
Fundamentals of Physics Extended
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781118230725
Author: David Halliday, Robert Resnick, Jearl Walker
Publisher: Wiley, John & Sons, Incorporated
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 27, Problem 49P
ILW (a) In Fig. 27-56, what current does the ammeter read if ℰ = 5.0 V (ideal battery), R1 = 2.0 Ω, R2 = 4.0 Ω, and R3 = 6.0 Ω? (b) The ammeter and battery are now interchanged. Show that the ammeter reading is unchanged.
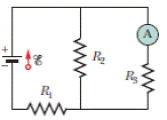
Figure 27-56 Problem 49.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Uniform Circular motion.
1. Mini Lecture
2. Let the position of a particle be given by:
(t) = Rcos (wt)i + Rsin (wt)j
3. Calculate the expression for the velocity
vector and show that the velocity vector is
tangential to the circumference of the circle.
4. Calculate the expression for the acceleration
vector and show that the acceleration vector
points radially inward.
5. Calculate the magnitude of the velocity and
magnitude of the acceleration, and therefore
show that
v2
a =
R
4. A ball is thrown vertically up, its speed.
slowing under the influence of gravity.
Suppose (A) we film this motion and play
the tape backward (so the tape begins with
the ball at its highest point and ends with it
reaching the point from which it was
released), and (B) we observe the motion of
the ball from a frame of reference moving
up at the initial speed of the ball. The ball
has a downward acceleration g in:
a. A and B
b. Only A
c. Only B
d. Neither A nor B
2. Consider a 2.4 m long propeller that
operated at a constant 350 rpm. Find the
acceleration of a particle at the tip of the
propeller.
Chapter 27 Solutions
Fundamentals of Physics Extended
Ch. 27 - a In Fig. 27-18a, with R1R2, is the potential...Ch. 27 - a In Fig. 27-18a, are resistors R1 and R3 in...Ch. 27 - You are to connect resistors R1 and R2, with R1R2,...Ch. 27 - In Fig. 27-19, a circuit consists of a battery and...Ch. 27 - For each circuit in Fig 27-20, are the resistors...Ch. 27 - Res-monster maze. In Fig. 27-21, all the resistors...Ch. 27 - A resistor R1 is wired to a battery, then resistor...Ch. 27 - What is the equivalent resistance of three...Ch. 27 - Two resistors are wired to a battery. a In which...Ch. 27 - Cap-monster maze. In Fig. 27-22, all the...
Ch. 27 - Initially, a single resistor, R1 is wired to a...Ch. 27 - After the switch in Fig. 27-15 is closed on point...Ch. 27 - Figure 27-24 shows three sections of circuit that...Ch. 27 - SSM WWW In Fig. 27-25, the ideal batteries have...Ch. 27 - In Fig. 27-26, the ideal batteries have emfs 1 =...Ch. 27 - ILW A car battery with a 12 V emf and an internal...Ch. 27 - GO Figure 27-27 shows a circuit of four resistors...Ch. 27 - A 5.0 A current is set up in a circuit for 6.0 min...Ch. 27 - A standard flashlight battery can deliver about...Ch. 27 - A wire of resistance 5.0 is connected to a...Ch. 27 - A certain car battery with a 12.0 V emf has an...Ch. 27 - a In electron-volts, how much work does an ideal...Ch. 27 - a In Fig. 27-28, what value must R have if the...Ch. 27 - SSM In Fig. 27-29, circuit section AB absorbs...Ch. 27 - Figure 27-30 shows a resistor of resistance R =...Ch. 27 - A 10-km-long underground cable extends east to...Ch. 27 - GO In Fig. 27-32a, both batteries have emf = 1.20...Ch. 27 - ILW The current in a single-loop circuit with one...Ch. 27 - A solar cell generates a potential difference of...Ch. 27 - SSM In Fig. 27-33, battery 1 has emf 1 = 12.0 V...Ch. 27 - In Fig. 27-9, what is the potential difference Vd ...Ch. 27 - A total resistance of 3.00 is to be produced by...Ch. 27 - When resistors 1 and 2 are connected in series,...Ch. 27 - Prob. 21PCh. 27 - Figure 27-34 shows five 5.00 resistors. Find the...Ch. 27 - In Fig. 27-35, R1 = 100 , R2 = 50 , and the ideal...Ch. 27 - In Fig. 27-36, R1 = R2 = 4.00 and R3 = 2.50 ....Ch. 27 - SSM Nine copper wires of length l and diameter d...Ch. 27 - Figure 27-37 shows a battery connected across a...Ch. 27 - Side flash. Figure 27-38 indicates one reason no...Ch. 27 - The ideal battery in Fig. 27-39a has emf = 6.0 V....Ch. 27 - In Fig. 27-40, R1 = 6.00 , R2 = 18.0 , and the...Ch. 27 - GO In Fig. 27-41, the ideal batteries have emfs 1...Ch. 27 - SSMGO In Fig. 27-42, the ideal batteries have emfs...Ch. 27 - Both batteries in Fig. 27-43a are ideal. Emf 1 of...Ch. 27 - GO In Fig. 27-44. the current in resistance 6 is...Ch. 27 - The resistances in Figs. 27-45a and b are all 6.0...Ch. 27 - GO In Fig. 27-46, = 12.0 V, R1, = 2000 , R2 =...Ch. 27 - GO In Fig. 27-47, 1 = 6.00 V, 2 = 12.0 V, R1, =...Ch. 27 - In Fig. 27-48, the resistances are R1 = 2.00 , R2...Ch. 27 - Figure 27-49 shows a section of a circuit. The...Ch. 27 - GO In Fig. 27-50, two batteries with an emf =...Ch. 27 - GO Two identical batteries of emf = 12.0 V and...Ch. 27 - In Fig. 27-41, 1 = 3.00 V, 2 = 1.00 V, R1 = 4.00 ,...Ch. 27 - In Fig. 27-52, an array of n parallel resistors is...Ch. 27 - You are given a number of 10 resistors, each...Ch. 27 - GO In Fig. 27-53, R1 = 100 , R2 = R3 = 50.0 , R4 =...Ch. 27 - ILW In Fig. 27-54, the resistances are R1 = 1.0 ...Ch. 27 - In Fig. 27-55a, resistor 3 is a variable resistor...Ch. 27 - SSM A copper wire of radius a = 0.250 mm has an...Ch. 27 - GO In Fig. 27-53, the resistors have the values R1...Ch. 27 - ILW a In Fig. 27-56, what current does the ammeter...Ch. 27 - In Fig. 27-57, R1 = 2.00R, the ammeter resistance...Ch. 27 - In Fig. 27-58, a voltmeter of resistance Rv= 300 ...Ch. 27 - A simple ohmmeter is made by connecting a 1.50V...Ch. 27 - In Fig. 27-14, assume that = 3.0 V, r = 100 , R1 =...Ch. 27 - When the lights of a car are switched on, an...Ch. 27 - In Fig. 27-61, Rsis to be adjusted in value by...Ch. 27 - In Fig. 27-62. a voltmeter of resistance Rv = 300 ...Ch. 27 - Switch S in Fig. 27-63 is closed at time t = 0, to...Ch. 27 - In an RC series circuit, emf = 12.0 V, resistance...Ch. 27 - SSM What multiple of the time constant gives the...Ch. 27 - A capacitor with initial charge q0 is discharge...Ch. 27 - ILW A 15.0 k resistor and a capacitor are...Ch. 27 - Figure 27-64 shows the circuit of a flashing lamp,...Ch. 27 - SSM WWWIn the circuit of Fig. 27-65, = 1.2 kV, C=...Ch. 27 - A capacitor with an initial potential difference...Ch. 27 - GO In Fig. 27-66. R1 = 10.0 k, R2 = 15.0 k, C=...Ch. 27 - Figure 27-67 display two circuits with a charged...Ch. 27 - The potential difference between the plates of a...Ch. 27 - A 1.0 F capacitor with an initial stored energy of...Ch. 27 - GO A 3.00 M resistor and a 1.00 F capacitor are...Ch. 27 - GO Each of the six real batteries in Fig. 27-68...Ch. 27 - In Fig. 27-69, R1 = 20.0 , R2 = 10.0 , and the...Ch. 27 - In Fig.27-70, the ideal battery has emf = 30.0 V,...Ch. 27 - SSM Wires A and B, having equal lengths of 40.0 m...Ch. 27 - What are the a size and b direction up or down of...Ch. 27 - Suppose that, while you are sitting in a chair,...Ch. 27 - GO In Fig. 27-72, the ideal batteries have emfs 1...Ch. 27 - SSM A temperature-stable resistor is made by...Ch. 27 - In Fig. 27-14, assume that = 5.0 V, r = 2.0 , R1...Ch. 27 - SSM An initially uncharged capacitor C is fully...Ch. 27 - In Fig. 27-73, R1 = 5.00 , R2 = 10.0 , R3 = 15.0 ,...Ch. 27 - In Fig. 27-5a, find the potential difference...Ch. 27 - In Fig. 27-8a, calculate the potential difference...Ch. 27 - SSM A controller on an electronic arcade game...Ch. 27 - An automobile gasoline gauge is shown...Ch. 27 - SSM The starting motor of a car is turning too...Ch. 27 - Two resistors R1 and R2 may be connected either in...Ch. 27 - The circuit of Fig. 27-25 shows a capacitor, two...Ch. 27 - In Fig. 27-41, R1 = 10.0 , R2 = 20.0 , and the...Ch. 27 - In Fig. 27-76, R= 10 . what is the equivalent...Ch. 27 - a In Fig. 27-4a, show that the rate at which...Ch. 27 - In Fig. 27-77, the ideal batteries have emfs 1 =...Ch. 27 - Figure 27-28 shows a portion of a circuit through...Ch. 27 - Thermal energy is to be generated in a 0.10 ...Ch. 27 - Figure 27-29 shows three 20.0 resistors. Find the...Ch. 27 - A 120 V power line is protected by a 15 A fuse....Ch. 27 - Figure 27-63 shows an ideal battery of emf = 12...Ch. 27 - SSM A group of N identical batteries of emf and...Ch. 27 - SSM In Fig. 27-48, R1 = R2 = 10.0 , and the ideal...Ch. 27 - SSM In Fig. 27-66, the ideal battery has emf = 30...Ch. 27 - In Fig. 27-81, the ideal batteries have emfs 1 =...Ch. 27 - In Fig. 27-82, an ideal battery of emf = 12.0 V...Ch. 27 - The following table gives the electric potential...Ch. 27 - In Fig. 27-83, 1 = 6.00 V, 2 = 12.0 V, R1= 200 ...Ch. 27 - A three-way 120 V lamp bulb that contains two...Ch. 27 - In Fig. 27-84, R1 = R2 = 2.0 , R3 = 4.0 , R4 = 3.0...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
16.
a. Calculate the standard free energy change as a pair of electrons is transferred from succinate to mole...
Biochemistry: Concepts and Connections (2nd Edition)
All of the following terms can appropriately describe humans except: a. primary consumer b. autotroph c. hetero...
Human Biology: Concepts and Current Issues (8th Edition)
What global policy changes and what individual choices can help us sustain the planet that sustains us?
Biology: Life on Earth with Physiology (11th Edition)
2. Whether an allele is dominant or recessive depends on
a. how common the allele is, relative to other alleles...
Campbell Biology: Concepts & Connections (9th Edition)
Why can algae and cyanobacteria be considered indicators of productivity as well as of pollution?
Laboratory Experiments in Microbiology (12th Edition) (What's New in Microbiology)
4. What five specific threats to biodiversity are described in this chapter? Provide an example of each.
Biology: Life on Earth (11th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 2. A football is kicked at an angle 37.0° above the horizontal with a velocity of 20.0 m/s, as Calculate (a) the maximum height, (b) the time of travel before the football hits the ground, and (c) how far away it hits the ground. Assume the ball leaves the foot at ground level, and ignore air resistance, wind, and rotation of the ball.arrow_forwardPlease don't use Chatgpt will upvote and give handwritten solutionarrow_forwardCam mechanisms are used in many machines. For example, cams open and close the valves in your car engine to admit gasoline vapor to each cylinder and to allow the escape of exhaust. The principle is illustrated in the figure below, showing a follower rod (also called a pushrod) of mass m resting on a wedge of mass M. The sliding wedge duplicates the function of a rotating eccentric disk on a camshaft in your car. Assume that there is no friction between the wedge and the base, between the pushrod and the wedge, or between the rod and the guide through which it slides. When the wedge is pushed to the left by the force F, the rod moves upward and does something such as opening a valve. By varying the shape of the wedge, the motion of the follower rod could be made quite complex, but assume that the wedge makes a constant angle of 0 = 15.0°. Suppose you want the wedge and the rod to start from rest and move with constant acceleration, with the rod moving upward 1.00 mm in 8.00 ms. Take m…arrow_forward
- A rectangular current loop (a = 15.0 cm, b = 34.0 cm) is located a distance d = 10.0 cm near a long, straight wire that carries a current (Iw) of 17.0 A (see the drawing). The current in the loop is IL = 21.0 A. Determine the magnitude of the net magnetic force that acts on the loop. Solve in N. a b IL Iwarrow_forwardTwo long, straight wires are separated by distance, d = 22.0 cm. The wires carry currents of I1 = 7.50 A and I2 = 5.50 A in opposite directions, as shown in the figure. Find the magnitude of the net magnetic field at point (B). Let r₁ = 12.0 cm, r2 = 7.00 cm, and r3 = 13.0 cm. Solve in T. 12 d A √3arrow_forwardI tried to solve this question, and I had an "expert" answer it and they got it wrong. I cannot answer this questionarrow_forward
- Eddie Hall is the current world record holder in the deadlift, a powerlifting maneuver in which a weighted barbell is lifted from the ground to waist height, then dropped. The figure below shows a side view of the initial and final positions of the deadlift. a 0 = 55.0° Fift h22.5 cm i hy = 88.0 cm b iarrow_forwardsolve for (_) Narrow_forwardTwo boxes of fruit on a frictionless horizontal surface are connected by a light string as in the figure below, where m₁ = 11 kg and m₂ = 25 kg. A force of F = 80 N is applied to the 25-kg box. mq m1 Applies T Peaches i (a) Determine the acceleration of each box and the tension in the string. acceleration of m₁ acceleration of m₂ tension in the string m/s² m/s² N (b) Repeat the problem for the case where the coefficient of kinetic friction between each box and the surface is 0.10. acceleration of m₁ acceleration of m₂ tension in the string m/s² m/s2 Narrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...
Physics
ISBN:9781305116399
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781285737027
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...
Physics
ISBN:9780078807213
Author:Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Ohm's law Explained; Author: ALL ABOUT ELECTRONICS;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=PV8CMZZKrB4;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY