
Concept explainers
a.
To find : the domain of the function
a.
Answer to Problem 26E
The domain is any real number
Explanation of Solution
Given information : The function is
Calculation :
This means it has no real zeroes. The denominator is never
b.
To state : the function is continuous
b.
Answer to Problem 26E
The function is continuous
Explanation of Solution
Given information : The function is
The function is defined for all real number so, the function continuous
c.
To identify : the horizontal and vertical asymptote and also verify the answer of part(a) by using the graphing utility and numerically
c.
Answer to Problem 26E
There is no vertical asymptote and the horizontal asymptote is
Explanation of Solution
Given information : The function is
Calculation :
There is no vertical asymptote for the reason which is provided in part (a)
The degree of the numerator and denominator are the same. There is a horizontal asymptote
| -20 | 3.0874 |
| -15 | 3.0868 |
| -10 | 3.0404 |
| -5 | 2.6207 |
| 0 | 0.1111 |
| 5 | 1.9487 |
| 10 | 2.5294 |
| 15 | 2.749 |
| 20 | 2.7995 |
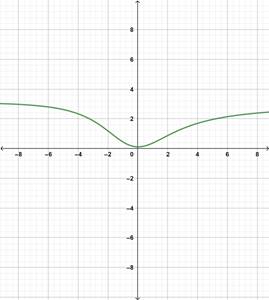
Graph : Sketch the graph using graphing utility.
Step 1: Press WINDOW button to access the Window editor.
Step 2: Press
Step 3: Enter the expression
Step 4: Press
The graph is obtained as:
Chapter 2 Solutions
PRECALCULUS W/LIMITS:GRAPH.APPROACH(HS)
- Explain the conditions under which the Radius of Convergence of the Power Series is a "finite positive real number" r>0arrow_forwardThis means that when the Radius of Convergence of the Power Series is a "finite positive real number" r>0, then every point x of the Power Series on (-r, r) will absolutely converge (x ∈ (-r, r)). Moreover, every point x on the Power Series (-∞, -r)U(r, +∞) will diverge (|x| >r). Please explain it.arrow_forwardExplain the conditions under which Radious of Convergence of Power Series is infinite. Explain what will happen?arrow_forward
- Explain the conditions under Radius of Convergence which of Power Series is 0arrow_forwardExplain the key points and reasons for 12.8.2 (1) and 12.8.2 (2)arrow_forwardQ1: A slider in a machine moves along a fixed straight rod. Its distance x cm along the rod is given below for various values of the time. Find the velocity and acceleration of the slider when t = 0.3 seconds. t(seconds) x(cm) 0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.6 30.13 31.62 32.87 33.64 33.95 33.81 33.24 Q2: Using the Runge-Kutta method of fourth order, solve for y atr = 1.2, From dy_2xy +et = dx x²+xc* Take h=0.2. given x = 1, y = 0 Q3:Approximate the solution of the following equation using finite difference method. ly -(1-y= y = x), y(1) = 2 and y(3) = −1 On the interval (1≤x≤3).(taking h=0.5).arrow_forward
- Consider the function f(x) = x²-1. (a) Find the instantaneous rate of change of f(x) at x=1 using the definition of the derivative. Show all your steps clearly. (b) Sketch the graph of f(x) around x = 1. Draw the secant line passing through the points on the graph where x 1 and x-> 1+h (for a small positive value of h, illustrate conceptually). Then, draw the tangent line to the graph at x=1. Explain how the slope of the tangent line relates to the value you found in part (a). (c) In a few sentences, explain what the instantaneous rate of change of f(x) at x = 1 represents in the context of the graph of f(x). How does the rate of change of this function vary at different points?arrow_forward1. The graph of ƒ is given. Use the graph to evaluate each of the following values. If a value does not exist, state that fact. и (a) f'(-5) (b) f'(-3) (c) f'(0) (d) f'(5) 2. Find an equation of the tangent line to the graph of y = g(x) at x = 5 if g(5) = −3 and g'(5) = 4. - 3. If an equation of the tangent line to the graph of y = f(x) at the point where x 2 is y = 4x — 5, find ƒ(2) and f'(2).arrow_forwardDoes the series converge or divergearrow_forward
 Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON
Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
 Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning





