
Fundamentals of Physics Extended
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781118230725
Author: David Halliday, Robert Resnick, Jearl Walker
Publisher: Wiley, John & Sons, Incorporated
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 27, Problem 11P
SSM In Fig. 27-29, circuit section AB absorbs energy at a rate of 50 W when current i = 1.0 A through it is in the indicated direction. Resistance R = 2.0 Ω. (a) What is the potential difference between A and B? Emf device X lacks internal resistance. (b) What is its emf? (c) Is point B connected to the positive terminal of X or to the negative terminal?
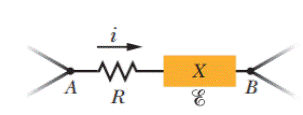
Figure 27-29 Problem 11.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Solve and answer the problem correctly and be sure to check your work. Thank you!!
The spring in the figure has a spring constant of 1300 N/m. It is compressed 17.0 cm, then launches a 200 g block. The horizontal surface is frictionless, but the block’s coefficient of kinetic friction on the incline is 0.200. What distance d does the block sail through the air?
Solve and answer the problem correctly and be sure to check your work. Thank you!!
Chapter 27 Solutions
Fundamentals of Physics Extended
Ch. 27 - a In Fig. 27-18a, with R1R2, is the potential...Ch. 27 - a In Fig. 27-18a, are resistors R1 and R3 in...Ch. 27 - You are to connect resistors R1 and R2, with R1R2,...Ch. 27 - In Fig. 27-19, a circuit consists of a battery and...Ch. 27 - For each circuit in Fig 27-20, are the resistors...Ch. 27 - Res-monster maze. In Fig. 27-21, all the resistors...Ch. 27 - A resistor R1 is wired to a battery, then resistor...Ch. 27 - What is the equivalent resistance of three...Ch. 27 - Two resistors are wired to a battery. a In which...Ch. 27 - Cap-monster maze. In Fig. 27-22, all the...
Ch. 27 - Initially, a single resistor, R1 is wired to a...Ch. 27 - After the switch in Fig. 27-15 is closed on point...Ch. 27 - Figure 27-24 shows three sections of circuit that...Ch. 27 - SSM WWW In Fig. 27-25, the ideal batteries have...Ch. 27 - In Fig. 27-26, the ideal batteries have emfs 1 =...Ch. 27 - ILW A car battery with a 12 V emf and an internal...Ch. 27 - GO Figure 27-27 shows a circuit of four resistors...Ch. 27 - A 5.0 A current is set up in a circuit for 6.0 min...Ch. 27 - A standard flashlight battery can deliver about...Ch. 27 - A wire of resistance 5.0 is connected to a...Ch. 27 - A certain car battery with a 12.0 V emf has an...Ch. 27 - a In electron-volts, how much work does an ideal...Ch. 27 - a In Fig. 27-28, what value must R have if the...Ch. 27 - SSM In Fig. 27-29, circuit section AB absorbs...Ch. 27 - Figure 27-30 shows a resistor of resistance R =...Ch. 27 - A 10-km-long underground cable extends east to...Ch. 27 - GO In Fig. 27-32a, both batteries have emf = 1.20...Ch. 27 - ILW The current in a single-loop circuit with one...Ch. 27 - A solar cell generates a potential difference of...Ch. 27 - SSM In Fig. 27-33, battery 1 has emf 1 = 12.0 V...Ch. 27 - In Fig. 27-9, what is the potential difference Vd ...Ch. 27 - A total resistance of 3.00 is to be produced by...Ch. 27 - When resistors 1 and 2 are connected in series,...Ch. 27 - Prob. 21PCh. 27 - Figure 27-34 shows five 5.00 resistors. Find the...Ch. 27 - In Fig. 27-35, R1 = 100 , R2 = 50 , and the ideal...Ch. 27 - In Fig. 27-36, R1 = R2 = 4.00 and R3 = 2.50 ....Ch. 27 - SSM Nine copper wires of length l and diameter d...Ch. 27 - Figure 27-37 shows a battery connected across a...Ch. 27 - Side flash. Figure 27-38 indicates one reason no...Ch. 27 - The ideal battery in Fig. 27-39a has emf = 6.0 V....Ch. 27 - In Fig. 27-40, R1 = 6.00 , R2 = 18.0 , and the...Ch. 27 - GO In Fig. 27-41, the ideal batteries have emfs 1...Ch. 27 - SSMGO In Fig. 27-42, the ideal batteries have emfs...Ch. 27 - Both batteries in Fig. 27-43a are ideal. Emf 1 of...Ch. 27 - GO In Fig. 27-44. the current in resistance 6 is...Ch. 27 - The resistances in Figs. 27-45a and b are all 6.0...Ch. 27 - GO In Fig. 27-46, = 12.0 V, R1, = 2000 , R2 =...Ch. 27 - GO In Fig. 27-47, 1 = 6.00 V, 2 = 12.0 V, R1, =...Ch. 27 - In Fig. 27-48, the resistances are R1 = 2.00 , R2...Ch. 27 - Figure 27-49 shows a section of a circuit. The...Ch. 27 - GO In Fig. 27-50, two batteries with an emf =...Ch. 27 - GO Two identical batteries of emf = 12.0 V and...Ch. 27 - In Fig. 27-41, 1 = 3.00 V, 2 = 1.00 V, R1 = 4.00 ,...Ch. 27 - In Fig. 27-52, an array of n parallel resistors is...Ch. 27 - You are given a number of 10 resistors, each...Ch. 27 - GO In Fig. 27-53, R1 = 100 , R2 = R3 = 50.0 , R4 =...Ch. 27 - ILW In Fig. 27-54, the resistances are R1 = 1.0 ...Ch. 27 - In Fig. 27-55a, resistor 3 is a variable resistor...Ch. 27 - SSM A copper wire of radius a = 0.250 mm has an...Ch. 27 - GO In Fig. 27-53, the resistors have the values R1...Ch. 27 - ILW a In Fig. 27-56, what current does the ammeter...Ch. 27 - In Fig. 27-57, R1 = 2.00R, the ammeter resistance...Ch. 27 - In Fig. 27-58, a voltmeter of resistance Rv= 300 ...Ch. 27 - A simple ohmmeter is made by connecting a 1.50V...Ch. 27 - In Fig. 27-14, assume that = 3.0 V, r = 100 , R1 =...Ch. 27 - When the lights of a car are switched on, an...Ch. 27 - In Fig. 27-61, Rsis to be adjusted in value by...Ch. 27 - In Fig. 27-62. a voltmeter of resistance Rv = 300 ...Ch. 27 - Switch S in Fig. 27-63 is closed at time t = 0, to...Ch. 27 - In an RC series circuit, emf = 12.0 V, resistance...Ch. 27 - SSM What multiple of the time constant gives the...Ch. 27 - A capacitor with initial charge q0 is discharge...Ch. 27 - ILW A 15.0 k resistor and a capacitor are...Ch. 27 - Figure 27-64 shows the circuit of a flashing lamp,...Ch. 27 - SSM WWWIn the circuit of Fig. 27-65, = 1.2 kV, C=...Ch. 27 - A capacitor with an initial potential difference...Ch. 27 - GO In Fig. 27-66. R1 = 10.0 k, R2 = 15.0 k, C=...Ch. 27 - Figure 27-67 display two circuits with a charged...Ch. 27 - The potential difference between the plates of a...Ch. 27 - A 1.0 F capacitor with an initial stored energy of...Ch. 27 - GO A 3.00 M resistor and a 1.00 F capacitor are...Ch. 27 - GO Each of the six real batteries in Fig. 27-68...Ch. 27 - In Fig. 27-69, R1 = 20.0 , R2 = 10.0 , and the...Ch. 27 - In Fig.27-70, the ideal battery has emf = 30.0 V,...Ch. 27 - SSM Wires A and B, having equal lengths of 40.0 m...Ch. 27 - What are the a size and b direction up or down of...Ch. 27 - Suppose that, while you are sitting in a chair,...Ch. 27 - GO In Fig. 27-72, the ideal batteries have emfs 1...Ch. 27 - SSM A temperature-stable resistor is made by...Ch. 27 - In Fig. 27-14, assume that = 5.0 V, r = 2.0 , R1...Ch. 27 - SSM An initially uncharged capacitor C is fully...Ch. 27 - In Fig. 27-73, R1 = 5.00 , R2 = 10.0 , R3 = 15.0 ,...Ch. 27 - In Fig. 27-5a, find the potential difference...Ch. 27 - In Fig. 27-8a, calculate the potential difference...Ch. 27 - SSM A controller on an electronic arcade game...Ch. 27 - An automobile gasoline gauge is shown...Ch. 27 - SSM The starting motor of a car is turning too...Ch. 27 - Two resistors R1 and R2 may be connected either in...Ch. 27 - The circuit of Fig. 27-25 shows a capacitor, two...Ch. 27 - In Fig. 27-41, R1 = 10.0 , R2 = 20.0 , and the...Ch. 27 - In Fig. 27-76, R= 10 . what is the equivalent...Ch. 27 - a In Fig. 27-4a, show that the rate at which...Ch. 27 - In Fig. 27-77, the ideal batteries have emfs 1 =...Ch. 27 - Figure 27-28 shows a portion of a circuit through...Ch. 27 - Thermal energy is to be generated in a 0.10 ...Ch. 27 - Figure 27-29 shows three 20.0 resistors. Find the...Ch. 27 - A 120 V power line is protected by a 15 A fuse....Ch. 27 - Figure 27-63 shows an ideal battery of emf = 12...Ch. 27 - SSM A group of N identical batteries of emf and...Ch. 27 - SSM In Fig. 27-48, R1 = R2 = 10.0 , and the ideal...Ch. 27 - SSM In Fig. 27-66, the ideal battery has emf = 30...Ch. 27 - In Fig. 27-81, the ideal batteries have emfs 1 =...Ch. 27 - In Fig. 27-82, an ideal battery of emf = 12.0 V...Ch. 27 - The following table gives the electric potential...Ch. 27 - In Fig. 27-83, 1 = 6.00 V, 2 = 12.0 V, R1= 200 ...Ch. 27 - A three-way 120 V lamp bulb that contains two...Ch. 27 - In Fig. 27-84, R1 = R2 = 2.0 , R3 = 4.0 , R4 = 3.0...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
Explain why the entire pattern of isotherms has a more northerly location on the July map than on the January m...
Applications and Investigations in Earth Science (9th Edition)
The way of finding the concentration of acid and base via using neutralization reaction is to be interpreted. C...
Living By Chemistry: First Edition Textbook
2. Figure P26.2 shows voltage and current graphs for a resistor.
a. What is the value of the resistance R?
b. W...
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
Another cross in Drosophila involved the recessive, X-linked genes yellow (y), white (w), and cut (ct). A yello...
Concepts of Genetics (12th Edition)
How did Pasteur’s experiment with “swan-necked” flasks disprove the theory of spontaneous generation?
Microbiology: Principles and Explorations
How could the metaphyseal area of a bone help determine the age of a skeleton?
