
Concept explainers
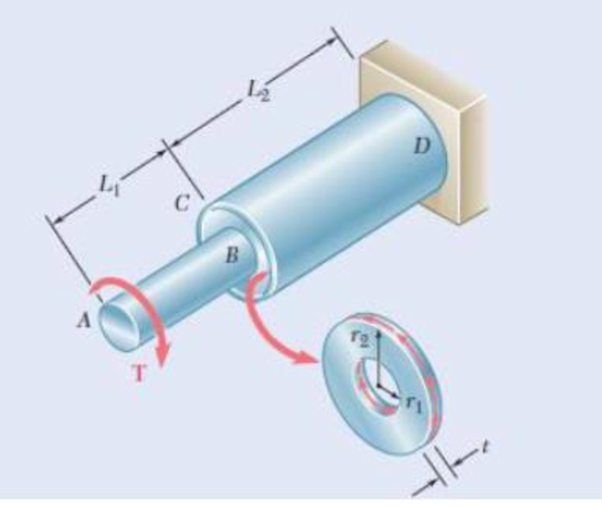
An annular plate of thickness t and modulus G is used to connect shaft AB of radius r1 to tube CD of radius r2. Knowing that a torque T is applied to end A of shaft AB and that end D of tube CD is fixed, (a) determine the magnitude and location of the maximum shearing stress in the annular plate, (b) show that the angle through which end B of the shah rotates with respect to end C of the tube is
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 3 Solutions
Mechanics of Materials, 7th Edition
- The fallowing question is from a reeds book on applied heat i am studying. Although the answer is provided, im struggling to understand the whole answer and the formulas and the steps theyre using. Also where some ov the values such as Hg and Hf come from in part i for example. Please explain step per step in detail thanks In an NH, refrigerator, the ammonia leaves the evaporatorand enters the cornpressor as dry saturated vapour at 2.68 bar,it leaves the compressor and enters the condenser at 8.57 bar with50" of superheat. it is condensed at constant pressure and leavesthe condenser as saturated liquid. If the rate of flow of the refrigerantthrough the circuit is 0.45 kglmin calculate (i) the compressorpower, (ii) the heat rejected to the condenser cooling water in kJ/s,an (iii) the refrigerating effect in kJ/s. From tables page 12, NH,:2.68 bar, hg= 1430.58.57 bar, hf = 275.1 h supht 50" = 1597.2Mass flow of refrigerant--- - - 0.0075 kgls 60Enthalpy gain per kg of refrigerant in…arrow_forwardstate the formulas for calculating work done by gasarrow_forwardExercises Find the solution of the following Differential Equations 1) y" + y = 3x² 3) "+2y+3y=27x 5) y"+y=6sin(x) 7) y"+4y+4y = 18 cosh(x) 9) (4)-5y"+4y = 10 cos(x) 11) y"+y=x²+x 13) y"-2y+y=e* 15) y+2y"-y'-2y=1-4x³ 2) y"+2y' + y = x² 4) "+y=-30 sin(4x) 6) y"+4y+3y=sin(x)+2 cos(x) 8) y"-2y+2y= 2e* cos(x) 10) y+y-2y=3e* 12) y"-y=e* 14) y"+y+y=x+4x³ +12x² 16) y"-2y+2y=2e* cos(x)arrow_forward
- The state of stress at a point is σ = -4.00 kpsi, σy = 16.00 kpsi, σ = -14.00 kpsi, Try = 11.00 kpsi, Tyz = 8.000 kpsi, and T = -14.00 kpsi. Determine the principal stresses. The principal normal stress σ₁ is determined to be [ The principal normal stress σ2 is determined to be [ The principal normal stress σ3 is determined to be kpsi. kpsi. The principal shear stress 71/2 is determined to be [ The principal shear stress 7½ is determined to be [ The principal shear stress T₁/, is determined to be [ kpsi. kpsi. kpsi. kpsi.arrow_forwardRepeat Problem 28, except using a shaft that is rotatingand transmitting a torque of 150 N * m from the left bearing to the middle of the shaft. Also, there is a profile keyseat at the middle under the load. (I want to understand this problem)arrow_forwardProb 2. The material distorts into the dashed position shown. Determine the average normal strains &x, Ey and the shear strain Yxy at A, and the average normal strain along line BE. 50 mm B 200 mm 15 mm 30 mm D ΕΙ 50 mm x A 150 mm Farrow_forward
- Prob 3. The triangular plate is fixed at its base, and its apex A is given a horizontal displacement of 5 mm. Determine the shear strain, Yxy, at A. Prob 4. The triangular plate is fixed at its base, and its apex A is given a horizontal displacement of 5 mm. Determine the average normal strain & along the x axis. Prob 5. The triangular plate is fixed at its base, and its apex A is given a horizontal displacement of 5 mm. Determine the average normal strain &x along the x' axis. x' 45° 800 mm 45° 45% 800 mm 5 mmarrow_forwardAn airplane lands on the straight runaway, originally travelling at 110 ft/s when s = 0. If it is subjected to the decelerations shown, determine the time t' needed to stop the plane and construct the s -t graph for the motion. draw a graph and show all work step by steparrow_forwarddny dn-1y dn-1u dn-24 +a1 + + Any = bi +b₂- + +bnu. dtn dtn-1 dtn-1 dtn-2 a) Let be a root of the characteristic equation 1 sn+a1sn- + +an = : 0. Show that if u(t) = 0, the differential equation has the solution y(t) = e\t. b) Let к be a zero of the polynomial b(s) = b₁s-1+b2sn−2+ Show that if the input is u(t) equation that is identically zero. = .. +bn. ekt, then there is a solution to the differentialarrow_forward
- B 60 ft WAB AB 30% : The crane's telescopic boom rotates with the angular velocity w = 0.06 rad/s and angular acceleration a = 0.07 rad/s². At the same instant, the boom is extending with a constant speed of 0.8 ft/s, measured relative to the boom. Determine the magnitude of the acceleration of point B at this instant.arrow_forwardThe motion of peg P is constrained by the lemniscate curved slot in OB and by the slotted arm OA. (Figure 1) If OA rotates counterclockwise with a constant angular velocity of 0 = 3 rad/s, determine the magnitude of the velocity of peg P at 0 = 30°. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. Determine the magnitude of the acceleration of peg P at 0 = 30°. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. 0 (4 cos 2 0)m² B Aarrow_forward5: The structure shown was designed to support a30-kN load. It consists of a boom AB with a 30 x 50-mmrectangular cross section and a rod BC with a 20-mm-diametercircular cross section. The boom and the rod are connected bya pin at B and are supported by pins and brackets at A and C,respectively.1. Calculate the normal stress in boom AB and rod BC,indicate if in tension or compression.2. Calculate the shear stress of pins at A, B and C.3. Calculate the bearing stresses at A in member AB,and in the bracket.arrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





