
Fundamentals of Physics Extended
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781118230725
Author: David Halliday, Robert Resnick, Jearl Walker
Publisher: Wiley, John & Sons, Incorporated
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 27, Problem 10P
(a) In Fig. 27-28, what value must R have if the current in the circuit is to be 1.0mA? Take ℰ1 = 2.0 V, ℰ2 = 3.0 V, and r1 = r2 = 3.0 Ω. (b) What is the rate at which thermal energy appears in R?
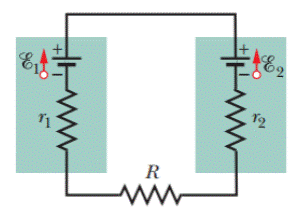
Figure 27-28 Problem 10.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
3
Set
ба
||Axl
49.32
6b
71
Ay
22
Magnitude of A
Angle of A
24.04
Angle of -A
22
54
155.96
° (pos Ax) 204.04
° (neg Ax) 335.96
°
(pos Ax)
° (neg Ax)
115.77
° (pos Ax) 295.77
° (pos Ax)
-39
81
208.78
° (neg Ax) 28.78
°
(neg Ax)
3AA . not sure what i am getting wrong
Chapter 27 Solutions
Fundamentals of Physics Extended
Ch. 27 - a In Fig. 27-18a, with R1R2, is the potential...Ch. 27 - a In Fig. 27-18a, are resistors R1 and R3 in...Ch. 27 - You are to connect resistors R1 and R2, with R1R2,...Ch. 27 - In Fig. 27-19, a circuit consists of a battery and...Ch. 27 - For each circuit in Fig 27-20, are the resistors...Ch. 27 - Res-monster maze. In Fig. 27-21, all the resistors...Ch. 27 - A resistor R1 is wired to a battery, then resistor...Ch. 27 - What is the equivalent resistance of three...Ch. 27 - Two resistors are wired to a battery. a In which...Ch. 27 - Cap-monster maze. In Fig. 27-22, all the...
Ch. 27 - Initially, a single resistor, R1 is wired to a...Ch. 27 - After the switch in Fig. 27-15 is closed on point...Ch. 27 - Figure 27-24 shows three sections of circuit that...Ch. 27 - SSM WWW In Fig. 27-25, the ideal batteries have...Ch. 27 - In Fig. 27-26, the ideal batteries have emfs 1 =...Ch. 27 - ILW A car battery with a 12 V emf and an internal...Ch. 27 - GO Figure 27-27 shows a circuit of four resistors...Ch. 27 - A 5.0 A current is set up in a circuit for 6.0 min...Ch. 27 - A standard flashlight battery can deliver about...Ch. 27 - A wire of resistance 5.0 is connected to a...Ch. 27 - A certain car battery with a 12.0 V emf has an...Ch. 27 - a In electron-volts, how much work does an ideal...Ch. 27 - a In Fig. 27-28, what value must R have if the...Ch. 27 - SSM In Fig. 27-29, circuit section AB absorbs...Ch. 27 - Figure 27-30 shows a resistor of resistance R =...Ch. 27 - A 10-km-long underground cable extends east to...Ch. 27 - GO In Fig. 27-32a, both batteries have emf = 1.20...Ch. 27 - ILW The current in a single-loop circuit with one...Ch. 27 - A solar cell generates a potential difference of...Ch. 27 - SSM In Fig. 27-33, battery 1 has emf 1 = 12.0 V...Ch. 27 - In Fig. 27-9, what is the potential difference Vd ...Ch. 27 - A total resistance of 3.00 is to be produced by...Ch. 27 - When resistors 1 and 2 are connected in series,...Ch. 27 - Prob. 21PCh. 27 - Figure 27-34 shows five 5.00 resistors. Find the...Ch. 27 - In Fig. 27-35, R1 = 100 , R2 = 50 , and the ideal...Ch. 27 - In Fig. 27-36, R1 = R2 = 4.00 and R3 = 2.50 ....Ch. 27 - SSM Nine copper wires of length l and diameter d...Ch. 27 - Figure 27-37 shows a battery connected across a...Ch. 27 - Side flash. Figure 27-38 indicates one reason no...Ch. 27 - The ideal battery in Fig. 27-39a has emf = 6.0 V....Ch. 27 - In Fig. 27-40, R1 = 6.00 , R2 = 18.0 , and the...Ch. 27 - GO In Fig. 27-41, the ideal batteries have emfs 1...Ch. 27 - SSMGO In Fig. 27-42, the ideal batteries have emfs...Ch. 27 - Both batteries in Fig. 27-43a are ideal. Emf 1 of...Ch. 27 - GO In Fig. 27-44. the current in resistance 6 is...Ch. 27 - The resistances in Figs. 27-45a and b are all 6.0...Ch. 27 - GO In Fig. 27-46, = 12.0 V, R1, = 2000 , R2 =...Ch. 27 - GO In Fig. 27-47, 1 = 6.00 V, 2 = 12.0 V, R1, =...Ch. 27 - In Fig. 27-48, the resistances are R1 = 2.00 , R2...Ch. 27 - Figure 27-49 shows a section of a circuit. The...Ch. 27 - GO In Fig. 27-50, two batteries with an emf =...Ch. 27 - GO Two identical batteries of emf = 12.0 V and...Ch. 27 - In Fig. 27-41, 1 = 3.00 V, 2 = 1.00 V, R1 = 4.00 ,...Ch. 27 - In Fig. 27-52, an array of n parallel resistors is...Ch. 27 - You are given a number of 10 resistors, each...Ch. 27 - GO In Fig. 27-53, R1 = 100 , R2 = R3 = 50.0 , R4 =...Ch. 27 - ILW In Fig. 27-54, the resistances are R1 = 1.0 ...Ch. 27 - In Fig. 27-55a, resistor 3 is a variable resistor...Ch. 27 - SSM A copper wire of radius a = 0.250 mm has an...Ch. 27 - GO In Fig. 27-53, the resistors have the values R1...Ch. 27 - ILW a In Fig. 27-56, what current does the ammeter...Ch. 27 - In Fig. 27-57, R1 = 2.00R, the ammeter resistance...Ch. 27 - In Fig. 27-58, a voltmeter of resistance Rv= 300 ...Ch. 27 - A simple ohmmeter is made by connecting a 1.50V...Ch. 27 - In Fig. 27-14, assume that = 3.0 V, r = 100 , R1 =...Ch. 27 - When the lights of a car are switched on, an...Ch. 27 - In Fig. 27-61, Rsis to be adjusted in value by...Ch. 27 - In Fig. 27-62. a voltmeter of resistance Rv = 300 ...Ch. 27 - Switch S in Fig. 27-63 is closed at time t = 0, to...Ch. 27 - In an RC series circuit, emf = 12.0 V, resistance...Ch. 27 - SSM What multiple of the time constant gives the...Ch. 27 - A capacitor with initial charge q0 is discharge...Ch. 27 - ILW A 15.0 k resistor and a capacitor are...Ch. 27 - Figure 27-64 shows the circuit of a flashing lamp,...Ch. 27 - SSM WWWIn the circuit of Fig. 27-65, = 1.2 kV, C=...Ch. 27 - A capacitor with an initial potential difference...Ch. 27 - GO In Fig. 27-66. R1 = 10.0 k, R2 = 15.0 k, C=...Ch. 27 - Figure 27-67 display two circuits with a charged...Ch. 27 - The potential difference between the plates of a...Ch. 27 - A 1.0 F capacitor with an initial stored energy of...Ch. 27 - GO A 3.00 M resistor and a 1.00 F capacitor are...Ch. 27 - GO Each of the six real batteries in Fig. 27-68...Ch. 27 - In Fig. 27-69, R1 = 20.0 , R2 = 10.0 , and the...Ch. 27 - In Fig.27-70, the ideal battery has emf = 30.0 V,...Ch. 27 - SSM Wires A and B, having equal lengths of 40.0 m...Ch. 27 - What are the a size and b direction up or down of...Ch. 27 - Suppose that, while you are sitting in a chair,...Ch. 27 - GO In Fig. 27-72, the ideal batteries have emfs 1...Ch. 27 - SSM A temperature-stable resistor is made by...Ch. 27 - In Fig. 27-14, assume that = 5.0 V, r = 2.0 , R1...Ch. 27 - SSM An initially uncharged capacitor C is fully...Ch. 27 - In Fig. 27-73, R1 = 5.00 , R2 = 10.0 , R3 = 15.0 ,...Ch. 27 - In Fig. 27-5a, find the potential difference...Ch. 27 - In Fig. 27-8a, calculate the potential difference...Ch. 27 - SSM A controller on an electronic arcade game...Ch. 27 - An automobile gasoline gauge is shown...Ch. 27 - SSM The starting motor of a car is turning too...Ch. 27 - Two resistors R1 and R2 may be connected either in...Ch. 27 - The circuit of Fig. 27-25 shows a capacitor, two...Ch. 27 - In Fig. 27-41, R1 = 10.0 , R2 = 20.0 , and the...Ch. 27 - In Fig. 27-76, R= 10 . what is the equivalent...Ch. 27 - a In Fig. 27-4a, show that the rate at which...Ch. 27 - In Fig. 27-77, the ideal batteries have emfs 1 =...Ch. 27 - Figure 27-28 shows a portion of a circuit through...Ch. 27 - Thermal energy is to be generated in a 0.10 ...Ch. 27 - Figure 27-29 shows three 20.0 resistors. Find the...Ch. 27 - A 120 V power line is protected by a 15 A fuse....Ch. 27 - Figure 27-63 shows an ideal battery of emf = 12...Ch. 27 - SSM A group of N identical batteries of emf and...Ch. 27 - SSM In Fig. 27-48, R1 = R2 = 10.0 , and the ideal...Ch. 27 - SSM In Fig. 27-66, the ideal battery has emf = 30...Ch. 27 - In Fig. 27-81, the ideal batteries have emfs 1 =...Ch. 27 - In Fig. 27-82, an ideal battery of emf = 12.0 V...Ch. 27 - The following table gives the electric potential...Ch. 27 - In Fig. 27-83, 1 = 6.00 V, 2 = 12.0 V, R1= 200 ...Ch. 27 - A three-way 120 V lamp bulb that contains two...Ch. 27 - In Fig. 27-84, R1 = R2 = 2.0 , R3 = 4.0 , R4 = 3.0...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
16. Explain some of the reasons why the human species has been able to expand in number and distribution to a g...
Campbell Biology: Concepts & Connections (9th Edition)
Write a balanced chemical equation for each chemical reaction. a. Solid copper reacts with solid sulfur to form...
Introductory Chemistry (6th Edition)
The glycine cleavage system is a group of four enzymes that together catalyze the following reaction: glycine+T...
Organic Chemistry (8th Edition)
Choose the best answer to each of the following. Explain your reasoning. Which of a planets fundamental propert...
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
Could an organism be a fermenter and also be both MR and V—P negative? Explain.
Laboratory Experiments in Microbiology (12th Edition) (What's New in Microbiology)
In pea plants, plant height, seed shape, and seed color are governed by three independently assorting genes. Th...
Genetic Analysis: An Integrated Approach (3rd Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill University Physics Volume 3PhysicsISBN:9781938168185Author:William Moebs, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax
University Physics Volume 3PhysicsISBN:9781938168185Author:William Moebs, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781285737027
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...
Physics
ISBN:9781305116399
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...
Physics
ISBN:9780078807213
Author:Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill

University Physics Volume 3
Physics
ISBN:9781938168185
Author:William Moebs, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:OpenStax
Ohm's law Explained; Author: ALL ABOUT ELECTRONICS;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=PV8CMZZKrB4;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY