
Concept explainers
The reduction of
The Grignard reagent is rarely isolated It is formed in solution and used immediately in the desired reaction. The alkylmetal bond is highly polar, with the partial negative charge on the C atom, which makes the C atom highly nucIeophilic The Grignard reagent ((R MgJ3r) ) can attack a carbonyl group in an aldehyde or ketone as follows:
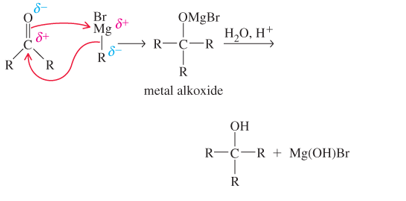
Addition of dilute aqueous acid solution to the metal alkoxide furnishes the alcohol. The important synthetic consequence of this procedure is that we have prepared a product with more carbon atoms than present in the starting material. A simple starting material can be transformed into a more complex molecule.
a. What is the product of the reaction between methanal and the Grignard reagent formed from 1-bromobutane after the addition of dilute acid?
b. By using a Grignard reagent, devise a synthesis for hexan-2-ol
c. By using a Grignard reagent, devise a synthesis for 2-methylhexan-2-ol. d. Grignard reagents can also be formed with aryl halides, such as chlorobenzene. What would be the product of the reaction between the Grignard reagent of chlorobenzene and propanone? Can you think of an alternative synthesis of this product, again using a Grignard reagent?
e. The basicity of the C atom bound to the magnesium in the Grignard reagent can be used to make Grignard reagents of terminal
f. By using a Grignard reagent, suggest a synthesis for hept-2-yn-1-oi
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 27 Solutions
General Chemistry: Principles and Modern Applications (11th Edition)
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology (12th Edition)
Human Biology: Concepts and Current Issues (8th Edition)
Organic Chemistry
Biology: Life on Earth (11th Edition)
Laboratory Experiments in Microbiology (12th Edition) (What's New in Microbiology)
- What functional group distinguishes each of the following hydrocarbon derivatives? a. halohydrocarbons b. alcohols c. ethers d. aldehydes e. ketones f. carboxylic acids g. esters h. amines Give examples of each functional group. What prefix or suffix is used to name each functional group? What are the bond angles in each? Describe the bonding in each functional group. What is the difference between a primary, secondary, and tertiary alcohol? For the functional groups in ah, when is a number required to indicate the position of the functional group? Carboxylic acids are often written as RCOOH. What does COOH indicate and what does R indicate? Aldehydes are sometimes written as RCHO. What does CHO indicate?arrow_forwardThe addition of water to aldehydes and ketones occurs rapidly, although it is not thermodynamically favored. What would be the product for the reaction above? Hint: Think of the self-ionization of water and the polarity of the carbonyl group.arrow_forwardTrue or False Considering that two carbon chains have equal number of carbons, but one has Fluorine and the other has Iodine, the one with iodine will have a higher boiling point. Mild oxidation of alkenes results to similar product as that of nucleophilic addition of water to aldehydes.arrow_forward
- Question 18.c of 20 Aldehydes and ketones are common carbonyl functional groups. Identify the structures and provide names of these molecules. Provide a systematic name for this structure. سکتے 5- H 1- 4- cyclo tert- 6- di n- tri 3- 2- sec- hex eth but Submit +arrow_forwardThree components of the sex pheromone of the female sand bee (Ophrys sphegodes) are saturated hydrocarbons containing 23, 25, and 27 carbon atoms. How many H atoms does each of these alkanes contain? Interestingly, the early spider orchid emits a similar hydrocarbon mixture to attract male sand bees to pollinate its owers.arrow_forwardExplain the Hydroboration–oxidation two-step reaction sequence that converts an alkene to an alcohol.arrow_forward
- Please complete the reactionsarrow_forward3. Complete the chemical equations for the following reactions. Draw the structure (condensed structural formulas) for the dominant product and write the names of the reactants and products (organic compounds only.) d) CHy Name reactant: Name product: e) CH=C-CH + 2 HBr 4-Cて。 Name reactant: Name product:arrow_forward2. Using structural diagrams to explain the synthesis of butyl ethanoate from an alkane and an alcohol. Make sure you have the names of the substances and the reaction conditions of the reactions of the steps that consists your synthesis HC-C H- styrene HH ethane-1,2-diol OH НО. JOL -0-H benzene-1.4-dicarboxylic acid.arrow_forward
- Draw an ester with the formula C3H6O2 AND Draw the structures for a specific aldehyde and a specific ketone that have the formula C3H6Oarrow_forward1. Which functional group is found in aldehydes? a. CHO b. -CH;OH c. -COOH d. RCOR' 2. Which functional group is found in ketones? a. -CHO CH:OH c. -COOH RCOR' 3. Which structural feature is common to aldehydes and ketones? a, an oxygen atom bonded to both a carbon atom and a hydrogen atom b. an oxygen atom bonded to two carbon atoms c. an oxygen atom double bonded to a carbon atom d. two oxygen atoms bonded to the same carbon atom 4. What is the IUPAC name for the following compound? a. I-pentaldehyde b. l-pentanal c. pentanal d. pentanealdehyde Cetoa of Fiarrow_forwardHow could you get alkenes from: • Alkyl halides• Alcohols• Alkynes• Aldehydes or ketonesarrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning





