
Concept explainers
Three strains of green-seeded lentil plants appear to have the same
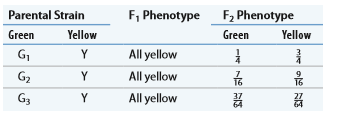
For what number of genes are variable alleles segregating in the
b. Using the allele symbols A and a, B and b, and D and d to represent alleles at segregating genes, give the genotypes of parental and
c. For each set of
d. If green-seeded strains
e. What proportion of the
f. If strains
g. What proportion of the
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 4 Solutions
Genetic Analysis: An Integrated Approach (3rd Edition)
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Fundamentals of Anatomy & Physiology Plus Mastering A&P with eText - Access Card Package (10th Edition) (New A&P Titles by Ric Martini and Judi Nath)
Becker's World of the Cell (9th Edition)
- Individuals of genotype AaBb were mated to individuals of genotype aabb. One thousand offspring were counted, with the following results: 474 Aabb, 480 aaBb, 20 AaBb, and 26 aabb. What type of cross is it? Are these loci linked? What are the two parental classes and the two recombinant classes of offspring? What is the percentage of recombination between these two loci? How many map units apart are they?arrow_forwardMendelian ratios are modified in crosses involving autotetraploids.Assume that one plant expresses the dominant trait greenseeds and is homozygous (WWWW). This plant is crossed to onewith white seeds that is also homozygous (wwww). If only onedominant allele is sufficient to produce green seeds, predict theF1 and F2 results of such a cross. Assume that synapsis betweenchromosome pairs is random during meiosis.arrow_forwardIn pea plants, yellow seeds (Y) are dominant to green seeds (y) and round seeds (R) are dominant to wrinkled seeds (). The genes for seed color and seed shape are on different chromosomes. Two true-breeding parents, one with yellow round peas and the other with green wrinkled peas, are crossed to produce a hybrid (heterozygous) F₁. Two F₁ individuals are crossed to give an F2; this is depicted in the Punnett square below. Place the correct genotypes in the Punnett square and the place the correct phenotypic ratios next to their appropriate phenotype on the right. YYRR YYRr YyRR YYrr yyRR yyRr Yyrr YyRr 3/16 1/16 yyrr 9/16 3/16 1/4 E 1/2 16/16 YR ✪✪✪ Yr yR YYRR Y YyRr Yr yR YR YYRr YYRR YyRr yr YyRr yyrr yr YyRr Yyrr yyRr F2 phenotype Phenotypic ratio Aarrow_forward
- In roses, purple flower color is determined by the dominant P allele, while pp homozygotes are white. The presence of long stems is determined by the dominant S allele, while ss homozygotes have short stems. Both mutations are completely penetrant. A test cross was performed between a rose plant of unknown genotype with a white flowered, short stemmed rose plant (pp ss) and the following 200 progeny plants were obtained: 84 white flowers, long stems 16 purple flowers, long stems 82 purple flowers, short stems 18 white flowers, short stems Select the statements below that are TRUE. Select 2 correct answer(s) The P and S genes independently assort during meiosis. The map distance between P and S is 17 CM. The genotype of the progeny plants with purple flowers and short stems is PP ss. The map distance between P and S is 83 CM. The homologs in the plant with unknown genotype are p S and Ps. The homologs in the plant with unknown genotype are PS and p s.arrow_forwardIn cucumbers, speckled fruit color (u') is dominant to uniform fruit color (u), and large spines (ss") are dominant to small spines (ss). These two genes are linked at a map distance of 20.4 m.u. A true-breeding cucumber plant with speckled fruit and large spines is crossed with a true-breeding plant with uniform fruit color and small spines. One of the F1 plants is crossed with a plant with uniform fruit color and small spines. What percentage of the offspring of this cross are expected to have uniform fruit color and small spines? 39.8% 10.2% 79.6% 20.4%arrow_forwardWhat are the expected phenotypic ratios from the following cross:Tt Rr yy Aa × Tt rr YY Aa, where T = tall, t = dwarf, R = round,r = wrinkled, Y = yellow, y = green, A = axial, a = terminal; T, R,Y, and A are dominant alleles. Note: Consider using the multiplication method in answering this problemarrow_forward
- A purple flowering, smooth seed dihybrid plant (genotype PpSs) is test crossed with a white flowering, wrinkled seed plant (genotype ppss). These produce progeny in the following numbers of four phenotypes: 24:76:74:26 (purple flower + smooth seed coat: purple flower + wrinkled seed coat: white flower + smooth seed coat: white flower + wrinkled seed coat). a) What is the genotype of the original dihybrid plant? Specify which alleles are on each chromosome of the purple flowering, smooth seed plant (i.e. AB/ab or Ab/aB). b) How many map units separate the colour and seed coat genes? Show your calculations.arrow_forwardIn some plants, a true-breeding, red-flowered variety gives all pink flowers when crossed with a white-flowered strain: RR (red) X rr (white) = Rr (pink). Flower position in this plant may either be axial (dominant) or terminal (recessive). What will be the phenotypic ratios of the F1 generation resulting from the following cross: axial-red (true-breeding) X terminal-white? What will the phenotypic ratios of the F2 be? SHOW ALL WORKarrow_forwardIn roses, purple flower color is determined by the dominant P allele, while pphomozygotes are white. The presence of long stems is determined by the dominant S allele, while ss homozygotes have short stems. Both mutations are completely penetrant. A test cross was performed between a rose plant of unknown genotype with a white flowered, short stemmed rose plant (pp ss) and the following 200 progeny plants were obtained: 84 white flowers, long stems 16 purple flowers, long stems 82 purple flowers, short stems 18 white flowers, short stems Select two statements below that are TRUE. options: The P and S genes independently assort during meiosis. The map distance between P and S is 17 cM. The genotype of the progeny plants with purple flowers and short stems is PP ss. The map distance between P and S is 83 cM. The homologs in the plant with…arrow_forward
- A pure breeding strain of squash that produced disk-shaped fruits was crossed with a pure- breeding strain having long fruits. The first filial generation had disk fruits, but the second filial generation showed a new phenotype, sphere, and was composed of the following proportions: disk 270, sphere 178, long 32. Propose an explanation for these results, and show the genotypes of P, First filial generation and second filial generation.arrow_forwardA series of three-point testcrosses is made to determine the genetic map order of seven linked allele pairs: A/a, B/b, G/g, H/h, Q/q, R/r, and Y/y.From each cross between a triply heterozygous parent listed below, two recombinant classes were noticed as the least frequent among all 8 progeny classes, and are listed at the right in the table. A. For each testcross write the genotype of the F1 heterozygous parent. F1 Parental Phenotype Least frequent F2 Phenotype 1.AHB&ahb AHb & ahB 2.RYh&ryH RYH & ryh 3.BhY&bHy Bhy & bHY 4.qYB&Qyb qYb & QyB 5.AbQ&aBq Abq & aBQ 6.ghR&GHr ghr & GHR B. Write the unified map order of these genes, showing your reasoning.arrow_forwardSuppose that the wild type phenotype for tomatoes is red, round fruit with three-parted leaves and that a strain of mutant tomatoes has yellow, pear-shaped fruit with entire leaves. A and a represent the alleles for fruit color, B and b represent the alleles for fruit shape, and C and c the leaf shape. Two tomatoes with the genotypes Aa Bb cc and Aa Bb CC are crossed. The resulting Punnett square is shown. One cell has been completed with the correct tomato phenotype. Fill in the rest of the Punnett square by placing a fruit and leaf phenotype in each cell. ABC AbC aBC abC ABC Abc aBc abc Answer Bankarrow_forward
 Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
