
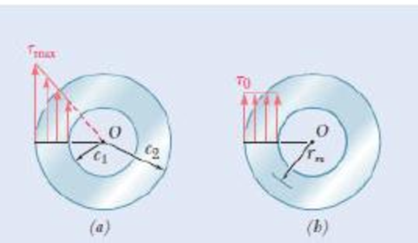
Fig. P3.29
3.29 While the exact distribution of the shearing stresses in a hollow-cylindrical shaft is as shown in Fig. P3.29a, an approximate value can be obtained for
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 3 Solutions
Mechanics of Materials, 7th Edition
- No chatgpt plsarrow_forwardA six cylinder petrol engine has a compression ratio of 5:1. The clearance volume of each cylinder is 110CC. It operates on the four-stroke constant volume cycle and the indicated efficiency ratio referred to air standard efficiency is 0.56. At the speed of 2400 rpm. 44000KJ/kg. Determine the consumes 10kg of fuel per hour. The calorific value of fuel average indicated mean effective pressure.arrow_forwardThe members of a truss are connected to the gusset plate as shown in (Figure 1). The forces are concurrent at point O. Take = 90° and T₁ = 7.5 kN. Part A Determine the magnitude of F for equilibrium. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. F= 7.03 Submit ? kN Previous Answers Request Answer × Incorrect; Try Again; 21 attempts remaining ▾ Part B Determine the magnitude of T2 for equilibrium. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. Figure T₂ = 7.03 C T2 |? KN Submit Previous Answers Request Answer × Incorrect; Try Again; 23 attempts remaining Provide Feedbackarrow_forward
- Consider the following acid-base reaction: Fe3+(aq) +3H2O -Fe(OH)3 (s) + 3H* ← A. Using thermodynamics, calculate the equilibrium constant K at 25°C (The AG° of formation of Fe(OH)3(s) is -699 kJ/mol). B. Using the value of K you calculated in part a, if a solution contains 10-4 M Fe3+ and has a pH of 7.5, will Fe(OH)3(s) precipitate? Show all calculations necessary to justify your answer. Note that the reaction as written is for precipitation, not dissolution like Ksp-arrow_forwardA vertical force of F = 3.4 kN is applied to the hook at A as shown in. Set d = 1 m. Part A 3 m 3m 0.75 m 1.5 m. Determine the tension in cable AB for equilibrium. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. FAB= Value Submit Request Answer Part B Units ? Determine the tension in cable AC for equilibrium. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. FAC = Value Submit Request Answer Part C ? Units Determine the tension in cable AD for equilibrium. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units.arrow_forwardConsider the heat engine operating at steady state between the two thermal reservoirs shown at the right while producing a net power output of 700 kW. If 1000 kW of heat (Q̇H) is transferred to the heat engine from a thermal reservoir at a temperature of TH = 900 K, and heat is rejected to a thermal reservoir at a temperature of TL = 300 K, is this heat engine possible? Can you answer this question for me and show all of the workarrow_forward
- 1.12 A disk of constant radius r is attached to a telescoping rod that is extending at a constant rate as shown in Fig. P1.12. Both the disk and the rod are rotating at a constant rate. Find the inertial velocity and acceleration of point P at the rim of the disk. ท2 L 0 SS P α e 0 O' êL Fig. P1.12 Rotating disk attached to telescoping rod. 60 LLarrow_forwardTwo different options A and B with brake pads for disc brakes are connected to the rope drum. The diameter of the rope drum is 150 mm. What distance must the pads B be at from the center of rotation to cover the same distance as A?A B- Width 50 mm - Width 60 mm- Evidence center 120mm - Construction power 900 N from rotation center.- Maintains a weight of 200 kgwhen the installation force is 1.4kN (μ is missing from the data)M=μF(Ry-Ri)Right answer R=187 mmarrow_forwardAssume the xy plane is level ground, and that the vertical pole shown in the diagram lies along the z-axis with its base at the origin. If the pole is 5 m tall, and a rope is used to pull on the top of the pole with a force of 400 N as shown, determine the magnitudes of the parallel and perpendicular components of the force vector with respect to the axis of the post i.e. with respect to the z-axis.arrow_forward
- 4-1 Q4: Q5: (20 Marks) Find √48 using False Position Method with three iterations. Hint: the root lies between 3 and 4. (20 Marks)arrow_forwardDetermine the angle between vectors FA and FB that is less than 180 degrees. FA is the vector drawn from the origin to point A (-4, 4, 2) while FB is the vector drawn from the origin to point B (3, 1, -3).arrow_forwardFind the resultant force vector from adding F1, F2 and F3, where … F1 = {-8i+10j-32k} N F2 is 40 N in magnitude with coordinate direction angles α, β, and γ, of 45, 120 and 60 degrees, respectively and F3 is 22 N in magnitude with transverse and azimuth angles of 65 and 40 degrees, respectively Express your final answer as a Cartesian vector as well as a magnitude with angles.arrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





