- I’m struggling with this topic and would really appreciate your help. I need to hand-draw a diagram and explain the process of sexual differentiation in humans, including structures, hormones, enzymes, and other details. Could you also make sure to include these terms in the explanation? • Gonads • Wolffian ducts • Müllerian ducts • Testes • Testosterone • Anti-Müllerian Hormone (AMH) • Epididymis • Vas deferens • Seminal vesicles • 5-alpha reductase • DHT • Penis • Scrotum • Ovaries • Uterus • Fallopian tubes • Vagina • Clitoris • Labia Thank you so much for your help!arrow_forwardI’m struggling with this topic and would really appreciate your help. I need to hand-draw a diagram and explain the process of sexual differentiation in humans, including structures, hormones, enzymes, and other details. Could you also make sure to include these terms in the explanation? • Gonads • Wolffian ducts • Müllerian ducts • Testes • Testosterone • Anti-Müllerian Hormone (AMH) • Epididymis • Vas deferens • Seminal vesicles • 5-alpha reductase • DHT • Penis • Scrotum • Ovaries • Uterus • Fallopian tubes • Vagina • Clitoris • Labia Thank you so much for your help!arrow_forwardOlder adults have unique challenges in terms of their nutrient needs and physiological changes. Some changes may make it difficult to consume a healthful diet, so it is important to identify strategies to help overcome these obstacles. From the list below, choose all the correct statements about changes in older adults. Select all that apply. Poor vision can make it difficult for older adults to get to a supermarket, and to prepare meals. With age, taste and visual perception decline. As people age, salivary production increases. In older adults with dysphagia, foods like creamy soups, applesauce, and yogurt are usually well tolerated. Lean body mass increases in older adults.arrow_forward
- When physical activity increases, energy requirements increase also. Depending on the type, intensity, and duration of physical activity, the body’s requirements for certain macronutrients may change as well. From the list below, choose all the correct statements about the effects of increased physical activity or athletic training. Select all that apply. An athlete who weighs 70 kg (154 lb) should consume 420 to 700 g of carbohydrate per day. How much additional energy an athlete needs depends on the specific activity the athlete engages in and the frequency of the activity. Those participating in vigorous exercise should restrict their fat intake to less than 15%% of total energy intake. Athletes who are following energy-restricted diets are at risk for consuming insufficient protein. The recommendation to limit saturated fat intake to less than 10%% of total energy intake does not apply to athletes or those who regularly engage in vigorous physical activity.arrow_forwardWhen taking vitamins and vitamin-mineral supplements, how can one be sure they are getting what they are taking?arrow_forwardHow many milligrams of zinc did you consume on average per day over the 3 days? (See the Actual Intakes vs. Recommended Intakes Report with all days checked.) Enter the number of milligrams of zinc rounded to the first decimal place in the box below. ______ mg ?arrow_forward
- the direct output from molecular replacement is a coordinate file showing the orientation of the unknown target protein in the unit cell. true or false?arrow_forwardthe direct output from molecular replacement is a coordinate file showing the orientation of the unknown target protein in the unit cell. true or false?arrow_forwardDid your intake of vitamin C meet or come very close to the recommended amount? yes noarrow_forward
 Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College
Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College





