
Concept explainers
a.
To write:The total area A of play areas of child-care centers as a function of ‘x’ .
a.
Answer to Problem 60E
The total area of the child-care center as a function of ‘x’ is
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The view of child care center is shown in Figure-1. Total fencing of the center is 200 feet.
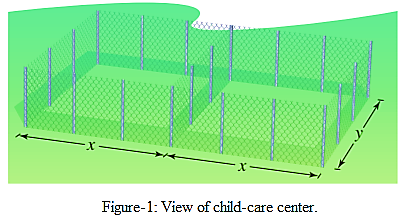
Formula/ concept used:
Area of rectangle is A= length
Calculations:
The total fencing of child-care center
Total area of the center
Thus, total area of the child-care center as a function of ‘x’ is
Conclusion:
The total area of the child-care center as a function of ‘x’ is
b.
To create:A table showing possible values of “x ” and the corresponding total area A of the plays areas, and estimate dimensions that will produce the maximum enclosed area.
b.
Answer to Problem 60E
The total enclosed area of child-care center is maximum
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The expression for total area of the play areas as function of x :
Concept used:
We choose values of x arbitrarily such that A is positive.
Calculations:
The expression for Ais
The table for total area of the play areas A and x is given below:
| x (in feet) | 5 | 10 | 15 | 20 | 25 | 30 | 35 |
| A(in sq. ft) | 900 | 1600 | 2100 | 2400 | 2500 | 2400 | 2100 |
From the table, we observe that total area A is maximum
For
Thus, the total enclosed area of child-care center is maximum
Conclusion:
The total enclosed area of child-care center is maximum
c.
To approximate:The dimensions of child-care center so that total play area is maximum, using graphing utility.
c.
Answer to Problem 60E
Using graphing utility, the total area
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The expression
Method used:
We use graphing calculator.
Graph:
The graph of A versus x is shown in Figure-2 here.
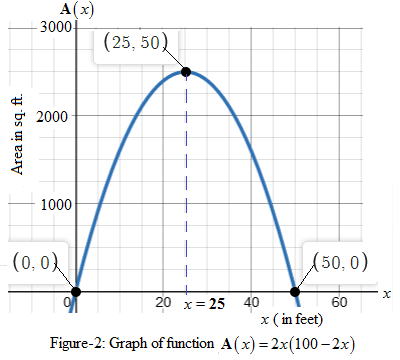
We see that the total area
Conclusion:
Using graphing utility, the total area
d.
To write:The area
d.
Answer to Problem 60E
The total area
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The area function
Formula used:
The standard form of quadratic function that represent a parabola is
Calculations:
The areafunction is
Thus,
Since,
Conclusion:
The total area
e.
To compare: The results from parts (b), (c), and (d).
e.
Answer to Problem 60E
The results obtained parts (b), (c), and (d) are identical.
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The results obtained in parts (b), (c), and (d).
Explanations:
In parts (b), (c), and (d) we find that the area
Thus, the results obtained parts (b), (c), and (d) are identical.
Chapter 2 Solutions
PRECALCULUS W/LIMITS:GRAPH.APPROACH(HS)
- Solve the next ED: (see image)arrow_forwardWrite an equation for the polynomial graphed below. It will probably be easiest to leave your "a" value as a fraction. 8 7 + 9+ H 6 5 4 3 + 3 2 1 (-30) (-1,0) (1,0) (3,0) + -5 -4 -3 -2 2 3 4 7 2 -1 -2 3 (0,-3) f(x) = 456 -4 -5 -6+arrow_forwardWrite an equation for the polynomial graphed below 5+ 4 - 3 2 1 + + -5 4-3 -2 -1 1 2 3 4 5 -1 -2 y(x) = -3 -4 5 -5+ Qarrow_forward
- Write an equation for the polynomial graphed below 6+ 5 + -5 -4 3 y(x) = 4 3 2 1 -1 1 1 -1 -2 -3 -4 -5 2 3 4 5arrow_forwardWrite an equation for the polynomial graphed below 5+ 4 3 1 + + + -5-4-3-2 1 13 4 5 -1 -2 -3 -4 -5+ 4 5 Q y(x) =arrow_forward3. Solve the inequality, and give your answer in interval notation. - (x − 4)³ (x + 1) ≥ 0arrow_forward
- 1. Find the formula to the polynomial at right. Show all your work. (4 points) 1- 2 3 сл 5 6 -4 -3 -2 -1 0 2 3arrow_forward2. Find the leading term (2 points): f(x) = −3x(2x − 1)²(x+3)³ -arrow_forward1- √ √ √³ e³/√xdy dx 1 cy² 2- √ √² 3 y³ exy dx dy So 3- √ √sinx y dy dx 4- Jo √² Sy² dx dyarrow_forward
- A building that is 205 feet tall casts a shadow of various lengths æ as the day goes by. An angle of elevation is formed by lines from the top and bottom of the building to the tip of the shadow, as de seen in the following figure. Find the rate of change of the angle of elevation when x 278 feet. dx Round to 3 decimal places. Γ X radians per footarrow_forwardUse the information in the following table to find h' (a) at the given value for a. x|f(x) g(x) f'(x) g(x) 0 0 0 4 3 1 4 4 3 0 2 7 1 2 7 3 3 1 2 9 4 0 4 5 7 h(x) = f(g(x)); a = 0 h' (0) =arrow_forwardUse the information in the following table to find h' (a) at the given value for a. x f(x) g(x) f'(x) g'(x) 0 0 3 2 1 1 0 0 2 0 2 43 22 4 3 3 2 3 1 1 4 1 2 0 4 2 h(x) = (1/(2) ²; 9(x) h' (3)= = ; a=3arrow_forward
 Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON
Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
 Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning





