
Concept explainers
a.
To draw: A
a.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Following data is given in the form of a table
Graph:
By using a graphing utility, a scatter plot is drawn below for given data.
Interpretation:
The given graph shows growth similar to an exponential growth.
b.
To find: The linear model for the data given and identify the coefficient of determination.
b.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Following data is given in the form of a table
Graph:
Interpretation:
From the given graph it can said the coefficient of determination is
c.
To graph: A linear model with the scatter plot from part (a).
c.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Following data is given in the form of a table
Graph:
Interpretation:
The linear model of scatter plot gives a graph similar to a parabola thus indicating its exponential growth.
d.
To find:The find the quadratic model for the data and identify the coefficient of determination.
d.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Following data is given in the form of a table
Graph:
Interpretation:
From the graph it can be observed that coefficient of determination of quadratic model is
e.
To graph: A quadratic model with the scatter plot from part (a).
e.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Following data is given in the form of a table
Graph:
Interpretation:
The quadratic model of the scatter plot is much more continuous as compared to linear model thus increasing the accuracy to predict the future growth.
f.
To conclude: Which model (linear or quadratic) is better for the given set of data.
f.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Following data is given in the form of a table
For the given data, quadratic model will be better fit for data as it has a variable and positive increase in the y-axis.The difference between 2 points is not constant and it keeps on increasing just like a graph for
The linear model doesn’t consider the increasing slope of the equation, which is it fails to identify a relation between two adjacent slopes of a line.
g.
To find: The year when the revenue will reach approximately 8185 million dollars.
g.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Following data is given in the form of a table
To determine a year where the revenue becomes approximately 8185 million, quadratic model can be used.
Graph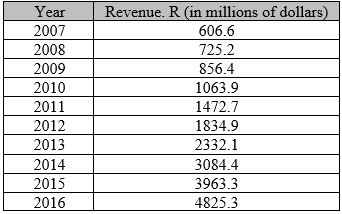
Interpretation:
From the quadratic model , it can be inferred that the revenue of company will become approximately 8185 million dollars by
Chapter 2 Solutions
PRECALCULUS W/LIMITS:GRAPH.APPROACH(HS)
- 2. Consider the following: Prove that x, x2, and 1/x are the solutions to the homogeneous equation corresponding to x³y"" + x²y" + 2xy' + 2y = 2x4. b. use variation of parameters to find a particular solution and complete the general solution to the differential equation. I am interested in process. You may use a computer for integration, finding determinants and doing Kramer's.arrow_forward3. A spring is stretched 6 in. by a mass that weighs 8 lb. The mass is attached to a dashpot mechanism that has a damping constant of 0.25 lb-sec./ft. and is acted on by an external force of 4 cos 2t lb. a. Set-up the differential equation and initial value problem for the system. b. Write the function in phase-amplitude form. C. Determine the transient solution to the system. Show your work. d. Determine the steady state of this system. Show your work. e. Is the system underdamped, overdamped or critically damped? Explain what this means for the system.arrow_forward4. Suppose that you have a circuit with a resistance of 20, inductance of 14 H and a capacitance of 11 F. An EMF with equation of E(t) = 6 cos 4t supplies a continuous charge 60 to the circuit. Suppose that the q(0)= 8 V and the q'(0)=7. Use this information to answer the following questions a. Find the function that models the charge of this circuit. b. Is the circuit underdamped, overdamped or critically damped?arrow_forward
- 1. Solve the initial value problem: y" -11y' + 30y = x³e6x y(0) 11, y'(0) = 36 =arrow_forwardWhat is the particular solution to the differential equation y′′ + y = 1/cos t ?arrow_forwardWhich of the following is the general solution to y′′ + 4y = e^2t + 12 sin(2t) ?A. y(t) = c1 cos(2t) + c2 sin(2t) + 1/8 e^2t − 3t cos(2t)B. y(t) = c1e^2t + c2e^−2t + 1/4 te^2t − 3t cos(2t)C. y(t) = c1 + c2e^−4t + 1/12 te^2t − 3t cos(2t)D. y(t) = c1 cos(2t) + c2 sin(2t) + 1/8 e^2t + 3 sin(2t)E. None of the above. Please include all steps! Thank you!arrow_forward
- Show that i cote +1 = cosec 20 tan 20+1 = sec² O २ cos² + sin 20 = 1 using pythagon's theoremarrow_forwardFind the general solution to the differential equationarrow_forwardcharity savings Budget for May travel food Peter earned $700 during May. The graph shows how the money was used. What fraction was clothes? O Search Submit clothes leisurearrow_forward
- Exercise 11.3 A slope field is given for the equation y' = 4y+4. (a) Sketch the particular solution that corresponds to y(0) = −2 (b) Find the constant solution (c) For what initial conditions y(0) is the solution increasing? (d) For what initial conditions y(0) is the solution decreasing? (e) Verify these results using only the differential equation y' = 4y+4.arrow_forwardAphids are discovered in a pear orchard. The Department of Agriculture has determined that the population of aphids t hours after the orchard has been sprayed is approximated by N(t)=1800−3tln(0.17t)+t where 0<t≤1000. Step 1 of 2: Find N(63). Round to the nearest whole number.arrow_forward3. [-/3 Points] DETAILS MY NOTES SCALCET8 7.4.032. ASK YOUR TEACHER PRACTICE ANOTHER Evaluate the integral. X + 4x + 13 Need Help? Read It SUBMIT ANSWER dxarrow_forward
 Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON
Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
 Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning





