
Fundamentals of Physics Extended
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781118230725
Author: David Halliday, Robert Resnick, Jearl Walker
Publisher: Wiley, John & Sons, Incorporated
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 33, Problem 79P
SSM emerges from the opposite face parallel to its initial direction but displaced sideways, as in Fig. 33-69. (b) Show that, for small angles of incidence θ, this displacement is given by
where n is the index of refraction of the glass and θ is measured in radians.
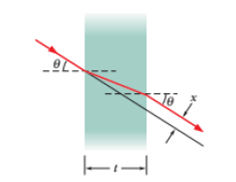
Figure 33-69 Problem 79.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Solve and answer correctly please.Thank you!!
A cart on wheels (assume frictionless) with a mass of 20 kg is pulled rightward with a 50N force. What is its acceleration?
Two-point charges of 5.00 µC and -3.00 µC are placed 0.250 m apart.a) What is the electric force on each charge? Include strength and direction and a sketch.b) What would be the magnitude of the force if both charges are positive? How about the direction?
c) What will happen to the electric force on each piece of charge if they are moved twice as far apart? (Give a numerical answer as well as an explanation.)
Chapter 33 Solutions
Fundamentals of Physics Extended
Ch. 33 - Prob. 1QCh. 33 - Prob. 2QCh. 33 - a Figure 33-27 shows light reaching a polarizing...Ch. 33 - Prob. 4QCh. 33 - In the arrangement of Fig. 33-l5a, start with...Ch. 33 - Prob. 6QCh. 33 - Figure 33-30 shows fays of monochromatic Light...Ch. 33 - Figure 33-31 shows the multiple reflections of a...Ch. 33 - Figure 33-32 shows four long horizontal layers AD...Ch. 33 - The leftmost block in Fig. 33-33 depicts total...
Ch. 33 - Prob. 11QCh. 33 - Prob. 12QCh. 33 - Prob. 1PCh. 33 - Prob. 2PCh. 33 - Prob. 3PCh. 33 - About how far apart must you hold your hands for...Ch. 33 - SSM What inductance must be connected to a 17 pF...Ch. 33 - Prob. 6PCh. 33 - Prob. 7PCh. 33 - Prob. 8PCh. 33 - Prob. 9PCh. 33 - Prob. 10PCh. 33 - Prob. 11PCh. 33 - Prob. 12PCh. 33 - Sunlight just outside Earths atmosphere has an...Ch. 33 - Prob. 14PCh. 33 - An airplane flying at a distance of 10 km from a...Ch. 33 - Prob. 16PCh. 33 - Prob. 17PCh. 33 - Prob. 18PCh. 33 - Prob. 19PCh. 33 - Radiation from the Sun reaching Earth just outside...Ch. 33 - ILW What is the radiation pressure 1.5 m away from...Ch. 33 - Prob. 22PCh. 33 - Someone plans to float a small, totally absorbing...Ch. 33 - Prob. 24PCh. 33 - Prob. 25PCh. 33 - Prob. 26PCh. 33 - Prob. 27PCh. 33 - The average intensity of the solar radiation that...Ch. 33 - SSM A small spaceship with a mass of only 1.5 103...Ch. 33 - A small laser emits light at power 5.00 mW and...Ch. 33 - Prob. 31PCh. 33 - Prob. 32PCh. 33 - Prob. 33PCh. 33 - Prob. 34PCh. 33 - Prob. 35PCh. 33 - At a beach the light is generally partially...Ch. 33 - Prob. 37PCh. 33 - Prob. 38PCh. 33 - Prob. 39PCh. 33 - Prob. 40PCh. 33 - A beam of polarized light is sent into a system of...Ch. 33 - Prob. 42PCh. 33 - A beam of partially polarized light can be...Ch. 33 - Prob. 44PCh. 33 - When the rectangular metal tank in Fig. 33-46 is...Ch. 33 - In Fig. 33-47a, a light ray in an underlying...Ch. 33 - Light in vacuum is incident on the surface of a...Ch. 33 - In Fig. 33-48a, a light ray in water is incident...Ch. 33 - Figure 33-49 shows light reflecting from two...Ch. 33 - In Fig. 33-50a, a beam of light in material 1 is...Ch. 33 - GO In Fig. 33-51, light is incident at angle 1 =...Ch. 33 - In Fig. 33-52a, a beam of light in material 1 is...Ch. 33 - SSM WWW ILW in Fig. 33-53, a ray is incident on...Ch. 33 - Prob. 54PCh. 33 - Prob. 55PCh. 33 - Rainbows from square drops. Suppose that, on some...Ch. 33 - A point source of light is 80.0 cm below the...Ch. 33 - The index of refraction of benzene is 1.8. What is...Ch. 33 - SSM ILW In Fig. 33-57, a ray of light is...Ch. 33 - In Fig. 33-58, light from ray A refracts from...Ch. 33 - GO In Fig. 33-59, light initially in material 1...Ch. 33 - GO A catfish is 2.00 m below the surface of a...Ch. 33 - In Fig. 33-60, light enters a 90 triangular prism...Ch. 33 - Suppose the prism of Fig. 33-53 has apex angle =...Ch. 33 - GO Figure 33-61 depicts a simplistic optical...Ch. 33 - Prob. 66PCh. 33 - GO In the ray diagram of Fig. 33-63, where the...Ch. 33 - a At what angle of incidence will the light...Ch. 33 - Prob. 69PCh. 33 - In Fig. 33-64, a light ray in air is incident on a...Ch. 33 - Prob. 71PCh. 33 - An electromagnetic wave with frequency 4.00 1014...Ch. 33 - Prob. 73PCh. 33 - A particle in the solar system is under the...Ch. 33 - SSM In Fig, 33-65, a light ray enters a glass slab...Ch. 33 - Prob. 76PCh. 33 - Rainbow. Figure 33-67 shows a light ray entering...Ch. 33 - The primary rainbow described in Problem 77 is the...Ch. 33 - SSM emerges from the opposite face parallel to its...Ch. 33 - Prob. 80PCh. 33 - Prob. 81PCh. 33 - Prob. 82PCh. 33 - SSM A ray of white light traveling through fused...Ch. 33 - Three polarizing sheets are stacked. The first and...Ch. 33 - In a region of space where gravirational forces...Ch. 33 - An unpolarized beam of light is sent into a stack...Ch. 33 - SSM During a test, a NATO surveillance radar...Ch. 33 - The magnetic component of an electromagnetic wave...Ch. 33 - Calculate the a upper and b lower limit of the...Ch. 33 - In Fig. 33-71, two light rays pass from air...Ch. 33 - Prob. 91PCh. 33 - In about A D 150, Claudius Ptolemy gave the...Ch. 33 - Prob. 93PCh. 33 - Prob. 94PCh. 33 - Prob. 95PCh. 33 - Prob. 96PCh. 33 - Two polarizing sheets, one directly above the...Ch. 33 - Prob. 98PCh. 33 - Prob. 99PCh. 33 - Prob. 100PCh. 33 - Prob. 101PCh. 33 - Prob. 102PCh. 33 - Prob. 103PCh. 33 - Prob. 104PCh. 33 - Prob. 105PCh. 33 - In Fig. 33-78, where n1 = l.70, n2 = l .50, and n3...Ch. 33 - When red light in vacuum is incident at the...Ch. 33 - Prob. 108PCh. 33 - SSM a Show that Eqs. 33-1 land 33-2 satisfy the...Ch. 33 - Prob. 110P
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
Solubility of calcium has to be predicted and explained. Concept introduction: From the periodic table, one can...
Living By Chemistry: First Edition Textbook
EVOLUTION CONNECTION The percentages of naturally occurring elements making up the human body (see Table 2.1) a...
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
How does the velocity of seismic waves change with increasing depth in the lower mantle? ______________________...
Applications and Investigations in Earth Science (9th Edition)
APPLY 1.2 Express the following quantities in scientific notation
using fundamental SI units of mass and lengt...
Chemistry (7th Edition)
The elevator in a hotel has a mass of 750kg , and it carries six people with a total mass of 450kg . How much f...
Fundamentals Of Thermodynamics
Why is an endospore called a resting structure? Of what advantage is an endospore to a bacterial cell?
Microbiology: An Introduction
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- y[m] The figure shows two snapshots of a single wave on a string. The wave is traveling to the right in the +x direction. The solid line is a snapshot of the wave at time t=0 s, while the dashed line is a snapshot of the wave at t=0.48s. 0 0.75 1.5 2.25 3 8 8 6 6 4 2 4 2 0 -2 -2 -4 -4 -6 -6 -8 -8 0 0.75 1.5 2.25 3 x[m] Determine the period of the wave in units of seconds. Enter your numerical answer below including at least 3 significant figures. Do not enter a fraction, do not use scientific notation.arrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwardAn extremely long, solid nonconducting cylinder has a radius Ro. The charge density within the cylinder is a function of the distance R from the axis, given by PE (R) = po(R/Ro)², po > 0.arrow_forward
- An extremely long, solid nonconducting cylinder has a radius Ro. The charge density within the cylinder is a function of the distance R from the axis, given by PE (R) = po(R/Ro)², po > 0.arrow_forwardA sky diver of mass 90 kg (with suit and gear) is falling at terminal speed. What is the upward force of air drag, and how do you know?arrow_forwardA car is traveling at top speed on the Bonneville salt flats while attempting a land speed record. The tires exert 25 kN of force in the backward direction on the ground. Why backwards? How large are the forces resisting the forward motion of the car, and why?arrow_forward
- Please help by: Use a free body diagram Show the equations State your assumptions Show your steps Box your final answer Thanks!arrow_forwardPlease help by: Use a free body diagram Show the equations State your assumptions Show your steps Box your final answer Thanks!arrow_forwardBy please don't use Chatgpt will upvote and give handwritten solutionarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning An Introduction to Physical SciencePhysicsISBN:9781305079137Author:James Shipman, Jerry D. Wilson, Charles A. Higgins, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
An Introduction to Physical SciencePhysicsISBN:9781305079137Author:James Shipman, Jerry D. Wilson, Charles A. Higgins, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 3PhysicsISBN:9781938168185Author:William Moebs, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax
University Physics Volume 3PhysicsISBN:9781938168185Author:William Moebs, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...
Physics
ISBN:9781337553292
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

An Introduction to Physical Science
Physics
ISBN:9781305079137
Author:James Shipman, Jerry D. Wilson, Charles A. Higgins, Omar Torres
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 3
Physics
ISBN:9781938168185
Author:William Moebs, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:OpenStax
Polarization of Light: circularly polarized, linearly polarized, unpolarized light.; Author: Physics Videos by Eugene Khutoryansky;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8YkfEft4p-w;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY