
Fundamentals of Physics Extended
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781118230725
Author: David Halliday, Robert Resnick, Jearl Walker
Publisher: Wiley, John & Sons, Incorporated
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 27, Problem 35P
GO In Fig. 27-46, ℰ = 12.0 V, R1, = 2000 Ω, R2 = 3000 Ω, and R3 = 4000 Ω. What are the potential differences (a) VA −VB, (b) VB − Vc, (c) Vc − VD, and (d) VA − VC?
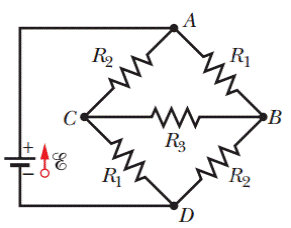
Figure 27-46 Problem 35.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Calculate the center of mass of the hollow cone
shown below. Clearly specify the origin and the
coordinate system you are using.
Z
r
Y
h
X
12. If all three collisions in the figure below are
totally inelastic, which will cause more damage?
(think about which collision has a larger amount of
kinetic energy dissipated/lost to the environment?
I
m
II
III
A. I
B. II
C. III
m
m
v
brick wall
ע
ע
0.5v
2v
0.5m
D. I and II
E. II and III
F. I and III
G. I, II and III (all of them)
2m
Can you solve this 2 question teach me step by step and draw for me
Chapter 27 Solutions
Fundamentals of Physics Extended
Ch. 27 - a In Fig. 27-18a, with R1R2, is the potential...Ch. 27 - a In Fig. 27-18a, are resistors R1 and R3 in...Ch. 27 - You are to connect resistors R1 and R2, with R1R2,...Ch. 27 - In Fig. 27-19, a circuit consists of a battery and...Ch. 27 - For each circuit in Fig 27-20, are the resistors...Ch. 27 - Res-monster maze. In Fig. 27-21, all the resistors...Ch. 27 - A resistor R1 is wired to a battery, then resistor...Ch. 27 - What is the equivalent resistance of three...Ch. 27 - Two resistors are wired to a battery. a In which...Ch. 27 - Cap-monster maze. In Fig. 27-22, all the...
Ch. 27 - Initially, a single resistor, R1 is wired to a...Ch. 27 - After the switch in Fig. 27-15 is closed on point...Ch. 27 - Figure 27-24 shows three sections of circuit that...Ch. 27 - SSM WWW In Fig. 27-25, the ideal batteries have...Ch. 27 - In Fig. 27-26, the ideal batteries have emfs 1 =...Ch. 27 - ILW A car battery with a 12 V emf and an internal...Ch. 27 - GO Figure 27-27 shows a circuit of four resistors...Ch. 27 - A 5.0 A current is set up in a circuit for 6.0 min...Ch. 27 - A standard flashlight battery can deliver about...Ch. 27 - A wire of resistance 5.0 is connected to a...Ch. 27 - A certain car battery with a 12.0 V emf has an...Ch. 27 - a In electron-volts, how much work does an ideal...Ch. 27 - a In Fig. 27-28, what value must R have if the...Ch. 27 - SSM In Fig. 27-29, circuit section AB absorbs...Ch. 27 - Figure 27-30 shows a resistor of resistance R =...Ch. 27 - A 10-km-long underground cable extends east to...Ch. 27 - GO In Fig. 27-32a, both batteries have emf = 1.20...Ch. 27 - ILW The current in a single-loop circuit with one...Ch. 27 - A solar cell generates a potential difference of...Ch. 27 - SSM In Fig. 27-33, battery 1 has emf 1 = 12.0 V...Ch. 27 - In Fig. 27-9, what is the potential difference Vd ...Ch. 27 - A total resistance of 3.00 is to be produced by...Ch. 27 - When resistors 1 and 2 are connected in series,...Ch. 27 - Prob. 21PCh. 27 - Figure 27-34 shows five 5.00 resistors. Find the...Ch. 27 - In Fig. 27-35, R1 = 100 , R2 = 50 , and the ideal...Ch. 27 - In Fig. 27-36, R1 = R2 = 4.00 and R3 = 2.50 ....Ch. 27 - SSM Nine copper wires of length l and diameter d...Ch. 27 - Figure 27-37 shows a battery connected across a...Ch. 27 - Side flash. Figure 27-38 indicates one reason no...Ch. 27 - The ideal battery in Fig. 27-39a has emf = 6.0 V....Ch. 27 - In Fig. 27-40, R1 = 6.00 , R2 = 18.0 , and the...Ch. 27 - GO In Fig. 27-41, the ideal batteries have emfs 1...Ch. 27 - SSMGO In Fig. 27-42, the ideal batteries have emfs...Ch. 27 - Both batteries in Fig. 27-43a are ideal. Emf 1 of...Ch. 27 - GO In Fig. 27-44. the current in resistance 6 is...Ch. 27 - The resistances in Figs. 27-45a and b are all 6.0...Ch. 27 - GO In Fig. 27-46, = 12.0 V, R1, = 2000 , R2 =...Ch. 27 - GO In Fig. 27-47, 1 = 6.00 V, 2 = 12.0 V, R1, =...Ch. 27 - In Fig. 27-48, the resistances are R1 = 2.00 , R2...Ch. 27 - Figure 27-49 shows a section of a circuit. The...Ch. 27 - GO In Fig. 27-50, two batteries with an emf =...Ch. 27 - GO Two identical batteries of emf = 12.0 V and...Ch. 27 - In Fig. 27-41, 1 = 3.00 V, 2 = 1.00 V, R1 = 4.00 ,...Ch. 27 - In Fig. 27-52, an array of n parallel resistors is...Ch. 27 - You are given a number of 10 resistors, each...Ch. 27 - GO In Fig. 27-53, R1 = 100 , R2 = R3 = 50.0 , R4 =...Ch. 27 - ILW In Fig. 27-54, the resistances are R1 = 1.0 ...Ch. 27 - In Fig. 27-55a, resistor 3 is a variable resistor...Ch. 27 - SSM A copper wire of radius a = 0.250 mm has an...Ch. 27 - GO In Fig. 27-53, the resistors have the values R1...Ch. 27 - ILW a In Fig. 27-56, what current does the ammeter...Ch. 27 - In Fig. 27-57, R1 = 2.00R, the ammeter resistance...Ch. 27 - In Fig. 27-58, a voltmeter of resistance Rv= 300 ...Ch. 27 - A simple ohmmeter is made by connecting a 1.50V...Ch. 27 - In Fig. 27-14, assume that = 3.0 V, r = 100 , R1 =...Ch. 27 - When the lights of a car are switched on, an...Ch. 27 - In Fig. 27-61, Rsis to be adjusted in value by...Ch. 27 - In Fig. 27-62. a voltmeter of resistance Rv = 300 ...Ch. 27 - Switch S in Fig. 27-63 is closed at time t = 0, to...Ch. 27 - In an RC series circuit, emf = 12.0 V, resistance...Ch. 27 - SSM What multiple of the time constant gives the...Ch. 27 - A capacitor with initial charge q0 is discharge...Ch. 27 - ILW A 15.0 k resistor and a capacitor are...Ch. 27 - Figure 27-64 shows the circuit of a flashing lamp,...Ch. 27 - SSM WWWIn the circuit of Fig. 27-65, = 1.2 kV, C=...Ch. 27 - A capacitor with an initial potential difference...Ch. 27 - GO In Fig. 27-66. R1 = 10.0 k, R2 = 15.0 k, C=...Ch. 27 - Figure 27-67 display two circuits with a charged...Ch. 27 - The potential difference between the plates of a...Ch. 27 - A 1.0 F capacitor with an initial stored energy of...Ch. 27 - GO A 3.00 M resistor and a 1.00 F capacitor are...Ch. 27 - GO Each of the six real batteries in Fig. 27-68...Ch. 27 - In Fig. 27-69, R1 = 20.0 , R2 = 10.0 , and the...Ch. 27 - In Fig.27-70, the ideal battery has emf = 30.0 V,...Ch. 27 - SSM Wires A and B, having equal lengths of 40.0 m...Ch. 27 - What are the a size and b direction up or down of...Ch. 27 - Suppose that, while you are sitting in a chair,...Ch. 27 - GO In Fig. 27-72, the ideal batteries have emfs 1...Ch. 27 - SSM A temperature-stable resistor is made by...Ch. 27 - In Fig. 27-14, assume that = 5.0 V, r = 2.0 , R1...Ch. 27 - SSM An initially uncharged capacitor C is fully...Ch. 27 - In Fig. 27-73, R1 = 5.00 , R2 = 10.0 , R3 = 15.0 ,...Ch. 27 - In Fig. 27-5a, find the potential difference...Ch. 27 - In Fig. 27-8a, calculate the potential difference...Ch. 27 - SSM A controller on an electronic arcade game...Ch. 27 - An automobile gasoline gauge is shown...Ch. 27 - SSM The starting motor of a car is turning too...Ch. 27 - Two resistors R1 and R2 may be connected either in...Ch. 27 - The circuit of Fig. 27-25 shows a capacitor, two...Ch. 27 - In Fig. 27-41, R1 = 10.0 , R2 = 20.0 , and the...Ch. 27 - In Fig. 27-76, R= 10 . what is the equivalent...Ch. 27 - a In Fig. 27-4a, show that the rate at which...Ch. 27 - In Fig. 27-77, the ideal batteries have emfs 1 =...Ch. 27 - Figure 27-28 shows a portion of a circuit through...Ch. 27 - Thermal energy is to be generated in a 0.10 ...Ch. 27 - Figure 27-29 shows three 20.0 resistors. Find the...Ch. 27 - A 120 V power line is protected by a 15 A fuse....Ch. 27 - Figure 27-63 shows an ideal battery of emf = 12...Ch. 27 - SSM A group of N identical batteries of emf and...Ch. 27 - SSM In Fig. 27-48, R1 = R2 = 10.0 , and the ideal...Ch. 27 - SSM In Fig. 27-66, the ideal battery has emf = 30...Ch. 27 - In Fig. 27-81, the ideal batteries have emfs 1 =...Ch. 27 - In Fig. 27-82, an ideal battery of emf = 12.0 V...Ch. 27 - The following table gives the electric potential...Ch. 27 - In Fig. 27-83, 1 = 6.00 V, 2 = 12.0 V, R1= 200 ...Ch. 27 - A three-way 120 V lamp bulb that contains two...Ch. 27 - In Fig. 27-84, R1 = R2 = 2.0 , R3 = 4.0 , R4 = 3.0...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
In the datura plant, purple flower color is controlled by a dominant allele P. White flowers are found in plant...
Genetic Analysis: An Integrated Approach (3rd Edition)
Draw the structure of the monomer or monomers used to synthesize the following polymers, and indicate whether e...
Organic Chemistry (8th Edition)
Does the change in velocity of seismic waves with increasing depth in the lower mantle indicate that the rock i...
Applications and Investigations in Earth Science (9th Edition)
Heat lamps are commonly used to maintain foods at about 50C for as long as 12 hours in cafeteria serving lines....
Microbiology: An Introduction
2. Whether an allele is dominant or recessive depends on
a. how common the allele is, relative to other alleles...
Campbell Biology: Concepts & Connections (9th Edition)
What are the four types of tissues, and what are their characteristics?
Human Anatomy & Physiology (2nd Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- From this question and answer can you explain how get (0,0,5) and (5,0,,0) and can you teach me how to solve thisarrow_forwardCan you solve this 2 question and teach me using ( engineer method formula)arrow_forward11. If all three collisions in the figure below are totally inelastic, which brings the car of mass (m) on the left to a halt? I m II III m m ע ע ע brick wall 0.5v 2m 2v 0.5m A. I B. II C. III D. I and II E. II and III F. I and III G. I, II and III (all of them)arrow_forward
- How can you tell which vowel is being produced here ( “ee,” “ah,” or “oo”)? Also, how would you be able to tell for the other vowels?arrow_forwardYou want to fabricate a soft microfluidic chip like the one below. How would you go about fabricating this chip knowing that you are targeting a channel with a square cross-sectional profile of 200 μm by 200 μm. What materials and steps would you use and why? Disregard the process to form the inlet and outlet. Square Cross Sectionarrow_forward1. What are the key steps involved in the fabrication of a semiconductor device. 2. You are hired by a chip manufacturing company, and you are asked to prepare a silicon wafer with the pattern below. Describe the process you would use. High Aspect Ratio Trenches Undoped Si Wafer P-doped Si 3. You would like to deposit material within a high aspect ratio trench. What approach would you use and why? 4. A person is setting up a small clean room space to carry out an outreach activity to educate high school students about patterning using photolithography. They obtained a positive photoresist, a used spin coater, a high energy light lamp for exposure and ordered a plastic transparency mask with a pattern on it to reduce cost. Upon trying this set up multiple times they find that the full resist gets developed, and they are unable to transfer the pattern onto the resist. Help them troubleshoot and find out why pattern of transfer has not been successful. 5. You are given a composite…arrow_forward
- Two complex values are z1=8 + 8i, z2=15 + 7 i. z1∗ and z2∗ are the complex conjugate values. Any complex value can be expessed in the form of a+bi=reiθ. Find r and θ for (z1-z∗2)/z1+z2∗. Find r and θ for (z1−z2∗)z1z2∗ Please show all stepsarrow_forwardAn electromagnetic wave is traveling through vacuum in the positive x direction. Its electric field vector is given by E=E0sin(kx−ωt)j^,where j^ is the unit vector in the y direction. If B0 is the amplitude of the magnetic field vector, find the complete expression for the magnetic field vector B→ of the wave. What is the Poynting vector S(x,t), that is, the power per unit area associated with the electromagnetic wave described in the problem introduction? Give your answer in terms of some or all of the variables E0, B0, k, x, ω, t, and μ0. Specify the direction of the Poynting vector using the unit vectors i^, j^, and k^ as appropriate. Please explain all stepsarrow_forwardAnother worker is performing a task with an RWL of only 9 kg and is lifting 18 kg, giving him an LI of 2.0 (high risk). Questions:What is the primary issue according to NIOSH?Name two factors of the RWL that could be improved to reduce risk.If the horizontal distance is reduced from 50 cm to 30 cm, how does the HM change and what effect would it have?arrow_forward
- Two complex values are z1=8 + 8i, z2=15 + 7 i. z1∗ and z2∗ are the complex conjugate values. Any complex value can be expessed in the form of a+bi=reiθ. Find r and θ for z1z2∗. Find r and θ for z1/z2∗? Find r and θ for (z1−z2)∗/z1+z2∗. Find r and θ for (z1−z2)∗/z1z2∗ Please explain all steps, Thank youarrow_forwardAn ac series circuit consists of a voltage source of frequency 60 Hz and voltage amplitude V, a 505-Ω resistor, and a capacitor of capacitance 7.2 μF. What must be the source voltage amplitude V for the average electrical power consumed in the resistor to be 236 W? There is no inductance in the circuit.arrow_forwardAn L−R−C series circuit has R= 280 Ω . At the frequency of the source, the inductor has reactance XLL= 905 Ω and the capacitor has reactance XC= 485 Ω . The amplitude of the voltage across the inductor is 445 V . What is the amplitude of the voltage across the resistor and the capacitor? What is the voltage amplitude of the source? What is the rate at which the source is delivering electrical energy to the circuit?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 3PhysicsISBN:9781938168185Author:William Moebs, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax
University Physics Volume 3PhysicsISBN:9781938168185Author:William Moebs, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...
Physics
ISBN:9781305116399
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 3
Physics
ISBN:9781938168185
Author:William Moebs, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:OpenStax

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781938168000
Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Publisher:OpenStax College
Ohm's law Explained; Author: ALL ABOUT ELECTRONICS;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=PV8CMZZKrB4;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY