
Concept explainers
Describe what is meant by each of the following reaction types, and illustrate with an example:
(a) nucleophilic substitution reaction: (b) electrophilic substitution reaction; (c) addition reaction;
(d) elimination reaction, (e) rearrangement reaction.
(a)
Interpretation:
The nucleophilic substitution reaction should be defined with example.
Concept introduction:
Nucleophilic substitution reaction describes the attack of the electron-rich group that is nucleophile on electron deficient groups that is electrophile.
Answer to Problem 1E
Nucleophilic substitution reaction is the type of reaction in which the nucleophile (electron rich species) attacks the electron-deficient carbon atom which is electrophilic.
Explanation of Solution
Nucleophilic substitution reaction is defined as an organic reaction which includes the attack of a nucleophile on electrophilic center along with the removal of the leaving group.
The example of the nucleophilic substitution reaction is,
In this reaction, chlorine of chloroethane is replaced by a hydroxyl group
(b)
Interpretation:
The electrophilic substitution reaction should be defined with example.
Concept introduction:
The electrophilic substitution reaction describes the displacement of functional group or hydrogen atom by an electron deficient group or electrophile.
Answer to Problem 1E
Electrophilic substitution reaction is defined as the organic reaction in which the electrophile replaces a functional group of a compound or hydrogen atom.
Explanation of Solution
Electrophilic substitution reaction is defined as the organic reaction which includes the replacement of functional group or
Example of electrophilic substitution reaction is,
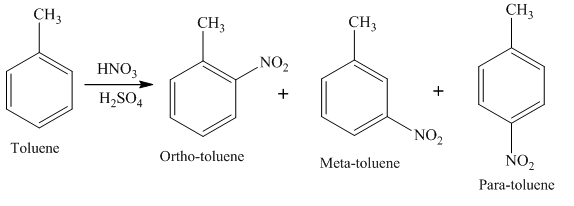
In this reaction, Toluene undergoes electrophilic substitution to form para nitrotoluene, meta nitrotoluene, and ortho nitrotoluene.
(c)
Interpretation:
The addition reaction should be defined with example.
Concept introduction:
The addition reaction describes the combination of two or more smaller molecules to form a larger molecule.
Answer to Problem 1E
Addition reaction is defined as the reaction in which two or more molecules combine to form a single and large molecule.
Explanation of Solution
The reaction of the addition of the two or more reactants that is A and B to produce a single product C is termed as addition reaction.
The example of addition reaction is,
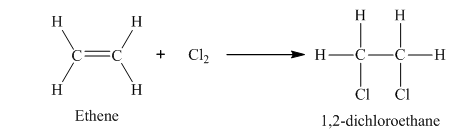
In this reaction, chlorine molecule combines with ethene to form 1, 2-dichloroethane.
(d)
Interpretation:
The elimination reaction should be defined with example.
Concept introduction:
The elimination reaction describes the removal of two substituents from the reactant molecule to form the product.
Answer to Problem 1E
Elimination reaction is the reaction by which the reactant molecule or compound breaks into two or more products.
Explanation of Solution
Elimination reaction is the type of reaction in which two substituents are removed from the reactant molecule to form the product. Generally, unsaturated compounds are formed in an elimination reaction.
The example of the elimination reaction is,
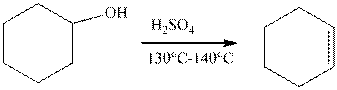
The reaction of cyclohexanol in the presence of
(e)
Interpretation:
The rearrangement reaction should be defined with example.
Concept introduction:
The rearrangement reaction describes the rearrangement of bonds in a molecule to form the product.
Answer to Problem 1E
It is the process of movement of bonds within a molecule to give rise to structural isomers.
Explanation of Solution
It is defined as a reaction in which an atom or a bond migrates from one atom in reactant molecule to adjacent atom to give rise to the product.
Example of rearrangement reaction is,
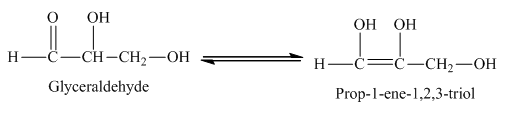
The glyceraldehyde undergoes rearrangement to form enediol.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 27 Solutions
General Chemistry: Principles and Modern Applications (11th Edition)
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Human Physiology: An Integrated Approach (8th Edition)
Organic Chemistry
Physical Universe
Campbell Biology: Concepts & Connections (9th Edition)
General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry - 4th edition
- Briefly indicate the coordination forms of B and Si in borates and silicates, respectively.arrow_forwardCan you please draw out the Lewis structure for these two formulasarrow_forwardIn a rotational Raman spectrum of a diatomic molecule it is correct to say that:a) anti-Stokes lines occur at frequencies higher than the excitatory oneb) Stokes lines occur at frequencies higher than the excitatory onec) Rayleigh scattering is not observedd) Rayleigh scattering corresponds to delta J = 0arrow_forward
- Of the molecules: H2, N2, HCl, CO2, indicate which ones can give Raman vibration-rotation spectra:a) H2, N2 and HClb) H2, N2, HCl and CO2c) H2 and N2d) all of themarrow_forwardCan you please help me with drawing the Lewis structure of each molecular formula?I truly appreciate you!arrow_forwardCan you please help me with drawing the Lewis structure of each molecular formula?I truly appreciate you!arrow_forward
- Describe each highlighted bond in terms of the overlap of atomic orbitals. (a) Н Н H H [References] HIC H H C H H-C-CC-N: H σ character n character (b) HIC H H H H-C-C-C HIC H Н H O-H σ character n character Submit Answer Try Another Version 3 item attempts remainingarrow_forward11 Naming and drawing alcohols Write the systematic (IUPAC) name for each of the following organic molecules: structure OH HO OH Explanation Check name ☐arrow_forwardwhat is the drawn mechanism for diethyl carbonate and 4 - bromo - N, N -dimethylaniline to create crystal violet?arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