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Solve and answer the problem correctly and be sure to check your work. Thank you!!arrow_forwardA 10-m-long glider with a mass of 680 kg (including the passengers) is gliding horizontally through the air at 28 m/s when a 60 kg skydiver drops out by releasing his grip on the glider. What is the glider's speed just after the skydiver lets go?arrow_forwardPROBLEM 2 A cube of mass m is placed in a rotating funnel. (The funnel is rotating around the vertical axis shown in the diagram.) There is no friction between the cube and the funnel but the funnel is rotating at just the right speed needed to keep the cube rotating with the funnel. The cube travels in a circular path of radius r, and the angle between the vertical and the wall of the funnel is 0. Express your answers to parts (b) and (c) in terms of m, r, g, and/or 0. (a) Sketch a free-body diagram for the cube. Show all the forces acting on it, and show the appropriate coordinate system to use for this problem. (b) What is the normal force acting on the cube? FN=mg58 (c) What is the speed v of the cube? (d) If the speed of the cube is different from what you determined in part (c), a force of friction is necessary to keep the cube from slipping in the funnel. If the funnel is rotating slower than it was above, draw a new free-body diagram for the cube to show which way friction…arrow_forward
- Circular turns of radius r in a race track are often banked at an angle θ to allow the cars to achieve higher speeds around the turns. Assume friction is not present. Write an expression for the tan(θ) of a car going around the banked turn in terms of the car's speed v, the radius of the turn r, and g so that the car will not move up or down the incline of the turn. tan(θ) =arrow_forwardThe character Min Min from Arms was a DLC character added to Super Smash Bros. Min Min’s arms are large springs, with a spring constant of 8.53 ⋅ 10^3 N/m, which she uses to punch and fling away her opponents. Min Min pushes her spring arm against Steve, who is not moving, compressing it 1.20 m as shown in figure A. Steve has a mass of 81.6 kg. Assuming she uses only the spring to launch Steve, how fast is Steve moving when the spring is no longer compressed? As Steve goes flying away he goes over the edge of the level, as shown in figure C. What is the magnitude of Steve’s velocity when he is 2.00 m below where he started?arrow_forwardSlinky dog whose middle section is a giant spring with a spring constant of 10.9 N/m. Woody, who has a mass of 0.412 kg, grabs onto the tail end of Slink and steps off the bed with no initial velocity and reaches the floor right as his velocity hits zero again. How high is the bed? What is Woody’s velocity halfway down? Enter just the magnitude of velocity.arrow_forward
- No chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwardA positive charge of 91 is located 5.11 m to the left of a negative charge 92. The charges have different magnitudes. On the line through the charges, the net electric field is zero at a spot 2.90 m to the right of the negative charge. On this line there are also two spots where the potential is zero. (a) How far to the left of the negative charge is one spot? (b) How far to the right of the negative charge is the other?arrow_forwardA charge of -3.99 μC is fixed in place. From a horizontal distance of 0.0423 m, a particle of mass 7.31 x 103 kg and charge -9.76 µC is fired with an initial speed of 84.1 m/s directly toward the fixed charge. How far does the particle travel before its speed is zero?arrow_forward
- a) What is the minimum tension in N that the cable must be able to support without breaking? Assume the cable is massless. T = b) If the cable can only support a tension of 10,000 N what is the highest mass the ball can have in kg? mm =arrow_forwardCurve Fitter CURVE FITTER Open Update Fit Save New Exclusion Rules Select Validation Data Polynomial Exponential Logarithmic Auto Fourier Fit Fit Duplicate Data Manual FILE DATA FIT TYPE FIT Harmonic Motion X us 0.45 mi ce 0.4 0.35 0.3 0.25 0.2 Residuals Plot Contour Plot Plot Prediction Bounds None VISUALIZATION Colormap Export PREFERENCES EXPORT Fit Options COA Fourier Equation Fit Plot x vs. t -Harmonic Motion a0+ a1*cos(x*w) + b1*sin(x*w) Number of terms Center and scale 1 ▸ Advanced Options Read about fit options Results Value Lower Upper 0.15 a0 0.1586 0.1551 0.1620 a1 0.0163 0.0115 0.0211 0.1 b1 0.0011 -0.0093 0.0115 W 1.0473 0.9880 1.1066 2 8 10 t 12 14 16 18 20 Goodness of Fit Value Table of Fits SSE 0.2671 Fit State Fit name Data Harmonic Motion x vs. t Fit type fourier1 R-square 0.13345 SSE DFE 0.26712 296 Adj R-sq 0.12467 RMSE 0.030041 # Coeff Valic R-square 0.1335 4 DFE 296.0000 Adj R-sq 0.1247 RMSE 0.0300arrow_forwardWhat point on the spring or different masses should be the place to measure the displacement of the spring? For instance, should you measure to the bottom of the hanging masses?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...
Physics
ISBN:9781305116399
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781938168000
Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Publisher:OpenStax College

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781285737027
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Ohm's law Explained; Author: ALL ABOUT ELECTRONICS;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=PV8CMZZKrB4;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY